Cousin
Relationships (Outline) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Types
| |||||||||
Activities
| |||||||||
Endings
| |||||||||
Emotions and feelings
| |||||||||
Practices
| |||||||||
Abuse
| |||||||||
Commonly, "cousin" refers to a "first cousin", people whose most recent common ancestor is a grandparent.[1] A first cousin used to be known as a cousin-german, though this term is rarely used today.[2]
More generally, cousin is a type of familial relationship in which people with a known common ancestor are both two or more generations away from their most recent common ancestor. This distinguishes a cousin from an ancestor, descendant, sibling, aunt, uncle, niece, or nephew.[3]
Systems of "degrees" and "removals" are used in the English-speaking world to describe the exact relationship between two cousins (in the broad sense) and the ancestor they have in common.[4] Various governmental entities have established systems for legal use that can precisely specify kinship with common ancestors any number of generations in the past.[citation needed] Common usage often eliminates the degrees and removals, and refers to people with common ancestry as simply "distant cousins" or "relatives".[5]
Contents
1 Basic definitions
1.1 Multiplicities
1.2 Gendered relationships
1.3 Non-blood relations
1.4 Examples
2 Relationship charts
3 Cousin marriage
4 Genetics
5 Additional terms
6 See also
7 References
8 External links
Basic definitions
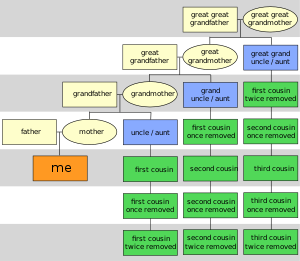
Family tree. Cousins are colored green. Generations are shown by alternating stripes of gray and white.
People are related with a type of cousin relationship if they share a common ancestor and the most recent common ancestor is two or more generations away from both people. This means neither person is an ancestor of the other, they do not share a parent (siblings), and neither is a sibling of a common ancestor (aunts/uncles and nieces/nephews).[3]
The cousin relationship is further detailed by degree and removal. For example, the second cousin once removed relationship is a second-degree cousin with one removal.
The removal of the cousin relationship is the number of generations the cousins are apart. When the cousins are separated by a different number of generations from the most recent common ancestor, the cousin relationship is removed. The difference between the number of generations for each cousin is the removal.[4] For example, if the most recent common ancestor is 2 generations prior for one person and 3 generations prior for the other (one person's grandfather is the other person's great-grandfather) or the most recent common ancestor is 3 generations prior for one person and 4 generations prior for the other (one person's great-grandfather is the other person's great-great-grandfather) the cousins are separated by one generation and therefore once removed. Note that two people can be removed but be around the same age due to differences in birth dates of parents children and other relevant ancestors.[4][6]
The degree of the cousin relationship is the number of generations prior to the parents before a most recent common ancestor is found. If the cousins are removed, the smaller number of generations to the most recent common ancestor is used to determine the degree of the cousin relationship.[4] For example, if one of the cousins has to go back one generation beyond their parents (the grandparents) before finding the most recent common ancestor and the other has to go back one or more they are first cousins. If one had to go back two generations beyond the parents (great grandparents) and the other had to go back two or more they would be second cousins[6][4].
Multiplicities
Double cousins arise when two siblings of one family mate with two siblings of another family. This may also be referred to as 'cousins on both sides.' The resulting children are related to each other through both of their parents and are thus doubly related. Double first cousins share both sets of grandparents and have twice the degree of consanguinity of ordinary first cousins.
Half cousins are descended from half siblings. The children of two half siblings are first half cousins. If half siblings have children with another pair of half siblings, the resulting children would be double first half cousins.
Gendered relationships
A maternal cousin is a cousin that is related to the mother's side of the family, while a paternal cousin is a cousin that is related to the father's side of the family. Unlike all the other cousin relationships discussed thus far, this relationship is not necessarily reciprocal, as the maternal cousin of one person could be the paternal cousin of the other.
Parallel and cross cousins on the other hand are reciprocal relationships. Parallel cousins are descended from same-sex siblings. Cousins that are related to same sex siblings of their most recent common ancestor are parallel cousins. A parallel first cousin is either the paternal cousin on the father's side of the family or the maternal cousin on the mother's side of the family. Cross cousins are descendants from opposite-sex siblings. A cross first cousin is either the maternal cousin on the father's side of the family or the paternal cousin on the mother's side of the family.
Non-blood relations
Stepcousins are either stepchildren of an individual's aunt or uncle, nieces and nephews of one's stepparent, or the children of one's parent's stepsibling. Cousins in law are the cousins of a person's spouse or the spouse of a person's cousin. Neither of these relationships have consanguinity.
Examples
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
First cousins- A person shares a first cousin or cousin relationship with the children of their parents' siblings. Cousins share at least one set of grandparents.[6] In the example family tree, Joseph and Julie are first cousins.
- Second cousins
- A person shares a second cousin relationship with the children of their parents' cousins. Second cousins share at least one set of great-grandparents.[6] In the example family tree, Gordon and Matt are second cousins.
- Third cousins
- A person shares a third cousin relationship with the children of their parents' second cousins. Third cousins share at least one set of great-great-grandparents.[6] In the example family tree, Sam and Lyla are third cousins.
First cousins once removed- A person shares a first cousins once removed relationship with their parents' cousins and their cousins' children. At least one set of one person's grandparents are the great-grandparents of the other person.[6] In the example family tree, Gordon and Julie, as well as Joseph and Matt, are first cousins once removed.
First cousins twice removed- A person shares a first cousins twice removed relationship with their grandparents' cousins and their cousins' grandchildren. At least one set of one person's grandparents are the great-great-grandparents of the other person.[6] In the example family tree, Sam and Julie, as well as Joseph and Lyla, are first cousins twice removed.
Second cousins once removed- A person shares a second cousin once removed relationship with their parents' second cousins and their second cousins' children. At least one set of one person's great-grandparents are the great-great-grandparents of the other person.[6] In the example family tree, Sam and Matt, as well as Gordon and Lyla, are second cousins once removed.
- Maternal first cousins
- A person's maternal first cousins are the children of their mother's siblings. In the example family tree, Julie is Joseph's maternal first cousin.
- Paternal first cousins
- A person's paternal first cousins are the children of their father's siblings. In the example family tree, Joseph is Julie's paternal first cousin.
- Cross first cousins
- A person shares a cross cousin relationship with their first cousin when the children of the most recent common ancestor are of different sexes. For cross first cousins the parents of each cousin are siblings and of different sexes. [6] In the example family tree, Joseph and Julie are cross first cousins.
- Cousin-in-law
- A person shares a cousin-in-law relationship with their spouses cousin or the cousin of one's spouse. In the example family tree, Joseph and Roger are first cousins-in-law to each other.
Relationship charts
A "table of consanguinity", is helpful in identifying the degree of cousin relationship between two people using their most recent common ancestor as the reference point. Cousinship between two people can be specifically described in degrees and removals by determining how close, generationally, the common ancestor is to each person.[7][4][6]
| If the relative's → | Parent | Grandparent | Great-grandparent | Great-great-grandparent | Great-great-great-grandparent | Great-great-great-great-grandparent | |
| Is the subject's ↓ | Then the relative is the subject's ↘ | ||||||
Parent | Sibling | Niece/Nephew | Grandnephew/Grandniece | Great-grandnephew/Great-grandniece | Great-great-grandnephew/Great-great-grandniece | Great-great-great-grandnephew/Great-great-great-grandniece | |
Grandparent | Uncle/Aunt | 1st cousins | 1st cousins once removed | 1st cousins twice removed | 1st cousins three times removed | 1st cousins four times removed | |
Great-grandparent | Granduncle/Grandaunt or Great Aunt/Uncle [8][9] | 1st cousins once removed | 2nd cousins | 2nd cousins once removed | 2nd cousins twice removed | 2nd cousins three times removed | |
Great-great-grandparent | Great-granduncle/Great-grandaunt | 1st cousins twice removed | 2nd cousins once removed | 3rd cousins | 3rd cousins once removed | 3rd cousins twice removed | |
Great-great-great-grandparent | Great-great-granduncle/Great-great-grandaunt | 1st cousins three times removed | 2nd cousins twice removed | 3rd cousins once removed | 4th cousins | 4th cousins once removed | |
Great-great-great-great-grandparent | Great-great-great-granduncle/Great-great-great-grandaunt | 1st cousins four times removed | 2nd cousins three times removed | 3rd cousins twice removed | 4th cousins once removed | 5th cousins | |

Canon Law Relationship Chart. See an example of how to use chart.
Another visual chart used in determining the legal relationship between two people who share a common ancestor is a "canon law relationship chart".
The chart is the same as the previous chart with the exception that the chart is symmetrical and has been rotated 45° so that the common progenitor (most recent common ancestor) is placed at the peak. Since the graph is symmetrical the placement of either party in the relationship on either side of the graph is arbitrary. The graph does not distinguish between parents and children, or aunts/uncles and nieces/nephews. For these non symmetrical relationships the relationship of the person from the most recent generation is displayed (i.e. children and nieces/nephews).
Cousin marriage
Cousin marriage is important in several anthropological theories which often differentiate between matriarchal and patriarchal parallel and cross cousins.
Currently about 10% and historically as high as 80% of all marriages are between first or second cousins.[10][11] Cousin marriages are often arranged.[10][11][12][13][14] Anthropologists believe it is used as a tool to strengthen the family, conserve its wealth, protect its cultural heritage, and retain the power structure of the family and its place in the community.
Some groups encourage cousin marriage while others attach a strong social stigma to it. In some regions in the Middle East over half of all marriages are between first and second cousins. In some of the countries in this region this may exceed 70%.[15] Just outside this region it is often legal but infrequent. In other places it is legally prohibited and culturally equivalent to incest.[16][17] Supporters of cousin marriage often view the prohibition as discrimination,[18][19] while opponents cite the potential immorality.[20]
Genetics
Married couples that possess higher than normal consanguinity, shared identical DNA and genetic material, have an increased chance of sharing genes for recessive traits.[21] The percentage of consanguinity between any two individuals decreases fourfold as the most recent common ancestor recedes one generation. First cousins have four times the consanguinity of second cousins, while first cousins once removed have half that of first cousins. Double first cousins share both sets of grandparents and have twice the degree of consanguinity of ordinary first cousins; genetically, they are as related as half-siblings.
Children of these marriages may have an increased risk of genetic disorders, particularly if their parents both carry a harmful recessive mutation. In a scenario where two monozygotic (identical) twins mate with another pair of monozygotic twins, the resulting double cousins would test as genetically similar as siblings.
Scientists through multiple studies have established a substantial and consistent positive correlation between the kinship of couples and the number of children and grandchildren they have. The 2008 deCODE study results show that couples related at the level of third cousins have the greatest number of offspring, with the greatest reproductive success observed for couples related at the level of third and fourth cousins.[22] This study provides the most comprehensive answer yet to the longstanding question of how kinship affects fertility in humans. The study result was somewhat counterintuitive from an evolutionary perspective because closely related parents have a higher probability of having offspring homozygous for deleterious recessive mutations, although closer parental kinship can also decrease the likelihood of immunological incompatibility between mother and offspring, for example in rhesus factor blood type.[23] The study confirmed that the offspring of first and second cousins died younger and reproduced less.[24]
Additional terms
The following is a list of less common cousin terms.
| Term | Definition | Example | Chart | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Double cousin | Double cousins arise when two siblings of one family mate with two siblings of another family. | Joseph and Julie are double first cousins because each is related through their mother's family and also their father's family, the result of a brother and sister (Helen and Eugene) having married another brother and sister (James and Mary). For Joseph and Julie, each has a mother who is an aunt by blood of the other and a father who is an uncle by blood of the other. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Half-cousin | Half-cousins are the children of two half-siblings, and their respective spouses. | Joseph and Lilian are half cousins because their parents (Helen and Charles) are half-siblings, their grandmother (Beatrice) having remarried. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stepcousin | Stepcousins are either stepchildren of an individual's aunt or uncle or nieces and nephews of one's stepparent. | Joseph and Rachel are stepcousins because Joseph's uncle (Eugene) has become Rachel's stepfather as a result of Rachel's mother (Corinda) having remarried Eugene. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
- Collateral descendant
- Consanguinity
- Cousin marriage
- Family
- Parallel and cross cousins
- Sibling
- Second-degree relative
References
^ "Cousin". Brewer's Dictionary of Phrase & Fable. Chambers Harrap Publishers. 2013. 19..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "Cousin-german definition and meaning | Collins English Dictionary". www.collinsdictionary.com. Retrieved 2018-02-26.
^ ab "Definition of Cousin by Merriam-Webster". merriam-webster.com. Merriam-Webster.
^ abcdef A Dictionary of Genetics. Oxford University Press. 2013. 8.
^ "Definition of cousin in English by Oxford Dictionaries". oxforddictionaries.com. Oxford University Press.
^ abcdefghij "Genetic And Quantitative Aspects Of Genealogy – Types Of Collateral Relationships". Genetic-genealogy.co.uk. Retrieved 28 October 2014.
^ "What is a First Cousin, Twice Removed?". Genealogy.com. Retrieved Sep 26, 2015.
^ "great-aunt, n." Oxford English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 4 December 2018.
^ "grand-aunt, n." Oxford English Dictonary. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 4 December 2018.
^ ab Kershaw, Sarah (26 November 2009). "Shaking Off the Shame". The New York Times.
^ ab "Go Ahead, Kiss Your Cousin - DiscoverMagazine.com".
^ Bittles, Alan H. (May 2001). A Background Summary of Consanguineous Marriage (PDF) (Technical report). Edith Cowan University.
^ Bittles 1994, p. 567
^ Bittles and Black 2009, Section 7
^ Dr. Alan Bittles; Dr. Michael Black. "Global prevalence". consang.net.
^ "The Surprising Truth About Cousins and Marriage". 14 February 2014.
^ Paul, Diane B.; Spencer, Hamish G. (23 December 2008). ""It's Ok, We're Not Cousins by Blood": The Cousin Marriage Controversy in Historical Perspective". PLOS Biology. 6 (12): e320. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0060320 – via PLoS Journals.
^ "Final Thoughts". Cousin Couples. Retrieved 4 June 2016.
^ Brandon Keim (23 December 2008). "Cousin Marriage OK by Science". Wired.
^ Saletan, William (10 April 2002). "The Love That Dare Not Speak Its Surname" – via Slate.
^ The Conversation: What’s the genetic disease risk for children of related couples? Date: September 27, 2012. Source: Tiong Tan, Clinical Geneticist at Victorian Clinical Genetics Services and Researcher in Craniofacial Research, Murdoch Children's Research Institute.
^ PubMed: An association between the kinship and fertility of human couples. Free Full Text. Date: 2008 Feb 8; Source: https://www.decode.com/publications/ deCODE Genetics.
^ Science Daily: Third Cousins Have Greatest Number Of Offspring, Data From Iceland Shows. Date: February 8, 2008; Source: deCODE genetics.
^ Nature: When kissing cousins are good for kids - A little inbreeding might boost fertility. By Heidi Ledford. Date: Published online 7 February 2008.
External links
| Look up cousin in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- European kinship system
- Genealogy.com definition of various cousins
- Genealogy.com: What makes a cousin?
- Genetic Genealogy
- Family Relationship Chart