Gainesville, Florida
| Gainesville, Florida | |||
|---|---|---|---|
City | |||
City of Gainesville | |||
 Downtown Gainesville at night | |||
| |||
Nickname(s): "Gville",[1] "Hogtown",[2] "GNV"[3] | |||
Motto(s): Every path starts with passion | |||
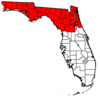
 Location in Alachua County and the state of Florida | |||
Coordinates: 29°39′7.19″N 82°19′29.97″W / 29.6519972°N 82.3249917°W / 29.6519972; -82.3249917Coordinates: 29°39′7.19″N 82°19′29.97″W / 29.6519972°N 82.3249917°W / 29.6519972; -82.3249917 | |||
| Country | United States | ||
| State | Florida | ||
| County | Alachua | ||
| Settled | 1854 | ||
| Incorporated | April 14, 1869 | ||
| Government | |||
| • Type | Council-manager | ||
| • Mayor | Lauren Poe (D) | ||
| • Commission | City Commissioners
[4] | ||
| • City Manager | Anthony Lyons | ||
| Area[5] | |||
| • City | 63.49 sq mi (164.43 km2) | ||
| • Land | 62.32 sq mi (161.41 km2) | ||
| • Water | 1.17 sq mi (3.02 km2) 1.74% | ||
| Elevation[6] | 151 ft (54 m) | ||
| Population (2010)[7] | |||
| • City | 124,354 | ||
| • Estimate (2017)[8] | 132,249 | ||
| • Rank | 206th | ||
| • Density | 2,111.50/sq mi (815.25/km2) | ||
| • Urban | 187,781 (US: 187th) | ||
| • Metro | 284,687 (168th) | ||
| Time zone | UTC−5 (EST) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) | ||
| ZIP code | 32601–32614, 32627, 32635, 32641, 32653 | ||
| Area code | 352 | ||
| FIPS code | 12-25175 | ||
GNIS feature ID | 0282874[9] | ||
| Website | www.cityofgainesville.org | ||

The Cade Innovation and Invention Museum at Depot Park.

Gainesville's Depot Park
Gainesville is the county seat and largest city in Alachua County, Florida, United States, and the principal city of the Gainesville, Florida Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA). The population of Gainesville in the 2017 US Census estimates was 132,249,[10] a 6.4% growth from 2010.[11][12] Gainesville is the largest city in the region of North Central Florida. It is also a component of the Gainesville-Lake City Combined Statistical Area, which had a 2013 population of 337,925.
Gainesville is home to the University of Florida, the nation's fifth-largest university campus by enrollment, as well as to Santa Fe College.
Contents
1 History
2 Geography
2.1 Climate
2.2 Cityscape
2.3 Developments and expansions
3 Demographics
3.1 Languages
4 Economy
4.1 Top employers
5 Education
5.1 Desegregation
5.2 Schools
5.3 Elementary schools
5.4 Middle schools
5.5 High schools
5.6 Private schools
5.7 Developmental Research Schools
5.8 Colleges and universities
5.9 City libraries
6 Government and infrastructure
6.1 City government
6.2 Mayor
6.3 Homelessness issues
7 Transportation
7.1 Major roads
7.2 Intercity rail
7.3 Airport, bus, and others
8 Culture
8.1 Marijuana culture
8.2 Music scene
8.3 Sports
8.4 Startup culture
8.5 Annual cultural events
9 Media
9.1 Print
9.2 Radio
9.3 Television
10 Points of interest
11 Sister cities
12 See also
13 References
14 Further reading
15 External links
History
Geography
Gainesville is located at 29°39'55" North, 82°20'10" West (29.665245, −82.336097),[13] which is roughly the same latitude as Houston, Texas. According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 62.4 square miles (161.6 km2), of which 61.3 square miles (158.8 km2) is land and 1.1 square miles (2.8 km2) is water. The total area is 1.74% water.[11]
Gainesville's tree canopy is both dense and species rich, including broadleaf evergreens, conifers, and deciduous species; the city has been recognized by the National Arbor Day Foundation every year since 1982 as a "Tree City, USA".
Gainesville is the only city with more than 10,000 residents in the Gainesville, Florida Metropolitan Statistical Area (Alachua and Gilchrist counties), and it is surrounded by rural area, including the 21,000-acre (8,500 ha) wilderness of Paynes Prairie on its southern edge. The city is characterized by its medium size and central location, about 90 minutes driving time from either Jacksonville or Orlando, two hours driving time from Tampa, and five hours driving time from either Atlanta or Miami. The area is dominated by the presence of the University of Florida,[14] which in 2008 had been the third largest university campus in the USA[15] and as of fall 2016 was the fifth largest campus by enrollment in the USA.
Climate
Gainesville's climate is defined as humid subtropical (Köppen: Cfa). Due to its inland location, Gainesville experiences wide temperature fluctuations for Florida, and it is part of USDA Plant hardiness zone 9a.[16] During the hot season, from roughly May 15 to September 30, the city's climate is similar to the rest of the state, with frequent afternoon thunderstorms and high humidity. Temperatures range from the low 70s (21–23 °C) at night to around 92 °F (33 °C) during the day on average.[17] The all-time record high of 104 °F (40 °C) was reached on June 27, 1952.[18] From November through March, however, the Gainesville area has a climate distinct from much of peninsular Florida with 16 nights[18] of freezing or below temperatures and sustained freezes occurring every few years. The all-time record low of 6 °F (−14 °C) was reached on February 13, 1899,[19] and the city experienced light snow and freezing rain on Christmas Eve, 1989. Traces of snow were also recorded in 1976, 1996, 2010 and 2016.[citation needed][20] The daily average temperature in January is 54.3 °F (12.4 °C); on average, the window for freezing temperatures is December 4 through February 24, allowing a growing season of 282 days.[18] As with the rest of the state, cold temperatures are almost always accompanied by clear skies and high pressure systems; snow is therefore rare. Temperatures reaching 100 °F (38 °C) or falling below 20 °F (−7 °C) are rare, having respectively occurred on June 16, 2015 and January 11, 2010.[18]
The city's flora and fauna are also distinct from coastal regions of the state, and include many deciduous species, such as dogwood, maple, hickory and sweet gum, alongside palms, live oaks, and other evergreens. Thus, the city enjoys brief periods of fall color in late November and December (though hardly comparable to areas further north) and a noticeable and prolonged spring from mid February through early April. This is a generally pleasant period, as colorful blooms of azalea and redbud complement a cloudless blue sky, for this is also the period of the lowest precipitation and lowest humidity. The city averages 47.33 inches (1,200 mm) of rain per year. June through September accounts for a majority of annual rainfall, while autumn and early winter is the driest period.[17]
| Climate data for Gainesville Regional Airport, Florida (1981−2010 normals,[21] extremes 1890−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 89 (32) | 88 (31) | 96 (36) | 96 (36) | 101 (38) | 104 (40) | 102 (39) | 103 (39) | 99 (37) | 96 (36) | 91 (33) | 87 (31) | 104 (40) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 80.1 (26.7) | 82.1 (27.8) | 85.9 (29.9) | 89.6 (32) | 94.0 (34.4) | 96.7 (35.9) | 96.4 (35.8) | 95.3 (35.2) | 93.0 (33.9) | 89.6 (32) | 84.9 (29.4) | 81.2 (27.3) | 97.9 (36.6) |
| Average high °F (°C) | 66.2 (19) | 69.6 (20.9) | 74.6 (23.7) | 80.3 (26.8) | 86.9 (30.5) | 90.0 (32.2) | 90.9 (32.7) | 90.2 (32.3) | 87.4 (30.8) | 81.3 (27.4) | 74.4 (23.6) | 67.9 (19.9) | 80.0 (26.7) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 54.3 (12.4) | 57.5 (14.2) | 62.3 (16.8) | 67.6 (19.8) | 74.7 (23.7) | 79.7 (26.5) | 81.2 (27.3) | 80.9 (27.2) | 78.2 (25.7) | 70.9 (21.6) | 62.8 (17.1) | 56.1 (13.4) | 68.9 (20.5) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 42.3 (5.7) | 45.3 (7.4) | 50.0 (10) | 54.9 (12.7) | 62.4 (16.9) | 69.3 (20.7) | 71.5 (21.9) | 71.6 (22) | 69.0 (20.6) | 60.5 (15.8) | 51.1 (10.6) | 44.4 (6.9) | 57.8 (14.3) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 23.6 (−4.7) | 27.5 (−2.5) | 32.5 (0.3) | 39.2 (4) | 50.8 (10.4) | 62.2 (16.8) | 66.7 (19.3) | 67.3 (19.6) | 59.6 (15.3) | 43.0 (6.1) | 33.2 (0.7) | 26.9 (−2.8) | 21.6 (−5.8) |
| Record low °F (°C) | 10 (−12) | 6 (−14) | 22 (−6) | 32 (0) | 42 (6) | 50 (10) | 60 (16) | 60 (16) | 48 (9) | 32 (0) | 20 (−7) | 13 (−11) | 6 (−14) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.33 (84.6) | 3.20 (81.3) | 4.33 (110) | 2.67 (67.8) | 2.48 (63) | 7.12 (180.8) | 6.07 (154.2) | 6.39 (162.3) | 4.42 (112.3) | 2.88 (73.2) | 2.06 (52.3) | 2.38 (60.5) | 47.33 (1,202.2) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 8.9 | 7.2 | 7.9 | 5.8 | 6.5 | 14.7 | 15.4 | 16.1 | 11.6 | 7.3 | 6.1 | 6.9 | 114.4 |
| Source: NOAA[18][22] | |||||||||||||
Cityscape

Alachua County Courthouse Family and Civil Justice Center

University Corners, viewed from the main entrance to the University of Florida, February 2012. This is now the site of the apartment complex "The Standard", which opened in 2017.

Gainesville's Downtown

Hippodrome State Theatre
Since the 1990s, suburban sprawl has been a concern for a majority of the city commissioners. However, the "New Urbanization" plan to gentrify the area between historic Downtown and the University of Florida may slow the growth of suburban sectors and spark a migration toward upper-level apartments in the inner city. The area immediately north of the University of Florida is also seeing active redevelopment. Many gentrification plans rely on tax incentives that have sparked controversy,[23] and even so are sometimes unsuccessful. University Corners, which would not have been proposed without a $98 million tax incentive program by the city[24] was to be "a crowning jewel of the city's redevelopment efforts",[25] 450 condos and hotel units and 98,000 square feet (9,100 m2) of retail space in eight stories covering three city blocks,[26] on 3.4 acres (1.4 ha) purchased for $15.5 million.[27] 19 thriving businesses[23] were demolished in April 2007,[27] but in May 2008 deposit checks were refunded to about 105 people who reserved units,[28] and in July 2008 developers spent "$120,000 to beautify the site, so we won't have this ugly green fence."[27]
The east side of Gainesville houses the majority of the African-American community within the city, while the west side consists of the mainly student and white resident population. West of the city limits there are large-scale planned communities, most notably Haile Plantation, which was built on the site of its eponymous former plantation.
The destruction of the city's landmark Victorian courthouse in the 1960s, which some considered unnecessary, brought the idea of historic preservation to the attention of the community. The bland county building that replaced the grand courthouse became known to some locals as the "air conditioner". Additional destruction of other historic buildings in the downtown followed. Only a small handful of older buildings are left, like the Hippodrome State Theatre, at one time a federal building. Revitalization of the city's core has picked up, and many parking lots and underutilized buildings are being replaced with infill development and near-campus housing that blend in with existing historic structures. There is a proposal to rebuild a replica of the old courthouse on a parking lot one block from the original location.
Helping in this effort are the number of areas and buildings added to the National Register of Historic Places. Dozens of examples of restored Victorian and Queen Anne style residences constructed in the city's agricultural heyday of the 1880s and 1890s can be found in the following districts:
- Northeast Gainesville Residential District
- Southeast Gainesville Residential District
- Pleasant Street Historic District
Additionally, the University of Florida Campus Historic District, consisting of eleven buildings, plus an additional fourteen contributing properties, lie within the boundaries of the city. Most of the buildings in the Campus Historic District are constructed in variations of Collegiate Gothic architecture, which returned to prominence in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Historic structures on the Register in and around downtown are:
Bailey Plantation House (1854)
Colson House (1905)
Matheson House (1867)
Thomas Hotel (1910)- The Old Post Office (now the Hippodrome State Theatre) (1911)
Masonic Temple (1908)
Seagle Building (1926), downtown Gainesville's tallest building.
Baird Hardware Company Warehouse (1890)
Cox Furniture Store (1875)
Cox Furniture Warehouse (c. 1890)
Epworth Hall (1884)
Old Gainesville Depot (1907)
Mary Phifer McKenzie House (1895)
Star Garage (1902)
Developments and expansions
- Celebration Pointe[29]
- Innovation Square[30]
- University Corners[31]
- The Continuum – Graduate and Professional Student Housing[32]
- Embassy Suites 12 Stories. (Would be Tallest building in Downtown Gainesville)[33]
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1890 | 2,790 | — | |
| 1900 | 3,633 | 30.2% | |
| 1910 | 6,183 | 70.2% | |
| 1920 | 6,860 | 10.9% | |
| 1930 | 10,465 | 52.6% | |
| 1940 | 13,757 | 31.5% | |
| 1950 | 26,861 | 95.3% | |
| 1960 | 29,701 | 10.6% | |
| 1970 | 64,510 | 117.2% | |
| 1980 | 81,371 | 26.1% | |
| 1990 | 84,770 | 4.2% | |
| 2000 | 95,447 | 12.6% | |
| 2010 | 124,354 | 30.3% | |
| Est. 2016 | 131,591 | [8] | 5.8% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[34] | |||
| Gainesville Demographics | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 Census | Gainesville | Alachua County | Florida |
| Total population | 124,354 | 247,336 | 18,801,310 |
| Population, percent change, 2000 to 2010 | +30.3% | +13.5% | +17.6% |
| Population density | 2,028.5/sq mi | 282.7/sq mi | 350.6/sq mi |
White or Caucasian (including White Hispanic) | 64.9% | 69.6% | 75.0% |
| (Non-Hispanic White or Caucasian) | 57.8% | 63.7% | 57.9% |
| Hispanic or Latino (of any race) | 10.0% | 8.4% | 22.5% |
| Black or African-American | 23.0% | 20.3% | 16.0% |
| Asian | 6.9% | 5.4% | 2.4% |
Native American or Native Alaskan | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.4% |
Pacific Islander or Native Hawaiian | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.1% |
| Two or more races (Multiracial) | 2.9% | 2.6% | 2.5% |
| Some Other Race | 1.9% | 1.7% | 3.6% |
The population of Gainesville was estimated to be 125,365 in 2011. The population of Gainesville was 124,354 at the 2010 census, a 30.3% change from 2000. At the 2010 census there were 51,029 households, with 2.2 persons per household. Children under the age of 5 were 4.4% of the population, under 18 13.4%, and people 65 years or over were 8.3% of the population. 64.9% of the population was white, 23.0% black, 6.9% Asian, 0.3% American Indians and Alaska Natives, 0.1% Native Hawaiians and Other Pacific Islanders, 1.9% some other race, and 2.9% reporting two or more races. 10.0 percent were Hispanic or Latino of any race, and 58.7% were non-Hispanic whites. 51.6% of the population were female. For the period 2007–11, the estimated median household income $30,952, and the per capita income was $19,100.[35]
Languages
As of 2000, 87.10% of residents spoke English as their first language, while 6.31% spoke Spanish, 1.28% spoke Chinese, 0.55% spoke French, 0.52% spoke Korean, and 0.50% spoke German as their mother tongue. In total, 12.89% of the total population spoke languages other than English.[36]
Economy
Numerous guides such as the 2004 book Cities Ranked and Rated: More than 400 Metropolitan Areas Evaluated in the U.S. and Canada have mentioned Gainesville's low cost of living. The restaurants near the University of Florida also tend to be inexpensive. The property taxes are high to offset the cost of the university, as the university's land is tax-exempt. However, the median home cost remains slightly below the national average, and Gainesville residents, like all Floridians, do not pay state income taxes.
The city's job market scored only 6 points out of a possible 100 in the Cities Ranked and Rated guide, as the downside to the low cost of living is an extremely weak local job market that is oversupplied with college-educated residents. The median income in Gainesville is slightly below the U.S. average.
The city of Gainesville heavily promoted solar power by creating the first feed-in tariff (FIT) in the United States. The FIT allowed small businesses and homeowners to supply electricity into the municipal power grid and paid a premium for the clean, on-site generated solar electricity. The FIT started with a rate set at $0.32 per kilowatt-hour and would allow the person or business to enter into a 20-year contract where Gainesville Regional Utilities would purchase the power for 20 years.[37] The FIT ended in 2013,[38] when the rate was set at $0.18 per kWh, but the city is still seen as a leader in solar power. This increase in solar installations put Gainesville at number 5 in the world, in solar installed per-capita, beating Japan, France, China and all of the US.[39]
The sports drink Gatorade was invented in Gainesville in the 1960s as a means of refreshing the UF football team. UF still receives a share of the profits from the beverage. However, Gatorade's headquarters are now in Chicago.

Spring Hill UF Health building
Top employers
According to Gainesville's 2017 Comprehensive Annual Financial Report,[40] the top employers in the city are:
| No. | Employer | No. of Employees |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | University of Florida | 27,567 |
| 2 | UF Health | 12,705 |
| 3 | Gainesville Veterans Administration Medical Center | 6,127 |
| 4 | Alachua County School Board | 3,904 |
| 5 | City of Gainesville | 2,072 |
| 6 | North Florida Regional Medical Center | 2,000 |
| 7 | Gator Dining Services | 1,200 |
| 8 | Nationwide Insurance | 960 |
| 9 | Alachua County | 809 |
| 10 | Publix | 780 |
Education

University of Florida
All of the Gainesville urban area is served by Alachua County Public Schools, which has some 75 different institutions in the county, most of which are in the Gainesville area. Gainesville is also home to the University of Florida and Santa Fe College. The University of Florida is a major financial boost to the community, and hundreds of thousands of dollars in additional revenues are created by the athletic events that occur at UF, including SEC football games. In all, the University of Florida contributes nearly $9 billion annually to Florida's economy and is responsible for more than 100,000 jobs.[41]
Desegregation
Gainesville began desegregating its schools in the 1960s. It integrated its high schools from 1968 to 1970. Its black schools were either closed or integrated.[42]
Schools
- 18 elementary schools
- 5 middle schools
- 6 high schools
- 4 Colleges
- 10 Private schools
Elementary schools
- Boulware Springs Charter School
- Chiles Elementary School
- Duval Elementary School
- JJ Finley Elementary School
- Foster Elementary School
- Glen Springs Elementary School
- Hidden Oak Elementary School
- Idylwilde Elementary School
- Lake Forest Elementary School
- Littlewood Elementary School
- Meadowbrook Elementary School
- WA Metcalfe Elementary School
- Norton Knights Elementary School
- Prairie View Elementary School
- Rawlings Elementary School
- Talbot Elementary School
- Terwilliger Elementary School
- Wiles Elementary School
- Williams Elementary School
Middle schools
Middle schools in the county run from 6th to 8th grades.
- Howard Bishop Middle School
- Fort Clarke Middle School
- Kanapaha Middle School
- Lincoln Middle School
- Westwood Middle School
High schools
High schools in Gainesville run from 9th to 12th grades.
- Buchholz High School
- Eastside High School
- Gainesville High School
- Loften High School

Oak Hall School Cofrin Arts Center
Private schools
- Brentwood School
- Countryside Christian School
- Cornerstone Academy
- Gainesville Country Day School
- Millhopper Montessori School
- Oak Hall School
- Queen of Peace Academy
- St. Patrick Interparish School
- The Rock School
- Trilogy School of Learning Alternatives
- Westwood Hills Christian School
- St. Francis Academy
- Newberry Christian Community School
Developmental Research Schools
- P.K. Yonge Developmental Research School

Sledd Hall at the University of Florida
Colleges and universities
- University of Florida
- Santa Fe College
Saint Leo University (Gainesville campus)
City College (Gainesville campus)
City libraries
The Alachua County Library District provides public library service to a county-wide population (in 2013) of 253,451. The Library District has reciprocal borrowing agreements with the surrounding counties of Baker, Bradford, Clay, Columbia, Dixie, Gilchrist, Lafayette, Levy, Marion, Putnam, and Union. These agreements are designed to facilitate access to the most conveniently located library facility regardless of an individual's county of residence.
Government and infrastructure
The Florida Department of Citrus has its department of economic research on the campus of the University of Florida.[43]
City government
Gainesville is administered by a 7-member city commission (4 commissioners are elected by district, 2 commissioners are elected at large plus a mayor elected at large). The commission and mayoral elections are non-partisan, with a runoff in case there is no majority winner.[4]
Gainesville's city hall is at 200 E University Avenue.
Law enforcement in Gainesville is provided by Gainesville Police Department, except for the University of Florida campus which operates the University Police Department.
Fire protection within the city limits is provided by the Gainesville Fire Rescue, while the surrounding county is served by the Alachua County Fire Rescue. Ambulance services are provided for the whole county by the Alachua County Fire Rescue.
Mayor
Mayor of Gainesville
William Reuben Thomas, 1901-1907- Horatio Davis, 1908-1909[44]
- ?
- Gordon Tison, circa 1918[45]
- ?
- Robert W. Davis, 1924-1925[44]
- ?
- J. Milton Brownlee, 1951[44]
- Fred M. Cone, 1952[44]
- Roy L. Purvis, 1953[44]
- C. B. Bohannon, Jr., 1954[44]
- Joseph C. Wise, 1955[44]
- Myrl J. Hanes, 1959[44]
Perry McGriff, circa 1960s??- ?
- Joseph W. Little, 1975-1976[46]
- ?
- Jean Chalmers, 1984-1985[46]
- Gary Gordon, 1985-1986
- N. David Flagg, 1987-1988[46]
- David Coffey, 1988-1989[46]
- Cynthia Moore Chestnut, 1989-1990[46]
- Rodney J. Long, 1991-1992[46]
- Paula M. DeLaney, 1994-1995, 1998-2001[46][47]
- Bruce L. Delaney, 1997-1998[46]
- Thomas D. Bussing, 2001-2004[46]
Pegeen Hanrahan, 2004-2010
Craig Lowe, 2010-2013- Ed Braddy, 2013-2016[48]
Lauren Poe, 2016–present
Homelessness issues
The National Coalition for the Homeless cited Gainesville as the 5th meanest city in the United States for the city's criminalization of homelessness in the Coalition's two most recent reports (in 2004 and 2009),[49][50] the latter time for its meal limit ordinance.[51] Gainesville has a number of ordinances that target the homeless, including an anti-panhandling measure and a measure making sleeping outdoors on public property illegal. In 2005, the Alachua Board of County Commissioners and the Gainesville City Commission responded by issuing a written "Ten Year Plan to End Homelessness";[52][53] which was followed by the 2010 "A Needs Assessment of Unsheltered Homeless Individuals In Gainesville, Florida" presentation to a joint meeting of Gainesville and Alachua County Commissions.[54] An indoor homeless shelter was built on the site of the former Gainesville Correctional Institution grounds, with surrounding area designated for tents.[55]
Transportation

Heading east on University Avenue, approaching 13th Street (US 441) intersection
In 2009, the Gainesville metropolitan statistical area (MSA) ranked as the seventh highest in the United States for percentage of commuters who biked to work (3.3 percent).[56]
Major roads
Gainesville has an extensive road system, which is served by Interstate 75, and several Florida State Routes, including State routes 20, 24, and 26, among others. Gainesville is also served by US 441 and nearby US 301, which give a direct route to Jacksonville, Ocala, and Orlando.
 I-75 runs northwest and southeast across the western edge of the city, with interchanges at SR 121/SR 331 (exit 382), SR 24 (exit 384), SR 26 (exit 387), and SR 222 (Exit 390).
I-75 runs northwest and southeast across the western edge of the city, with interchanges at SR 121/SR 331 (exit 382), SR 24 (exit 384), SR 26 (exit 387), and SR 222 (Exit 390).
 US 441 is the main local north and south road through Gainesville. It runs on the eastern edge of University of Florida. It is known to locals as 13th Street, before curving to the northwest and finally joining SR 20, thereby converting it into an additional hidden state road. At the intersection of SR 121, the DeSoto Trail moves from SR 121 to US 441.
US 441 is the main local north and south road through Gainesville. It runs on the eastern edge of University of Florida. It is known to locals as 13th Street, before curving to the northwest and finally joining SR 20, thereby converting it into an additional hidden state road. At the intersection of SR 121, the DeSoto Trail moves from SR 121 to US 441.
 SR 20 runs northwest and southeast through Gainesville. In east Gainesville, the road again becomes a stand-alone route that is four lanes wide highway as it heads to Hawthorne, Interlachen, and Palatka. Northwest of Gainesville, SR 20 coincides with US 441 as a hidden state road through the town of Alachua before splitting at the fork just a half-mile from downtown High Springs. SR 20 then coincides with US 27 as it heads to Fort White, Branford, Mayo, Perry, and Tallahassee.
SR 20 runs northwest and southeast through Gainesville. In east Gainesville, the road again becomes a stand-alone route that is four lanes wide highway as it heads to Hawthorne, Interlachen, and Palatka. Northwest of Gainesville, SR 20 coincides with US 441 as a hidden state road through the town of Alachua before splitting at the fork just a half-mile from downtown High Springs. SR 20 then coincides with US 27 as it heads to Fort White, Branford, Mayo, Perry, and Tallahassee.
 SR 24 runs northeast and southwest through Gainesville. The Northeast corner of SR 24 and SR 222 is the site of the Gainesville Regional Airport, before heading to Waldo, Starke, and Jacksonville (Via.U.S. Route 301)(Gainesville-Jacksonville Highway). Heading southwest of Gainesville, SR 24 passes through the towns of Archer and Bronson before ending at Cedar Key.
SR 24 runs northeast and southwest through Gainesville. The Northeast corner of SR 24 and SR 222 is the site of the Gainesville Regional Airport, before heading to Waldo, Starke, and Jacksonville (Via.U.S. Route 301)(Gainesville-Jacksonville Highway). Heading southwest of Gainesville, SR 24 passes through the towns of Archer and Bronson before ending at Cedar Key.
 SR 26 is the main local east and west road through Gainesville. West of the city, it spans from Fanning Springs, passing through Trenton, Newberry, and Jonesville. Eastward, SR 26 heads to Melrose before reaching its terminus at Putnam Hall in Putnam County.
SR 26 is the main local east and west road through Gainesville. West of the city, it spans from Fanning Springs, passing through Trenton, Newberry, and Jonesville. Eastward, SR 26 heads to Melrose before reaching its terminus at Putnam Hall in Putnam County.
 SR 120 runs east and west through the city. Its western end is at the junction with US 441, while its eastern end is at the junction with SR 24.
SR 120 runs east and west through the city. Its western end is at the junction with US 441, while its eastern end is at the junction with SR 24.
 SR 121 runs north and south on the western part of the city. The DeSoto Trail breaks away as SR 121 heads north to Lake Butler, Raiford, and Macclenny. Southward, it travels to Williston before reaching its terminus at Lebanon Station.
SR 121 runs north and south on the western part of the city. The DeSoto Trail breaks away as SR 121 heads north to Lake Butler, Raiford, and Macclenny. Southward, it travels to Williston before reaching its terminus at Lebanon Station.
 SR 222 runs east and west on the northern part of the city. Its western end of state maintenance is at the junction with I-75 before continuing as County Road 222 to County Road 241, while its eastern end is at the junction with SR 26 just miles east of the Gainesville Regional Airport.
SR 222 runs east and west on the northern part of the city. Its western end of state maintenance is at the junction with I-75 before continuing as County Road 222 to County Road 241, while its eastern end is at the junction with SR 26 just miles east of the Gainesville Regional Airport.
 SR 331 runs northeast and southwest through the City. It also serves as a truck route for State Roads 24, 26, and 121. Despite skirting the Gainesville City Limits, SR 331 runs north and south as a four-lane divided rural highway.
SR 331 runs northeast and southwest through the City. It also serves as a truck route for State Roads 24, 26, and 121. Despite skirting the Gainesville City Limits, SR 331 runs north and south as a four-lane divided rural highway.
The city's streets lie on a grid system, with four quadrants (NW, NE, SW and SE). All streets are numbered, except for a few major thoroughfares, which are often named for the towns they lead to (such as Waldo Road (SR 24), Hawthorne Road (SR 20), Williston Road (SR 121/SR 331), Archer Road (also SR 24) and Newberry Road (SR 26)). Streets ending in the suffixes Avenue, Place, Road or Lane (often remembered by use of the acronym "APRiL") run generally east-west, while all other streets run generally north-south.
Intercity rail
Amtrak Thruway Motorcoach buses connect with Jacksonville, Florida, to the north and Lakeland, Florida (to/from points south, LKL), to the south. Buses arrive/depart stations to connect with the Silver Service. Amtrak train service is available at Palatka, Florida, 32 miles (51 km) to the east.
At one time, Gainesville had railroad lines extending in six directions from the community and was served by several depots, the earliest route constructed reaching the town in 1859. As traffic and business patterns changed, the less heavily used railroads were abandoned beginning in 1943, and some routes realigned, with the last trains running in the middle of Main Street in 1948.[57]
Passenger service included different Atlantic Coast Line Railroad (ACL) trains: the Havana Special, the West Coast Champion from New York City, and the Dixie Flyer from Chicago. Chicago service was furnished by a transfer at Jacksonville onto the West Coast Champion. In 1967, the service continued on through Seaboard Coast Line Railroad which was created as a merger of ACL and Seaboard Air Line. However, service into Gainesville had ended by the time of Amtrak's 1971 creation.
By the 1980s, the only freight operator into the city was the Seaboard System (formerly the Seaboard Coast Line Railroad, now merged into CSX).
Airport, bus, and others
In addition to its extensive road network, Gainesville is served by Gainesville Regional Transit System, or RTS, which is the fourth-largest mass transit system in the state. The area is also served by Gainesville Regional Airport in the northeast part of the city, with daily service to Atlanta, Miami and Charlotte.
According to the 2000 census, 5.25 percent of Gainesville residents commuted to work by bike, among the highest figures in the nation for a major population center.
Culture
Gainesville is known as a supporter of the visual arts. Each year, two large art festivals attract artists and visitors from all over the southeastern United States.
Cultural facilities include the Florida Museum of Natural History, Harn Museum of Art, the Hippodrome State Theatre, and the Curtis M. Phillips Center for the Performing Arts. Smaller theaters include the Acrosstown Repertory Theatre (ART), Actors' Warehouse, and the Gainesville Community Playhouse (GCP). GCP is the oldest community theater group in Florida; in 2006, it christened a new theater building.[58]
The presence of a major university enhances the city's opportunities for cultural lifestyles. The University of Florida College of the Arts[59] is the umbrella college for the School of Music, School of Theatre and Dance, School of Art and Art History, and a number of other programs and centers including The University Galleries, the Center for World Art, and Digital Worlds. Collectively, the College offers many performance events and artist/lecture opportunities for students and the greater Gainesville community, the majority of which are offered at little or no cost.
Since 1989, Gainesville has been home to Theatre Strike Force, the University of Florida's premier improv troupe. In addition Gainesville also plays host to several sketch comedy troupes and stand-up comedians.
In April 2003, Gainesville became known as the "Healthiest Community in America" when it achieved the only "Gold Well City" award given by the Wellness Councils of America (WELCOA).[60] Headed up by Gainesville Health & Fitness Centers, and with the support of Shands HealthCare and the Gainesville Area Chamber of Commerce, 21 businesses comprising 60 percent of the city's workforce became involved in the "Gold Well City" effort. As of July 2011, Gainesville remained the only city in the country to reach the achievement.
The counties surrounding Alachua County vote strongly Republican, while Alachua County votes strongly Democratic.[61] In the 2008 election, there was a 22% gap in votes in Alachua County between Barack Obama and John McCain, while the remaining eleven candidates on the ballot and write-in votes received approximately 1.46% of the vote.[62]
Marijuana culture
Gainesville is renowned in the recreational drug culture for "Gainesville Green", a particularly potent strain of marijuana. Orange and Blue magazine published a feature article in 2003 about the history of Gainesville Green and the local marijuana culture in general.[63] In the mid-1990s, several Gainesville Hemp Festivals took place outside of the Alachua County courthouse.
Music scene
Gainesville is well known for its music scene and has spawned a number of bands and musicians, including Tom Petty and the Heartbreakers, Stephen Stills, Don Felder and Bernie Leadon of The Eagles, The Motels, Against Me!, Charles Bradley, Less Than Jake, Hot Water Music, Loyal Revival, John Vanderslice, Sister Hazel, Hundred Waters, and For Squirrels. It is also the location of independent labels No Idea Records and Elestial Sound, and the former home of Plan-It-X Records, which moved to Bloomington, Indiana. For two years, the Gainesville non-profit Harvest of Hope Foundation hosted the Harvest of Hope Festival in St. Augustine, Florida.[64] Gainesville is also the home of www.FLAROCKS.com, the founders of 'Santa Jam' who hold concerts every December throughout North Florida as a toy fundraiser for sick, injured, and homeless children and a showcase for local musicians. Since 2011 they have distributed nearly 700 toys to hospitals, local churches & homeless charities, and to needy families across the area.
No Idea Records puts on an annual three-day rock festival known as The Fest, which typically occurs during the last weekend in October, coinciding with the annual Florida-Georgia football game (played in Jacksonville) to minimize tensions between the largely out of town music festival goers with the University of Florida students and alumni.[65]
Between 1987 and 1998, Gainesville had a very active rock music scene, with Hollywood star River Phoenix having the local club Hardback Cafe as his main base. Phoenix's band Aleka's Attic was a constant feature of the rock scene, among others.[66] The Phoenix family is still a presence in Gainesville with Rain Phoenix's band Papercranes and Liberty Phoenix's store, Indigo.[67]
Today, Gainesville is still known for its strong music community and was named "Best Place to Start a Band in the United States" by Blender magazine in March 2008.[68] The article cited the large student population, cheap rent, and friendly venues as reasons.
Over the past decade, Gainesville has been home to a wide variety of bands, from the Latin/afrobeat sounds of Umoja Orchestra, to the rock of Morningbell, to ska staples The Know How.[69]
Gainesville's reputation as an independent music mecca can be traced back to 1984 when a local music video station was brought on the air. The station was called TV-69, broadcast on UHF 69 and was owned by Cozzin Communications.[70] The channel drew considerable media attention thanks to its promotion by Bill Cosby, who was part-owner of that station when it started. TV-69 featured many videos by punk and indie-label bands and had several locally produced videos ("Clone Love" by a local parody band, and a Dinosaur Jr. song).

Ben Hill Griffin Stadium
Sports
The Florida Gators is the varsity team of the University of Florida, and competes at the Southeastern Conference of the National Collegiate Athletic Association since 1933. It has been ranked in the top 10 in the NACDA ranking since the 1983–84 season. It has won 40 national team championships, including two men's basketball titles, three football titles, four men's golf titles, and seven women's tennis titles.
Opened in 1969, the Gainesville Raceway is a dragstrip that hosts the Gatornationals, one of the four NHRA major races.
Startup culture
Roughly since the 2006 founding of Grooveshark, a Gainesville-based music streaming service, Gainesville has seen an increase in the number of technology-based startup companies founded and developed in the city, particularly the downtown area.[71][72][73] Among them are Digital Brands, SharpSpring, Fracture, Feathr, and others. The city celebrates Josh Greenberg Day annually in April, in honor of the late founder of Grooveshark and his contributions to the community's startup culture.[74]
Annual cultural events
- The Spring Arts Festival, hosted each year, usually in early April, by Santa Fe College (formerly Santa Fe Community College), is one of the three largest annual events in Gainesville and is known for its high quality, unique artwork.[75]
- The nationally recognized The Downtown Festival and Art Show, hosted each fall by the City of Gainesville, attracts award-winning artists and draws a crowd of more than 100,000.[76]
- The Hoggetowne Medieval Faire has attracted thousands of fairgoers for over 20 years.[77]
- The Gainesville Improv Festival provides a venue for new talent.
The Fest, a multi-day, multiple-venue underground music festival held annually in Gainesville, FL since 2002.[78][79]
Media
Independent Florida Alligator Logo
Print
Gainesville is served by The Gainesville Sun and The Independent Florida Alligator, the student newspaper for the University of Florida and Santa Fe College.
The New York Times Editing Center also resides in Gainesville.[80]
Radio
Arbitron ranks the Gainesville-Ocala market as the nation's 83rd-largest.[81] Thirteen radio stations are licensed to operate in the city of Gainesville—five AM stations, six commercial FM stations, and two low-power non-commercial FM stations. Three of the stations (WRUF, WRUF-FM, and WUFT-FM) are operated by broadcasting students at the University of Florida. WUFT-FM is the city's NPR member station, while the WRUF stations are operated as commercial stations.
Television
Gainesville is the 162nd-largest television market in the nation, as measured by Nielsen Media Research.[82] Broadcast television stations in the Gainesville market include WCJB, an ABC/CW affiliate in Gainesville; WGFL, a CBS affiliate broadcasting from High Springs; WNBW, a NBC affiliate in Gainesville; WOGX, a Fox owned-and-operated station from Ocala; WMYG-LP, an analog MyNetworkTV affiliate broadcasting from Lake City; and WUFT, the PBS station affiliated with the University of Florida in Gainesville.
WOGX bears the distinction of being the smallest network O&O in the United States, as a semi-satellite of another Fox O&O, WOFL in Orlando.
Points of interest

Boardwalk at the Devil's Millhopper

Newnans Lake

Sweetwater Wetlands Park

The Oaks Mall
- 34th Street Wall
- Baughman Center
- Ben Hill Griffin Stadium at Florida Field
- Bivens Arm
- Civic Media Center
- Devil's Millhopper
Florida Museum of Natural History, including the Butterfly Rainforest exhibit- Gainesville-Hawthorne Trail State Park
- Gainesville Raceway
- Haile Homestead
- Harn Museum of Art
- Helyx Bridge
- Hippodrome State Theatre
- Ichetucknee Springs State Park
- Kanapaha Botanical Gardens
- Lake Alice
- Marjorie Kinnan Rawlings Historic State Park
- Newnan's Lake
- Morningside Nature Center
- Paynes Prairie Preserve State Park
- San Felasco Hammock Preserve State Park
- Santa Fe College Teaching Zoo
- Stephen C. O'Connell Center
- The Oaks Mall
- William Reuben Thomas Center
- Sweetwater Wetlands Park
- Depot Park
- "Dreamers sensory garden"[83]
Sister cities
Gainesville maintains sister city relationships with five cities in four separate arrangements:[84]
 Novorossiisk, Krasnodar Krai, Russia (since 1982)
Novorossiisk, Krasnodar Krai, Russia (since 1982)
 Kfar Saba, Israel (since 1998)
Kfar Saba, Israel (since 1998)
 Qalqilya, Palestine (since 1998)
Qalqilya, Palestine (since 1998)
 Duhok, Kurdistan, Iraq (since 2006)
Duhok, Kurdistan, Iraq (since 2006)
 Rzeszów, Podkarpackie, Poland (since 2013)
Rzeszów, Podkarpackie, Poland (since 2013)
See also
- List of people from Gainesville, Florida
References
^ Cunningham, Ron. "Gville can!". The Gainesville Sun. Retrieved 19 January 2018..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ http://homemagazinegainesville.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/08/Hogtown.jpg. Missing or empty|title=(help)
^ "Airport Codes". Retrieved 19 January 2018.
^ ab "City Of Gainesville > City Commission". Cityofgainesville.org. Retrieved October 23, 2017.
^ "2016 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved Jul 7, 2017.
^ "Gainesville, Florida". Weather Underground. Retrieved 2007-07-22.
^ "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Incorporated Places: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2012". U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on October 19, 2013. Retrieved June 1, 2015.
^ ab "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved June 9, 2017.
^ "US Board on Geographic Names". United States Geological Survey. 2007-10-25. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
^ "Population estimates, July 1, 2017, (V2017)". Archived from the original on July 10, 2012. Retrieved September 11, 2018.
^ ab "Geographic Identifiers: 2010 Demographic Profile Data (G001): Gainesville city, Florida". U.S. Census Bureau, American Factfinder. Retrieved May 6, 2013.
^ "U.S. Census Data 2013". 2015-02-05. Archived from the original on July 10, 2012. Retrieved 2015-02-22.
^ "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. 2011-02-12. Retrieved 2011-04-23.
^ "University of Florida Facts". University of Florida. Archived from the original on May 20, 2011. Retrieved 2011-05-18.
^ "Ohio State named nation's largest college – again". Dayton Business Journal. October 20, 2008. Retrieved 2011-06-30.
^ "USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map". United States Department of Agriculture. Retrieved 2018-03-22.
^ ab "Monthly Averages for Gainesville, Florida". The Weather Channel. Archived from the original on October 23, 2007. Retrieved July 22, 2007.
^ abcde "NowData - NOAA Online Weather Data". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2018-03-22.
^ "Gainesville Records for February". National Weather Service. Retrieved 2007-07-21.
^ Alexander, Jackie. "NWS confirms Sunday morning snow flurries for Gainesville". The Gainesville Sun. Retrieved 30 September 2018.
^ Mean monthly maxima and minima (i.e. the highest and lowest temperature readings during an entire month or year) calculated based on data at said location from 1981 to 2010.
^ "Station Name: FL GAINESVILLE RGNL AP". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2018-03-22.
^ ab Randy Jewett. "City shouldn't pay for University Corners". Alligator.org. Retrieved October 17, 2017.
^ KATIE GALLAGHER. "Court case makes future uncertain for University Corners". Alligator.org. Retrieved October 17, 2017.
^ JEFF ADELSON. "Will University Corners see daylight?". Gainesville.com. Retrieved October 17, 2017.
^ Anthony Clark. "Work on Stadium Club to resume; University Corners still on hold". Gainesville.com. Retrieved October 17, 2017.
^ abc Megan Rolland. "University Corners cleans up for church". Gainesville.com. Retrieved October 17, 2017.
^ APRIL DUDASH. "Developers of stalled University Corners complex return checks". Alligator.org. Retrieved October 17, 2017.
^ "Lifestyle Center with Outlet Shopping - Celebration Pointe- Gainesville, FL". Celebrationpointe.com. Retrieved October 5, 2016.
^ "Innovation Square » Innovation Square. Innovation and Community Redefined". Innovationsquare.ufl.edu. Retrieved October 5, 2016.
^ Curry, Christopher (2012-12-03). "University Corners project back before the city". Gainesville.com. Retrieved 2015-06-07.
^ "The Continuum Apartments". Thecontinuumforufgrads.com. Retrieved October 5, 2016.
^ Morgan Watkins. "12-story hotel may soon rise from city parking lot". Gainesville.com. Retrieved October 5, 2016.
^ "U.S. Decennial Census". Census.gov. Archived from the original on May 12, 2015. Retrieved June 1, 2013.
^ "State and County QuickFacts Gainesville (city), Florida". U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 10, 2012. Retrieved 20 June 2012.
^ "Data Center Results". Mla.org. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
^ "Gainesville, Florida Solar Power Feed-In Tariff Program Maxed Out Before It Begins". Treehugger.com. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
^ Curry, Christopher (2013-12-19). "City Commission will not add to feed-in tariff in 2014". Gainesville.com. Retrieved 2015-06-07.
^ Farrell, John (2012-01-06). "Gainesville, Florida, Becomes a World Leader in Solar". CleanTechnica. Retrieved 2015-06-07.
^ "City of Gainesville CAFR" (PDF). Cityofgainesville.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 2, 2018. Retrieved August 2, 2018.
^ Florida, University of. "03 » Study finds UF has $8.76 billion economic impact on Florida » University of Florida". Archived from the original on July 1, 2014. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
^ Michael Gengler, 'Alternet,' August 27, 2018 "Teachers Were the Real Heroes of School Desegregation: Often overlooked in histories of school desegregation are the teachers" https://www.alternet.org/news-amp-politics/teachers-were-real-heroes-school-desegregation
^ "Contact" (Archive). Florida Department of Citrus. Retrieved on September 13, 2015. "Florida Department of Citrus Economic Research 2125 McCarty Hall – University of Florida Gainesville, Florida 32611-0249 USA"
^ abcdefgh Lawrence Kestenbaum (ed.). "Mayors of Gainesville, Florida". Political Graveyard. Retrieved April 20, 2017.
^ History of Florida, Past and Present: Historical and Biographical. Chicago: Lewis Publishing Company. 1923.
^ abcdefghi "Gainesville mayors, past and present, oppose the road tax", Gainesville Sun, October 25, 2012
^ "City Commission". Gainesville, Florida Official Homepage. Archived from the original on December 5, 2000 – via Internet Archive, Wayback Machine.
^ "Poe Defeats Braddy In Gainesville Mayoral Race", WUFT.org, University of Florida, March 15, 2016
^ "Illegal to be Homeless". National Coalition for the Homeless. November 2004. Retrieved 2007-07-22.
^ ROBERTA O. ROBERTS. "City named fifth meanest to homeless". Alligator.org. Retrieved October 17, 2017.
^ "Parks as soup kitchens – Under The Sun - Gainesville Sun". October 30, 2011. Archived from the original on October 30, 2011. Retrieved October 17, 2017.
^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on July 7, 2011. Retrieved July 8, 2011.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link) "The City of Gainesville/Alachua County Ten Year Plan to End Homelessness", Retrieved 2011-07-07
^ "Ten Year Plan to End Homelessness" (PDF). Alachua County Commission. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 11, 2007. Retrieved 2007-07-22.
^ ""Alachua County/City of Gainesville Quarterly Special Meeting — Meeting Agenda August 30, 2010"" (PDF). Meetingdocs.alachuacounty.us. Retrieved 2011-07-07.
^ "Indoor homeless shelter opens Wednesday". Gainesville.com. Retrieved 2015-10-08.
^ "Commuting in the United States: 2009" (PDF). American Community Survey Reports. September 2011. Retrieved December 26, 2017.
^ Florida Railroad from Fernandina to Cedar Key history florida[permanent dead link]
^ DAVE SCHLENKER. "Time to raise the curtains". Gainesville.com. Retrieved October 17, 2017.
^ "College of the Arts - University of Florida". Arts.ufl.edu. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
^ "Gainesville Goes Gold!". The Wellness Councils of America. May 2003. Archived from the original on May 14, 2008. Retrieved April 21, 2008.
^ "County Results–Election 2008". CNN. November 7, 2008. Retrieved March 13, 2009.
^ "Official Results — General Election — November 4, 2008 — Summary For Jurisdiction Wide, All Counters, All Races" (PDF). Alachua County Supervisor of Elections. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 27, 2011. Retrieved 2011-07-24.
^ Battey, Brandon (Fall 2003). "Gainesville Green isn't just a color". Orange and Blue". Archived from the original on July 4, 2007. Retrieved 2007-07-22.
^ "Harvest of Hope Festival". No Idea Records. March 2009. Archived from the original on February 28, 2009. Retrieved March 3, 2009.
^ "Four arrested for punching and kicking GPD officer". The Independent Florida Alligator. November 2009.
^ "Hardback Cafe Archive". Alan Bushnell. May 2007. Archived from the original on December 31, 2008. Retrieved 2008-07-19.
^ "Liberty Phoenix's Indigo". The Gainesville Sun. May 2007. Retrieved 2008-07-19.
^ "Gainesville named best place to start a band in America". Blender Magazine. March 2008. Archived from the original on June 5, 2009. Retrieved 2008-07-19.
^ "Current Gainesville Bands". www.gainesvillebands.com. July 2008. Retrieved 2008-07-19.
^ Gainesille's Only Music Video Station, 1996, archived from the original on 2011-06-15, retrieved 2008-07-19
[dead link]
^ Frankel, Ryan. "An Insider's Perspective: The Good, The Bad and The Ugly of Gainesville Startups". Business in Greater Gainesville. Retrieved 20 November 2017.
^ Schweers, Jeff (28 April 2013). "Gainesville's Startup Alley covets UF computer grads". The Gainesville Sun. Retrieved 20 November 2017.
^ Stein, Ron. "Gainesville has become a tech hub for engineering entrepreneurs". Florida Trend. Retrieved 20 November 2017.
^ Whitely, Richard (20 April 2016). "Gainesville Remembers Grooveshark Co-Founder With 'Josh Greenberg Day'". WUFT. Retrieved 20 November 2017.
^ "Spring Arts Festival - My WordPress Blog". Spring Arts Festival. Retrieved October 17, 2017.
^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on July 14, 2011. Retrieved 2011-07-07.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link) "Downtown Festival & Art Show", Retrieved 2011-07-07
^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on July 14, 2011. Retrieved 2011-07-07.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link) "Hoggetowne Medieval Faire", Retrieved 2011-07-07
^ @thefestfl. "The Fest 16 » History". The Fest 16. Retrieved October 17, 2017.
^ Levi Bradford (Oct 26, 2016). "Fifteen years of Fest". The Gainesville Sun. Retrieved May 4, 2017.
^ "The New York Times is relocating some wire service positions to Gainesville, creating about 25 jobs". Ocala.com. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
^ "Market Ranks and Schedule". Arbitron, Inc. Retrieved 2007-09-06.
^ "Local Television Market Universe Estimates". The Nielsen Company. Retrieved 6 September 2007.
^ Jill Lederman. "The Sensory Garden is an oasis for the blind and visually impaired". Gainesville.com. Retrieved October 17, 2017.
^ "Sister City Program of Gainesville". Sister City Program of Gainesville, Inc. Retrieved January 16, 2010.
Further reading
Andersen, Lars (2004). Paynes Prairie: The Great Savanna: A History and Guide. Sarasota, Florida, USA: Pineapple Press. ISBN 1-56164-296-7. Retrieved 2011-05-18.
Braley, R. Olin (2004). The Killing of Harmon Murray: Being a True Account of the Life and Times of Florida's Premier Black Outlaw. Gainesville, Florida: The Alachua Press.
- Fox, Kathleen A. ; Lane, Jodi. "Perceptions of gangs among prosecutors in an emerging gang city" (Report). Journal of Criminal Justice, July–August, 2010, Vol.38(4), p. 595(9)
Hicks, Rob (2008). Images of America: Gainesville. Arcadia Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7385-5402-0.
Hildreth, Charles H.; Merlin G. Cox (1981). History of Gainesville, Florida 1854-1979. Gainesville, Florida: Alachua County Historical Society.
McCarthy, Kevin M.; Murray D. Laurie (1997). Guide to the University of Florida and Gainesville. Sarasota, florida: Pineapple Press. ISBN 1-56164-134-0.
Milanich, Jerald T. (1995). Florida Indians and the Invasion from Europe. Gainesville, Florida, USA: University Press of Florida. ISBN 0-8130-1636-3.
Milanich, Jerald T. (1998). Florida's Indians from Ancient Times to the Present. Gainesville, Florida, USA: University Press of Florida. ISBN 0-8130-1598-7.
Milanich, Jerald T. (1999). The Timucua. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishers. ISBN 0-631-21864-5.
Milanich, Jerald T. (2006). Laboring in the Fields of the Lord: Spanish Missions and Southeastern Indians. Gainesville, Florida, USA: University Press of Florida. ISBN 0-8130-2966-X.
Newton, Michael (2001). The Invisible Empire: The Ku Klux Klan in Florida. Gainesville, Florida: The University Press of Florida. ISBN 0-8130-2120-0.
Pickard, Ben (1991). Historic Gainesville: a tour Guide to the Past. Gainesville, Florida: Historic Gainesville, Inc.
Rajtar, Steve (2007). A Guide to Historic Gainesville. Charleston, South Carolina; London: History Press. ISBN 978-1-59629-217-8.
Taulbee, Lindsay. "Gainesville in the '70s: Changes roiling beneath a polite Southern surface". Gainesville Magazine. Gainesville Sun. Retrieved 13 May 2011.
Washington, Ray. "University of Florida: Unrest amid the boom times 1960-1980". Gainesville Sun. Gainesville Sun. Retrieved 13 May 2011.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Gainesville, Florida. |
- Official website
- Gainesville Florida Visitors & Convention Bureau
- Gainesville Area Chamber of Commerce
University of Florida Digital Collections, including vast materials from and about Gainesville
 Gainesville, Florida travel guide from Wikivoyage
Gainesville, Florida travel guide from Wikivoyage