Taupo Volcanic Zone

Mount Ngauruhoe
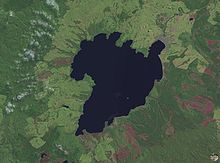
Satellite photo of the Lake Taupo caldera

Volcano and lake/caldera locations in the Taupo Volcanic Zone. The distance between the town of Rotorua and the town of Taupo is 80 km. (White Island is not shown.)

Whakaari/White Island
The Taupo Volcanic Zone (TVZ) is a volcanic area in the North Island of New Zealand that has been active for the past two million years and is still highly active. Mount Ruapehu marks its south-western end and the zone runs north-eastward through the Taupo and Rotorua areas and offshore into the Bay of Plenty. It is part of the larger Central Volcanic Region that extends further westward through the western Bay of Plenty to the eastern side of the Coromandel Peninsula and has been active for four million years.[1] The Taupo Volcanic Zone is widening east–west at the rate of about 8 mm per year. It is named after Lake Taupo, the flooded caldera of the largest volcano in the zone.
Contents
1 Activity
2 Extent and geological context
3 Scientific study
4 Volcanoes, lakes and geothermal fields
4.1 Note
5 See also
6 References
7 External links
Activity
There are numerous volcanic vents and geothermal fields in the zone, with Mount Ruapehu, Mount Ngauruhoe and White Island erupting most frequently. The zone's largest eruption since the arrival of Europeans was that of Mount Tarawera in 1886, which killed over 100 people. Early Maori would also have been affected by the much larger Kaharoa eruption from Tarawera around 1300 AD.[2]
The last major eruption from Lake Taupo, the Hatepe eruption, occurred in 232 AD. It is believed to have first emptied the lake then followed that feat with a pyroclastic flow that covered about 20,000 square kilometres (7,722 sq mi) of land with volcanic ash. A total of 120 km3 (29 cu mi) of material is believed to have been ejected, and over 30 km3 (7.2 cu mi) of material is estimated to have been ejected in just a few minutes. The date of this activity was previously thought to be 186AD as the ash expulsion was thought to be sufficiently large to turn the sky red over Rome and China (as documented in Hou Han Shu), but this has since been disproven.[citation needed]
Taupo erupted an estimated 1,170 km3 (280 cu mi) of material in its Oruanui eruption 26,500 years ago. This was Earth's most recent eruption reaching VEI-8, the highest level on the Volcanic Explosivity Index.
The Rotorua caldera has been dormant longer, with its main eruption occurring about 240,000 years ago, although lava dome extrusion has occurred within the last 25,000 years.[3]
Extent and geological context
The Taupo Volcanic Zone is approximately 350 kilometres (217 mi) long by 50 kilometres (31 mi) wide. Mount Ruapehu marks its southwestern end, while the submarine Whakatane volcano (85 kilometres (53 mi) beyond White Island) is considered its northeastern limit.[4]
It forms a southern portion of the active Lau-Havre-Taupo back-arc basin, which lies behind the Kermadec-Tonga subduction zone.[5] Volcanic activity continues to the north-northeast, along the line of the Taupo Volcanic Zone, through several undersea volcanoes (known as Clark, Tangaroa, the Silents and the Rumbles), then shifts eastward to the parallel volcanic arc of the Kermadec Islands and Tonga. Although the back-arc basin continues to propagate to the southwest, with the South Wanganui Basin forming an initial back-arc basin, volcanic activity has not yet begun in this region.[6]
South of Kaikoura the plate boundary changes to a transform boundary with oblique continental collision uplifting the Southern Alps in the South Island. A subduction zone reappears southwest of Fiordland, at the southwestern corner of the South Island, although here the subduction is in the opposite direction. Solander Island is an extinct volcano associated with this subduction zone, and the only one that protudes above the sea.
Scientific study
Recent scientific work indicates that the Earth's crust below the Taupo Volcanic Zone may be as little as 16 kilometres thick. A film of magma 50 kilometres (30 mi) wide and 160 kilometres (100 mi) long lies 10 kilometres under the surface.[7][8] The geological record indicates that some of the volcanoes in the area erupt infrequently but have large, violent and destructive eruptions when they do. There is also some possible rifting in the Taupo Volcanic Zone.
Volcanoes, lakes and geothermal fields
The following Volcanic Centers belong to the Taupo Volcanic Zone:
Rotorua, Okataina, Maroa, Taupo, Tongariro and Mangakino.[9][10]
Whakatane Graben – Bay of Plenty
- Submarine Whakatane volcano 36°48′S 177°30′E / 36.8°S 177.5°E / -36.8; 177.5 (Whakatane)
Mayor Island/Tuhua 37°17′S 176°15′E / 37.283°S 176.250°E / -37.283; 176.250 (Mayor Island)
Whale Island 37°51′S 176°59′E / 37.850°S 176.983°E / -37.850; 176.983 (Whale Island)
Whakaari/White Island 37°31′S 177°11′E / 37.52°S 177.18°E / -37.52; 177.18 (White Island)
- Te Paepae o Aotea
Mount Edgecumbe 38°06′S 176°48′E / 38.1°S 176.8°E / -38.1; 176.8 (Mount Edgecumbe)
- Geothermal field
Kawerau Power Station 38°03′47″S 176°43′38″E / 38.0631°S 176.7271°E / -38.0631; 176.7271 (Kawerau Power Station)
- Submarine Whakatane volcano 36°48′S 177°30′E / 36.8°S 177.5°E / -36.8; 177.5 (Whakatane)
Rotorua Volcanic Center
Rotorua Caldera, size: 22 km wide 38°05′S 176°16′E / 38.08°S 176.27°E / -38.08; 176.27 (Rotorua Caldera)[11]
- Ngongotaha (volcano)
- Lakes
Lake Rotorua 38°05′S 176°16′E / 38.08°S 176.27°E / -38.08; 176.27 (Lake Rotorua)
Mokoia Island 38°05′S 176°18′E / 38.083°S 176.300°E / -38.083; 176.300 (Mokoia Island)
- Geothermal fields
Tikitere/Hell's Gate
Whakarewarewa 38°9′44″S 176°15′23″E / 38.16222°S 176.25639°E / -38.16222; 176.25639 (Whakarewarewa)
- Pohutu Geyser
- Takeke

In 1886, Mount Tarawera produced New Zealand's largest historic eruption
Okataina Volcanic Center: The Haroharo and Tarawera complexes impounded the lakes against the outer margins of the Okataina Caldera. The Okareka Embayment and the Tarawera Volcanic Complex are inside the Haroharo Caldera which in turn is inside the Okataina Ring Structure, from Newhall (1988),[12] but newer maps show Okataina smaller.
- Okataina Caldera, size: roughly 27 x 20 km 38°13′S 176°30′E / 38.22°S 176.5°E / -38.22; 176.5 (Okataina Caldera)[13]
- Haroharo Caldera, size: 16 x 26 km[11]
- Haroharo volcanic complex, northern end of the Okataina Volcanic Center
Mount Tarawera and Tarawera volcanic complex 38°13′S 176°30′E / 38.22°S 176.5°E / -38.22; 176.5 (Mount Tarawera)
- Okareka vent[14]
- Okareka vent[14]
- Okareka Embayment
- Haroharo Caldera, size: 16 x 26 km[11]
- Rotoma Caldera[15]
- Lakes
Lake Okataina 38°07′S 176°25′E / 38.117°S 176.417°E / -38.117; 176.417 (Lake Okataina)
Lake Tarawera 38°12′S 176°27′E / 38.200°S 176.450°E / -38.200; 176.450 (Lake Tarawera)
Lake Rotokakahi (Green Lake) 38°13′S 176°20′E / 38.217°S 176.333°E / -38.217; 176.333 (Lake Rotokakahi)
Lake Tikitapu (Blue Lake) 38°12′S 176°20′E / 38.200°S 176.333°E / -38.200; 176.333 (Lake Tikitapu)
Lake Okareka 38°10′S 176°22′E / 38.167°S 176.367°E / -38.167; 176.367 (Lake Okareka)
Lake Rotomahana 38°16′S 176°27′E / 38.267°S 176.450°E / -38.267; 176.450 (Lake Rotomahana)
Lake Rotoiti 38°02′20″S 176°25′40″E / 38.0390°S 176.4277°E / -38.0390; 176.4277 (Lake Rotoiti)
Lake Rotoma 38°02′51″S 176°35′16″E / 38.0476°S 176.5878°E / -38.0476; 176.5878 (Lake Rotoma)
Lake Rotoehu 38°1′S 176°32′E / 38.017°S 176.533°E / -38.017; 176.533 (Lake Rotoehu)
- Geothermal fields
Waimangu Volcanic Rift Valley 38°16′57″S 176°23′56″E / 38.28250°S 176.39889°E / -38.28250; 176.39889 (Waimangu)
- Frying Pan Lake
- Rotoma
- Okataina Caldera, size: roughly 27 x 20 km 38°13′S 176°30′E / 38.22°S 176.5°E / -38.22; 176.5 (Okataina Caldera)[13]

Lady Knox Geyser, Waiotapu geothermal area

Craters of the Moon geothermal area
Maroa Volcanic Center: The Maroa Caldera formed in the Northeast corner of the Whakamaru Caldera, the Whakamaru Caldera partially overlaps with the Taupo Caldera on the South. The Waikato River course follows roughly the northern Maroa caldera rim on one side. The town of Whakamaru and the artificial Lake Whakamaru, on the Waikato River, have the same name too.[11]- Maroa Caldera, size: 16 x 25 km 38°25′S 176°05′E / 38.42°S 176.08°E / -38.42; 176.08 (Maroa Caldera)[11]
Reporoa Caldera, size: 10 x 15 km 38°25′S 176°20′E / 38.417°S 176.333°E / -38.417; 176.333 (Reporoa Caldera)[11]
- Whakamaru Caldera, size: 30 x 40 km[11]
- Geothermal fields
Waiotapu 38°21′34″S 176°22′11″E / 38.35944°S 176.36972°E / -38.35944; 176.36972 (Waiotapu)
Wairakei 38°37′36″S 176°06′13″E / 38.626686°S 176.103491°E / -38.626686; 176.103491 (Wairakei)
Craters of the Moon (Karapiti)
Orakei Korako 38°28′24″S 176°8′54″E / 38.47333°S 176.14833°E / -38.47333; 176.14833 (Orakei Korako)
- Ngatamariki
- Rotokaua
Ohaaki Power Station 38°31′37″S 176°17′31″E / 38.527°S 176.292°E / -38.527; 176.292 (Ohaaki Power Station)
- Maroa Caldera, size: 16 x 25 km 38°25′S 176°05′E / 38.42°S 176.08°E / -38.42; 176.08 (Maroa Caldera)[11]
Taupo Volcanic Center
Taupo Caldera, size: roughly 35 km wide 38°49′S 176°00′E / 38.82°S 176.00°E / -38.82; 176.00 (Taupo Caldera)[11]- Mount Tauhara
Ben Lomond rhyolite dome (contains obsidian) 38°35.7′S 175°57.2′E / 38.5950°S 175.9533°E / -38.5950; 175.9533 (Ben Lomond)
- Lakes
- Lake Taupo 38°49′S 176°00′E / 38.82°S 176.00°E / -38.82; 176.00 (Lake Taupo)
- Horomatangi Reefs
- Motutaiko Island
- Lake Taupo 38°49′S 176°00′E / 38.82°S 176.00°E / -38.82; 176.00 (Lake Taupo)
- Geothermal fields
- Tauhara-Taupo
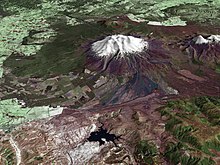
Composite satellite image of Mount Ruapehu

Satellite view of the Lake Rotorua Caldera. Mount Tarawera is in the lower right corner.

Southwest side of Mount Tarawera, Mount Edgecumbe on the background.
Tongariro Volcanic Center: Lake Taupo, Kakaramea, Pihanga, Tongariro and Ruapehu are roughly aligned on the main fault.
- Kakaramea
Pihanga 39°02′28.75″S 175°46′7″E / 39.0413194°S 175.76861°E / -39.0413194; 175.76861 (Pihanga)
Mount Tongariro and Tongariro volcanic complex 39°8′S 175°39′E / 39.133°S 175.650°E / -39.133; 175.650 (Mount Tongariro)
Mount Ngauruhoe, a main Tongariro vent 39°9′24.6″S 175°37′55.8″E / 39.156833°S 175.632167°E / -39.156833; 175.632167 (Mount Ngauruhoe)
Tama crater lakes, main Tongariro vents
- Upper Tama 39°11′07″S 175°37′20″E / 39.1854°S 175.6223°E / -39.1854; 175.6223 (Upper Tama)
- Lower Tama 39°12′09″S 175°36′24″E / 39.2025°S 175.6068°E / -39.2025; 175.6068 (Lower Tama)
- Upper Tama 39°11′07″S 175°37′20″E / 39.1854°S 175.6223°E / -39.1854; 175.6223 (Upper Tama)
Mount Ruapehu 39°11′S 175°21′E / 39.18°S 175.35°E / -39.18; 175.35 (Mount Ruapehu)
Hauhungatahi 39°14′S 175°26′E / 39.23°S 175.44°E / -39.23; 175.44 (Hauhungatahi)
- Lakes
Lake Rotoaira 39°03′16″S 175°42′51″E / 39.0545°S 175.7143°E / -39.0545; 175.7143 (Lake Rotoaira)
Lake Rotopounamu 39°01′36″S 175°44′18″E / 39.0267°S 175.7382°E / -39.0267; 175.7382 (Lake Rotopounamu)
- Geothermal fields
- Ketetahi Springs
Mangakino Volcanic Center: The Mangakino Volcanic Center is the westernmost and oldest rhyolitic caldera volcano in the Taupo Volcanic Zone.[16] The course of the Waikato River crosses this area, between the artificial Lake Ohakuri (38°25′22″S 176°07′32″E / 38.42273°S 176.125474°E / -38.42273; 176.125474 (Lake Ohakuri)), the town of Mangakino (38°23′S 175°47′E / 38.383°S 175.783°E / -38.383; 175.783 (Mangakino)) and Hamilton (37°47′S 175°17′E / 37.783°S 175.283°E / -37.783; 175.283 (Hamilton)).
- Artificial Lake Maraetai
- Artificial Lake Maraetai
Other important features of the TVZ include the Whakatane, Ngakuru and Ruapehu grabens.
Note
There is nowadays a somewhat different classification:[17][18]
- North part: Whakatane Graben – Bay of Plenty
- Central part:
- West of the main fault zone:
- Mangakino caldera complex; may be transitional between Coromandel Volcanic Zone (CVZ) and Taupo Volcanic Zone (TVZ) (1.62 – 0.91 mio. years old)
- Kapenga caldera; lies between the Maroa caldera and the Rotorua caldera, it is completely buried under more recent tephra (circa 700,000 years old)
- Okareka Embayment, lies inside the northern end of the Kapenga Caldera, between the Tarawera volcanic complex and the Lake Rotorua[15]
- Okareka Embayment, lies inside the northern end of the Kapenga Caldera, between the Tarawera volcanic complex and the Lake Rotorua[15]
- Rotorua single event caldera; Mamaku Ignimbrite (circa 240,000 years old)
- Main fault zone:
- Okataina caldera complex
- Haroharo caldera complex
- Tarawera volcanic complex
- Okareka Embayment
- Haroharo caldera complex
- Whakamaru caldera complex
- Maroa caldera
- Ohakuri single event caldera; Ohakuri Ignimbrite; lies West of the Ohakuri Dam, the Waikato River course follows roughly the southern caldera rim on one side (circa 240,000 years old).[19]
- Taupo caldera complex
- Okataina caldera complex
- East of the main fault zone:
- Reporoa single event caldera; Kaingaroa Ignimbrite (circa 240,000 years old)
- West of the main fault zone:
- South part: Tongariro Volcanic Centre
See also
- Geology of New Zealand
- Volcanism of New Zealand
- North Island Volcanic Plateau
- Geothermal areas in New Zealand
- Geothermal power in New Zealand
References
^ Cole, J.W.; Darby, D.J.; Stern, T.A. (1995). "Taupo Volcanic Zone and Central Volcanic Region: Backarc Structures of North Island, New Zealand". In Taylor, Brian. Backarc Basins: Tectonics and Magmatism. New York: Plenum. p. 3. ISBN 978-1-4615-1843-3..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ David, Lowe. "Polynesian settlement and impacts of volcanism on early Maori society". In Lowe, D.J. Guidebook for ‘Land and Lakes’ field trip, New Zealand Society of Soil Science Biennial Conference, Rotorua, held in 27–30 November 2006 (PDF). Lincoln: New Zealand Society of Soil Science. pp. 50–55.
^ "Rotorua". Global Volcanism Program. Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved 2010-08-31.
^ Gamble, J. A.; Wright, I. C.; Baker, J. A. (1993). "Seafloor geology and petrology in the oceanic to continental transition zone of the Kermadec-Havre-Taupo Volcanic Zone arc system, New Zealand". New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics. 36 (4): 417–435. doi:10.1080/00288306.1993.9514588. Archived from the original on 2008-11-22.
^ Parson, L. M.; Wright, I. C. (1996). "The Lau-Havre-Taupo back-arc basin: A southward-propagating, multi-stage evolution from rifting to spreading". Tectonophysics. 263: 1–22. Bibcode:1996Tectp.263....1P. doi:10.1016/S0040-1951(96)00029-7.
^ Villamor, P.; Berryman, K. R. (2006). "Evolution of the southern termination of the Taupo Rift, New Zealand". New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics. 49: 23–37. doi:10.1080/00288306.2006.9515145. Archived from the original on 2009-02-17.
^ Easton, Paul (15 September 2007). "Central North Island sitting on magma film". The Dominion Post. Retrieved 16 March 2008.
^ Heise, W.; Bibby, H.M.; Caldwell, T.G. (2007). "Imaging magmatic Processes in the Taupo Volcanic Zone (New Zealand) with Magnetotellurics" (PDF). Geophysical Research Abstracts. 9. 01311.
^ Cole, J.W. (1990). "Structural control and origin of volcanism in the Taupo volcanic zone, New Zealand". Bulletin of Volcanology. 52 (6): 445–459. Bibcode:1990BVol...52..445C. doi:10.1007/BF00268925.
^ "New Zealand".
^ abcdefg http://www.volcano.si.edu/world/largeeruptions.cfm
^ Newhall, Christopher G.; Dzurisin, Daniel (1988). "Historical unrest at large calderas of the world". USGS Bulletin. 1855: 1108. Citing Scott, B.J. (1986). Gregory, J.G.; Watters, W.A., eds. "Volcanic hazards assessment in New Zealand". New Zealand Geol. Surv. Rec. 10: 49–54.|chapter=ignored (help)
^ Okataina Volcanic Center, New Zealand
^ Nairn, I.A. (2002). "Geology of the Okatania Volcanic Centre". Geological Map 25. Institute of Geological and Nuclear Sciences: 156.
^ ab Hodgson, K. A.; Nairn, I. A. (August 2004). "The Sedimentation and Drainage History of Haroharo Caldera and The Tarawera River System, Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand" (PDF). Operations Publication 2004/03. Environment Bay of Plenty: 7. ISSN 1176-5550. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-05-22.
^ Krippner, Stephen J. P.; Briggs, Roger M.; Wilson, Colin J. N.; Cole, James W. (1998). "Petrography and geochemistry of lithic fragments in ignimbrites from the Mangakino Volcanic Centre: implications for the composition of the subvolcanic crust in western Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand". New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics. 41 (2): 187–199. doi:10.1080/00288306.1998.9514803. Archived from the original on 2008-10-21.
^ Cole, J. W.; Spinks, K. D. (2009). "Caldera volcanism and rift structure in the Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand". Special Publications. London: Geological Society. 327 (1): 9–29. Bibcode:2009GSLSP.327....9C. doi:10.1144/SP327.2.
^ Hiess, J; Cole, JW; Spinks, KD (2007). High-Alumina Basalts of the Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand: Influence of the Crust and Crustal Structure (PDF). p. 36. Part of a BSc Project by Hiess, J. (University of Canterbury).
^ Gravley, D. M.; Wilson, C. J. N.; Rosenberg, M. D.; Leonard, G. S. (2006). "The nature and age of Ohakuri Formation and Ohakuri Group rocks in surface exposures and geothermal drillhole sequences in the central Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand". New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics. 49 (3): 305–308. doi:10.1080/00288306.2006.9515169.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Taupo Volcanic Zone. |
- Further information on Taupo volcanics
- Tectonic plate information
- Earthquake risks
- New Zealand's volcanoes: The Taupo Volcanic Centre
- New Zealand's volcanoes: The Okataina Volcanic Centre
- Environment Bay of Plenty, Regional Council, Library
- Maps
- Environment Waikato, Regional Council, map
Lowe, D.J. (ed.). Guidebook for ‘Land and Lakes’ field trip, New Zealand Society of Soil Science Biennial Conference, Rotorua, held in 27–30 November 2006 (PDF). Lincoln: New Zealand Society of Soil Science. p. 63.
Hiess, J; Cole, JW; Spinks, KD (2007). High-Alumina Basalts of the Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand: Influence of the Crust and Crustal Structure (PDF). p. 36. Part of a BSc Project by Hiess, J. (University of Canterbury). Map modified from: Spinks, Karl D; Acocella, Valerio; Cole, Jim W; Bassett, Kari N (15 June 2005). "Structural control of volcanism and caldera development in the transtensional Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand". Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research. 144 (1–4): 7–22. Bibcode:2005JVGR..144....7S. doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2004.11.014.
- Geological Society of New Zealand & New Zealand Geophysical Society - Fieldtrip 2
Houghton, Bruce F. (2007). Field Guide - Taupo Volcanic Zone (PDF).
- New Zealand, Taupo and Coromandel volcanic zones
Newhall, Christopher G.; Dzurisin, Daniel (1988). "Historical unrest at large calderas of the world". USGS Bulletin. 1855: 1108.
- The Taupo Volcanic Zone with Māori Freehold Land (1995) - showing geothermal fields
