Harry S. Truman
| Harry S. Truman | |
|---|---|
 | |
| 33rd President of the United States | |
In office April 12, 1945 – January 20, 1953 | |
| Vice President | None (1945–1949)[a] Alben W. Barkley (1949–1953) |
| Preceded by | Franklin D. Roosevelt |
| Succeeded by | Dwight D. Eisenhower |
| 34th Vice President of the United States | |
In office January 20, 1945 – April 12, 1945 | |
| President | Franklin D. Roosevelt |
| Preceded by | Henry A. Wallace |
| Succeeded by | Alben W. Barkley |
United States Senator from Missouri | |
In office January 3, 1935 – January 17, 1945 | |
| Preceded by | Roscoe C. Patterson |
| Succeeded by | Frank P. Briggs |
| Presiding Judge of Jackson County, Missouri | |
In office January 1, 1927[1] – January 1, 1935[1] | |
| Preceded by | Elihu W. Hayes[2] |
| Succeeded by | Eugene I. Purcell[3] |
| Judge of Jackson County, Missouri's Eastern District | |
In office January 1, 1923[4] – January 1, 1925[4] | |
| Preceded by | James E. Gilday[5] |
| Succeeded by | Henry Rummel[3] |
| Personal details | |
| Born | (1884-05-08)May 8, 1884 Lamar, Missouri, U.S. |
| Died | December 26, 1972(1972-12-26) (aged 88) Kansas City, Missouri, U.S. |
| Resting place | Harry S. Truman Presidential Library and Museum Independence, Missouri, U.S. |
| Political party | Democratic |
| Spouse(s) | Bess Wallace (m. 1919) |
| Children | Margaret Truman |
| Parents |
|
| Education | Spalding's Commercial College UMKC School of Law (withdrew) |
| Signature |  |
| Military service | |
| Allegiance | United States |
| Service/branch | United States Army Missouri National Guard United States Army Reserve |
| Years of service | 1905–1911 (Missouri National Guard) 1917–1919 (United States Army) 1920–1953 (Reserve) |
| Rank | |
| Commands | Battery D, 129th Field Artillery, 60th Brigade, 35th Infantry Division 1st Battalion, 379th Field Artillery Regiment, 102nd Infantry Division 379th Field Artillery Regiment, 102nd Infantry Division |
| Battles/wars | World War I
|
Harry S. Truman[b] (May 8, 1884 – December 26, 1972) was the 33rd President of the United States (1945–1953), taking office upon the death of Franklin D. Roosevelt. A World War I veteran, he assumed the presidency during the waning months of World War II and the beginning of the Cold War. He is known for implementing the Marshall Plan to rebuild the economy of Western Europe, for establishing the Truman Doctrine and NATO against Soviet and Chinese Communism, and for intervening in the Korean War. In domestic affairs, he was a moderate Democrat whose liberal proposals were a continuation of Franklin Roosevelt's New Deal, but the conservative-dominated Congress blocked most of them. He used the veto power 180 times, more than any president since, and saw 12 overridden by Congress; only Grover Cleveland and Franklin D. Roosevelt used the veto more often, and only Gerald Ford and Andrew Johnson saw so many veto overrides.[7] He is the only world leader to have used nuclear weapons in war. He desegregated the U.S. Armed Forces, supported a newly independent Israel and was a founder of the United Nations.
Truman was born in Lamar, Missouri, and spent most of his youth on his family's 550-acre farm near Independence. In the last months of World War I, he served in combat in France as an artillery officer with his National Guard unit. After the war, he briefly owned a haberdashery in Kansas City, Missouri, and joined the Democratic Party and the political machine of Tom Pendergast. Truman was first elected to public office as a county official in 1922, and then as a U.S. Senator in 1934. He gained national prominence as chairman of the Truman Committee, formed in March 1941, which aimed to find and correct waste and inefficiency in Federal Government wartime contracts. After serving as a United States Senator from Missouri (1935–1945) and briefly as Vice President (1945), he succeeded to the presidency on April 12, 1945, upon the death of Franklin D. Roosevelt. Germany surrendered just a few weeks after he assumed the presidency, but the war with Imperial Japan raged on and was expected to last at least another year. Truman approved the use of atomic bombs to end the fighting and to spare the U.S. and Japanese lives that would inevitably be lost in the planned invasion of Japan and Japanese-held islands in the Pacific.[8] This decision and the numerous resulting issues remain the subject of debate to this day. Critics argue that the nuclear bombings were unnecessary since conventional methods could have achieved surrender, while defenders assert that it ultimately saved more lives that would have been lost during an invasion.[9][10] Truman presided over an unexpected surge in economic prosperity as the U.S. sought readjustment after long years of depression and war. His presidency was a turning point in foreign affairs as the United States engaged in an internationalist foreign policy and renounced isolationism. Truman helped found the United Nations in 1945, issued the Truman Doctrine in 1947 to contain Communism and got the $13 billion Marshall Plan enacted to rebuild Western Europe. His political coalition was based on the white South, labor unions, farmers, ethnic groups and traditional Democrats across the North. Truman was able to rally these groups of supporters during the 1948 presidential election and win a surprise victory that secured a presidential term in his own right.
The Soviet Union, then led by Joseph Stalin, became an enemy in the Cold War. Truman oversaw the Berlin Airlift of 1948 and the creation of NATO in 1949, but was unable to stop Communists from taking over China in 1949. In 1950, he survived unharmed from an assassination attempt. When Communist North Korea invaded South Korea in 1950, he sent U.S. troops and gained UN approval for the Korean War.[11] After initial successes in Korea, the UN forces were thrown back by Chinese intervention and the conflict was stalemated throughout the final years of Truman's presidency. On domestic issues, bills endorsed by Truman often faced opposition from a conservative Congress, but his administration was able to successfully guide the U.S. economy through the post-war economic challenges. Truman maintained that civil rights were a moral priority and in 1948 submitted the first comprehensive civil rights legislation and issued Executive Orders to start racial integration in the military and federal agencies. Allegations were raised of corruption in the Truman administration, linked to certain cabinet members and senior White House staff; this became a central campaign issue in the 1952 presidential election and helped account for Republican Dwight D. Eisenhower's electoral victory. Upon leaving office, Truman had a 19-year post-presidency marked by some financial difficulties, the founding of his presidential library, and the publication of his memoirs. When he left office, Truman's perceived ineffectiveness led to him being thought of as a poor president, but scholars began to rehabilitate his image in the 1960s.
Contents
1 Early life and career
1.1 World War I
1.2 Continued military service
2 Politics
2.1 Jackson County judge
2.2 U.S. Senator from Missouri
2.2.1 Truman Committee
3 Vice Presidency (1945)
4 Presidency (1945–1953)
4.1 First term (1945–1949)
4.1.1 Assuming office and the atomic bomb
4.1.2 Strikes and economic upheaval
4.1.3 United Nations, Marshall Plan, Cold War, and China
4.1.4 Berlin airlift
4.1.5 Recognition of Israel
4.2 1948 election
4.3 Full elected term (1949–1953)
4.3.1 Korean War
4.3.2 Worldwide defense
4.3.3 Soviet espionage and McCarthyism
4.3.4 White House renovations and assassination attempt
4.3.5 Steel and coal strikes
4.3.6 Scandals and controversies
4.4 Civil rights
4.5 Administration and cabinet
4.6 International trips
4.7 1952 election
5 Post-presidency
6 Death
7 Tributes and legacy
7.1 Legacy
7.2 Sites and honors
8 See also
9 Notes
10 References
11 Bibliography
11.1 Books
11.2 Primary sources
11.3 Journals
11.3.1 Time
11.3.2 The Washington Post
11.3.3 The New York Times
11.4 Harry S. Truman Library & Museum
11.5 Online sources
12 External links
Early life and career

Truman's birthplace and childhood home in Lamar, Missouri
Truman was born in Lamar, Missouri, on May 8, 1884, the oldest child of John Anderson Truman and Martha Ellen Young Truman. His parents chose the name Harry after his mother's brother, Harrison "Harry" Young. While the "S" did not stand for any one name, it was chosen as his middle initial to honor both of his grandfathers, Anderson Shipp Truman and Solomon Young.[12][13] The initial has been regularly written and printed followed by a period.[b] A brother, John Vivian, was born soon after Harry, followed by sister Mary Jane.[14] Truman's ancestry is primarily English, with a few forebears who were Scotch-Irish, German or French.[15][16]
John Truman was a farmer and livestock dealer. The family lived in Lamar until Harry was ten months old, when they moved to a farm near Harrisonville, Missouri. The family next moved to Belton, and in 1887 to his grandparents' 600-acre (240-ha) farm in Grandview.[17] When Truman was six, his parents moved to Independence, so he could attend the Presbyterian Church Sunday School. Truman did not attend a traditional school until he was eight.[18] While living in Independence, he served as a Shabbos goy for Jewish neighbors, doing tasks for them on Shabbat that their tradition prevented them doing on that day.[19][20][21]
As a boy, Truman was interested in music, reading, and history, all encouraged by his mother, with whom he was very close. As president, he solicited political as well as personal advice from her.[22] He rose at five every morning to practice the piano, which he studied more than twice a week until he was fifteen.[23] Truman worked as a page at the 1900 Democratic National Convention at Convention Hall in Kansas City;[24] his father had many friends who were active in the Democratic Party and helped young Harry to gain his first political position.[25]
After graduating from Independence High School in 1901, Truman enrolled in Spalding's Commercial College, a Kansas City business school; he studied bookkeeping, shorthand, and typing, but left after a year.[26] He made use of his business college experience to obtain a job as a timekeeper on the Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe Railway, sleeping in hobo camps near the rail lines.[27] He then took on a series of clerical jobs, and was employed briefly in the mail room of The Kansas City Star. Truman and his brother Vivian later worked as clerks at the National Bank of Commerce in Kansas City; one of their coworkers, who also lived in the same rooming house, was Arthur Eisenhower, the brother of Dwight and Milton.[28] Truman returned to the Grandview farm in 1906, where he lived until entering the army in 1917 after the beginning of the Great War.[29] During this period, he courted Bess Wallace; he proposed in 1911, but she turned him down. Truman later said he intended to propose again, but he wanted to have a better income than that earned by a farmer.[30] To that end, during his years on the farm and immediately after World War I, he became active in several business ventures, including a lead and zinc mine near Commerce, Oklahoma,[31] a company that bought land and leased the oil drilling rights to prospectors,[32] and speculation in Kansas City real estate.[33] Truman occasionally derived some income from these enterprises, but none proved successful in the long term.[34]
Truman is the most recent and only president since William McKinley (elected in 1897) who did not earn a college degree.[35] In addition to having briefly attended business college, from 1923 to 1925 he took night courses toward an LL.B. at the Kansas City Law School (now the University of Missouri–Kansas City School of Law), but dropped out after losing reelection as county judge.[36] He was informed by attorneys in the Kansas City area that his education and experience were probably sufficient to receive a license to practice law. However, he did not pursue it, because he won election as presiding judge.[37]
While serving as president in 1947, Truman applied for a license to practice law.[38] A friend who was an attorney began working out the arrangements, and informed Truman that his application had to be notarized. By the time Truman received this information he had changed his mind, so he never sought notarization. After rediscovery of Truman's application, in 1996 the Missouri Supreme Court issued Truman a posthumous honorary law license.[39]
World War I

Truman in uniform, ca. 1918
Because he was unable to afford to go to college, Truman had thought of attending the United States Military Academy at West Point, which had no tuition, but he was refused an appointment because of poor eyesight.[36] He enlisted in the Missouri Army National Guard in 1905, and served until 1911 in the Kansas City-based Battery B, 2nd Missouri Field Artillery Regiment, in which he attained the rank of corporal.[40] At his induction, his eyesight without glasses had been an unacceptable 20/50 in the right eye and 20/400 in the left (past the standard for legal blindness).[41] The second time he took the test, he passed by secretly memorizing the eye chart.[42]
When the United States entered World War I, Truman rejoined Battery B; he helped recruit new soldiers as the unit expanded, and his success led its members to elect him as their first lieutenant.[43] Before deployment to France, Truman was sent for training to Camp Doniphan, Fort Sill, near Lawton, Oklahoma when his regiment was federalized as the 129th Field Artillery.[44] The regimental commander during its training was Robert M. Danford, who later served as the Army's Chief of Field Artillery.[45] Truman later said he learned more practical, useful information from Danford in six weeks than from six months of formal Army instruction, and when Truman later served as an artillery instructor, he consciously patterned his approach on Danford's.[45]
Truman also ran the camp canteen with Edward Jacobson, a clothing store clerk he knew from Kansas City. Unlike most canteens funded by unit members, which usually lost money, the canteen operated by Truman and Jacobson turned a profit, returning each soldier's initial $2 investment and $10,000 in dividends in six months.[40] At Fort Sill, Truman met Lieutenant James M. Pendergast, nephew of Tom Pendergast, a Kansas City political boss, and this connection had a profound influence on Truman's later life.[46][47]
In mid-1918, about one million soldiers of the American Expeditionary Forces were in France.[48] Truman was promoted to captain in July 1918 and became commander of Battery D, 129th Field Artillery, 60th Artillery Brigade, 35th Division.[49] It was known for its discipline problems, and Truman was initially unpopular because of his efforts to restore order.[40] Despite attempts by the men to intimidate him into quitting, Truman succeeded by making his corporals and sergeants accountable for discipline; he promised to back them up if they performed capably, and reduce them to private and return them to the ranks if they did not.[50] In an event memorialized in battery lore as "The Battle of Who Run", his soldiers began to flee during a sudden night attack by the Germans in the Vosges Mountains; Truman succeeded at ordering his men to stay and fight, using profanity that he had first heard while working on the Santa Fe Railroad. The men were so surprised to hear Truman use such language that they immediately obeyed.[40]
Truman's unit joined in a massive prearranged assault barrage on September 26, 1918, at the opening of the Meuse-Argonne Offensive.[51] They advanced with difficulty over pitted terrain to follow the infantry, and they set up an observation post west of Cheppy.[52] On September 27, Truman saw through his binoculars an enemy artillery battery setting up across a river in a position allowing them to fire upon the neighboring 28th Division.[52] Truman's orders limited him to targets facing the 35th Division, but he ignored this and patiently waited until the Germans had walked their horses well away from their guns, ensuring they could not relocate out of range of Truman's battery.[52] He then ordered his men to open fire, and their attack destroyed the enemy battery.[52] His actions were credited with saving the lives of 28th Division soldiers who otherwise would have come under fire from the Germans.[53][54] Truman was given a dressing down by his regimental commander, Colonel Karl D. Klemm, who threatened to convene a court-martial, but Klemm never followed through, and Truman was not punished.[52]
In other action during the Meuse-Argonne fighting, Truman's battery provided support for George S. Patton's tank brigade,[55] and fired some of the last shots of the war on November 11, 1918. Battery D did not lose any men while under Truman's command in France. To show their appreciation of his leadership, his men presented him with a large loving cup upon their return to the United States after the war.[40]
The war was a transformative experience for Truman that brought out his leadership qualities. He had entered the service in 1917 as a family farmer who had worked in clerical jobs that did not require the ability to motivate and direct others, but during the war he gained leadership experience and a record of success that greatly enhanced and supported his post-war political career in Missouri.[40]
Truman was brought up in the Presbyterian and Baptist churches,[56] but avoided revivals and sometimes ridiculed revivalist preachers.[57] He rarely spoke about religion, which to him, primarily meant ethical behavior along traditional Protestant lines.[58] Most of the soldiers he commanded in the war were Catholics, and one of his close friends was the 129th Field Artillery's chaplain, Monsignor L. Curtis Tiernan.[59] Tiernan remained friendly with Truman until his death in 1960, and served as chief chaplain in the European Theater during World War II.[60] Developing leadership and interpersonal skills that later made him a successful politician helped Truman get along with his Catholic soldiers, as he did with soldiers of other Christian denominations and the unit's Jewish members.[61][62]
Continued military service
Truman was discharged from the Army as a major in May 1919.[63] In 1920 he was appointed a major in the Reserve Officer Corps; he became a lieutenant colonel in 1925 and a colonel in 1932.[64] In the 1920s and 1930s Truman commanded 1st Battalion, 379th Field Artillery Regiment, a unit of the 102nd Infantry Division.[65] After promotion to colonel, Truman advanced to command of the regiment.[66]
After his election to the U.S. Senate, Truman was transferred to the General Assignments Group, a holding unit for less active officers; he had not been consulted or notified in advance.[67] Truman protested his reassignment, which led to his resumption of regimental command.[67] He remained an active reservist until the early 1940s.[68] Truman volunteered for active military service during World War II, but was not accepted, partly because of age, and partly because President Franklin D. Roosevelt desired Senators and Congressman who belonged to the military reserves to support the war effort by remaining in Congress, or by ending their active duty service and resuming their Congressional seats.[69] He was an inactive reservist from the early 1940s until retiring on January 20, 1953.[70]
Politics
Jackson County judge

Harry and Bess Truman on their wedding day, June 28, 1919
After his wartime service, Truman returned to Independence, where he married Bess Wallace on June 28, 1919.[71] The couple had one child, Mary Margaret Truman.[72]
Shortly before the wedding, Truman and Jacobson opened a haberdashery together at 104 West 12th Street in downtown Kansas City. After brief initial success, the store went bankrupt during the recession of 1921.[22] Truman did not pay off the last of the debts from that venture until 1935, when he did so with the aid of banker William T. Kemper, who worked behind the scenes to enable Truman's brother Vivian to buy Truman's promissory note during the asset sale of a bank that had failed in the Great Depression.[73][74] The note had risen and fallen in value as it was bought and sold, interest accumulated and Truman made payments, so by the time the last bank to hold it failed, it was worth nearly $9,000.[75] Thanks to Kemper's efforts, Vivian Truman was able to buy it for $1,000.[74] Jacobson and Truman remained close friends even after their store failed, and Jacobson's advice to Truman on Zionism later played a role in the U.S. government's decision to recognize Israel.[76]
With the help of the Kansas City Democratic machine led by Tom Pendergast, Truman was elected in 1922 as County Court judge of Jackson County's eastern district—this was an administrative rather than judicial position, somewhat similar to county commissioners elsewhere. Truman was not re-elected in 1924, losing in a Republican wave led by President Calvin Coolidge's landslide election to a full term. Two years selling automobile club memberships convinced him that a public service career was safer for a family man approaching middle age, and he planned a countywide run for presiding judge in 1926.[77]
In 1926, Truman was elected presiding judge with the support of the Pendergast machine, and he was re-elected in 1930. Truman helped coordinate the Ten Year Plan, which transformed Jackson County and the Kansas City skyline with new public works projects, including an extensive series of roads and construction of a new Wight and Wight-designed County Court building. Also in 1926, he became president of the National Old Trails Road Association (NOTRA). He oversaw the dedication in the late 1920s of a series of 12 Madonna of the Trail monuments honoring pioneer women, which were installed along the trail.[77][78]
In 1933, Harry S. Truman was named Missouri's director for the Federal Re-Employment program (part of the Civil Works Administration) at the request of Postmaster General James Farley. This was payback to Pendergast for delivering the Kansas City vote to Franklin D. Roosevelt in the 1932 presidential election. The appointment confirmed Pendergast's control over federal patronage jobs in Missouri and marked the zenith of his power. It also created a relationship between Truman and Roosevelt's aide Harry Hopkins and assured Truman's avid support for the New Deal.[79]
U.S. Senator from Missouri

Drawer from the Senate desk used by Truman
After serving as a county judge, Truman wanted to run for Governor or Congress, but Pendergast rejected these ideas. Truman then thought he might serve out his career in some well-paying county sinecure, but circumstances changed when Pendergast reluctantly backed him in the 1934 Democratic primary for the U.S. Senate after four other potential candidates turned him down.[80] In the primary, Truman defeated Congressmen John J. Cochran and Jacob L. Milligan with the solid support of Jackson County, which was crucial to his candidacy. Also crucial were the contacts he had made statewide as a county official, Mason, military reservist, and member of the American Legion.[81] In the general election, Truman defeated incumbent Republican Roscoe C. Patterson by nearly 20 percentage points as part of a continuing wave of pro-New Deal Democrats elected in response to the Great Depression.[80][82][83]
Truman assumed office with a reputation as "the Senator from Pendergast." He turned over patronage decisions to Pendergast, though Truman always maintained that he voted with his conscience. He later defended the patronage decisions by saying that "by offering a little to the machine, [he] saved a lot".[83][84] In his first term, Truman spoke out against corporate greed and the dangers of Wall Street speculators and other moneyed special interests attaining too much influence in national affairs.[85] Though he served on the high-profile Appropriations and Interstate Commerce Committees, he was largely ignored by Democratic President Roosevelt and had trouble getting calls returned from the White House.[83][86]
During the U.S. Senate election in 1940, United States Attorney Maurice Milligan (Jacob Milligan's brother) and former governor Lloyd Stark both challenged Truman in the Democratic primary. Truman was politically weakened by Pendergast's imprisonment for income tax evasion the previous year; the senator had remained loyal, having claimed that Republican judges (not the Roosevelt administration) were responsible for the boss's downfall.[87]St. Louis party leader Robert E. Hannegan's support of Truman proved crucial; he later brokered the deal that put Truman on the national ticket. In the end, Stark and Milligan split the anti-Pendergast vote in the Senate Democratic primary and Truman won by a total of 8,000 votes. In the November election, Truman defeated Republican Manvel H. Davis by 51–49 percent.[88] As Senator Truman opposed both Nazi Germany and Communist Russia. One week after Hitler invaded the Soviet Union in 1941, he said:
If we see that Germany is winning we ought to help Russia, and if Russia is winning we ought to help Germany, and that way let them kill as many as possible although I don't want to see Hitler victorious under any circumstances.[89]
Truman Committee
In late 1940, Truman traveled to various military bases. The waste and profiteering he saw led him to use his subcommittee chairmanship in the Committee on Military Affairs to start investigations into abuses while the nation prepared for war. A new special committee was set up under Truman to conduct a formal investigation; the Roosevelt administration supported this plan rather than weather a more hostile probe by the House of Representatives. The main mission of the committee was to expose and fight waste and corruption in the gigantic government wartime contracts. Truman's initiative convinced Senate leaders of the necessity for the committee, which reflected his demands for honest and efficient administration and his distrust of big business and Wall Street. Truman managed the committee "with extraordinary skill" and usually achieved consensus, generating heavy media publicity that gave him a national reputation.[90][91] Activities of the Truman Committee ranged from criticizing the "dollar-a-year men" hired by the government, many of whom proved ineffective, to investigating a shoddily built New Jersey housing project for war workers.[92][93] The committee reportedly saved as much as $15 billion (equivalent to $262.02 billion in 2017),[94][95][96][97] and its activities put Truman on the cover of Time magazine.[98] According to the Senate's historical minutes, in leading the committee, "Truman erased his earlier public image as an errand-runner for Kansas City politicos", and "no senator ever gained greater political benefits from chairing a special investigating committee than did Missouri's Harry S. Truman."[99]
Vice Presidency (1945)
@media all and (max-width:720px){.mw-parser-output .tmulti>.thumbinner{width:100%!important;max-width:none!important}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsingle{float:none!important;max-width:none!important;width:100%!important;text-align:center}}


Roosevelt/Truman poster from 1944

Lauren Bacall lounges on top of the piano while Vice President Truman plays for servicemen at the National Press Club Canteen in Washington, D.C. (February 10, 1945).
Vice President Henry Wallace was popular among Democratic voters, but he was viewed as too far to the left and too friendly to labor for some of Roosevelt's advisers. The President and several of his confidantes wanted to replace Wallace with someone more acceptable to Democratic Party leaders and Roosevelt's advisors, knowing that Roosevelt might not live out a fourth term. Outgoing Democratic National Committee chairman Frank C. Walker, incoming chairman Hannegan, party treasurer Edwin W. Pauley, strategist Ed Flynn, Chicago Mayor Edward Joseph Kelly, and lobbyist George E. Allen all wanted to keep Wallace off the ticket.[100] Roosevelt told party leaders that he would accept either Truman or Supreme Court Justice William O. Douglas. State and city party leaders strongly preferred Truman, and Roosevelt agreed. Truman did not campaign for the Vice-Presidential spot, though he welcomed the attention as evidence that he had become more than the "Senator from Pendergast".[101]
Truman's nomination was dubbed the "Second Missouri Compromise" and was well received. The Roosevelt–Truman ticket achieved a 432–99 electoral-vote victory in the election, defeating the Republican ticket of Governor Thomas E. Dewey of New York and running mate Governor John Bricker of Ohio. Truman was sworn in as vice president on January 20, 1945.[102]
Truman's brief vice-presidency was relatively uneventful. On April 10, 1945,[103] Truman cast his only tie-breaking vote as President of the Senate, against a Robert A. Taft amendment that would have blocked the postwar delivery of Lend-Lease Act items contracted for during the war.[104][105] Roosevelt rarely contacted him, even to inform him of major decisions; the President and Vice President met alone together only twice during their time in office.[106] In one of his first acts as vice president, Truman created some controversy when he attended the disgraced Pendergast's funeral. He brushed aside the criticism, saying simply, "He was always my friend and I have always been his."[22] He had rarely discussed world affairs or domestic politics with Roosevelt; he was uninformed about major initiatives relating to the war and the top-secret Manhattan Project, which was about to test the world's first atomic bomb.[107] In an event that generated negative publicity for Truman, he was photographed with actress Lauren Bacall sitting atop the piano at the National Press Club as he played for soldiers.[108]
Truman had been vice president for 82 days when President Roosevelt died on April 12, 1945.[107] That afternoon, Truman presided over the Senate as usual. He had just adjourned the session for the day and was preparing to have a drink in House Speaker Sam Rayburn's office when he received an urgent message to go immediately to the White House. Truman assumed President Roosevelt wanted to meet with him, but Eleanor Roosevelt informed him her husband had died after suffering a massive cerebral hemorrhage. Truman's first concern was for Mrs. Roosevelt. He asked if there was anything he could do for her, to which she replied, "Is there anything we can do for you? For you are the one in trouble now!"[109][110][111]
Presidency (1945–1953)
Truman surrounded himself with his old friends, and appointed several to high positions that seemed well beyond their competence, including his two secretaries of the treasury, Fred Vinson and John Snyder. His closest friend in the White House was his military aide Harry H. Vaughan, who was criticized for trading access to the White House for expensive gifts.[112][113]
Truman loved to spend as much time as possible playing poker, telling stories and sipping bourbon. Alonzo Hamby notes that:
to many in the general public, gambling and bourbon swilling, however low-key, were not quite presidential. Neither was the intemperant "give 'em hell" campaign style nor the occasional profane phrase uttered in public. Poker exemplified a larger problem: the tension between his attempts at an image of leadership necessarily a cut above the ordinary and an informality that at times appeared to verge on crudeness.[114][115]
First term (1945–1949)
Assuming office and the atomic bomb

Joseph Stalin, Harry S. Truman, and Winston Churchill in Potsdam, July 1945
Shortly after taking the oath of office, Truman spoke to reporters: "Boys, if you ever pray, pray for me now. I don't know if you fellas ever had a load of hay fall on you, but when they told me what happened yesterday, I felt like the moon, the stars, and all the planets had fallen on me."[116]
Upon assuming the presidency, Truman asked all the members of Roosevelt's cabinet to remain in place, and told them he was open to their advice. He emphasized a central principle of his administration: he would be the one making decisions, and they were to support him.[117] Although Truman was told briefly on the afternoon of April 12 that the Allies had a new, highly destructive weapon, it was not until April 25 that Secretary of War Henry Stimson told him the details. Truman benefited from a honeymoon period after Roosevelt's death, and from the Allies' success in Europe, ending the war against Nazi Germany. Truman was pleased to issue the proclamation of V-E Day on May 8, 1945, his 61st birthday.[118][119]
.mw-parser-output .templatequote{overflow:hidden;margin:1em 0;padding:0 40px}.mw-parser-output .templatequote .templatequotecite{line-height:1.5em;text-align:left;padding-left:1.6em;margin-top:0}
We have discovered the most terrible bomb in the history of the world. It may be the fire destruction prophesied in the Euphrates Valley Era, after Noah and his fabulous Ark.
— Harry Truman, writing about the atomic bomb in his diary[120] on July 25, 1945[121]
In the wake of Allied victory, Truman journeyed to Europe for the Potsdam Conference. He was there when he learned that the Trinity test of the first atomic bomb on July 16 had been successful. He hinted to Joseph Stalin that the U.S. was about to use a new kind of weapon against the Japanese. Though this was the first time the Soviets had been officially given information about the atomic bomb, Stalin was already aware of the bomb project, having learned about it (through espionage) long before Truman did.[122][123][124]
In August, the Japanese government refused surrender demands as specifically outlined in the Potsdam Declaration. With the invasion of mainland Japan imminent, Truman approved the schedule for dropping the two available bombs. Truman always said that attacking Japan with atomic bombs saved many lives on both sides; military estimates for the invasion of mainland Japan were that it could take a year and result in 250,000 to 500,000 U.S. casualties. Hiroshima was bombed on August 6, and Nagasaki three days later, leaving 105,000 dead.[125] The Soviet Union declared war on Japan on August 9 and invaded Manchuria. Japan agreed to surrender the following day.[126][127]

Truman announces Japan's surrender. Washington, D.C., August 14, 1945.
Supporters[c] of Truman's decision argue that, given the tenacious Japanese defense of the outlying islands, the bombings saved hundreds of thousands of lives of prisoners, civilians, and combatants on both sides that would have been lost in an invasion of Japan. Critics have argued that the use of nuclear weapons was unnecessary, given that conventional tactics such as firebombing and naval blockade or a demonstrative bombing of an uninhabited area would have forced Japan's surrender and therefore assert that the attack constituted a crime of war.[128][129][130][131][132][133][134][135]
During the 1948 presidential campaign, Truman defended his decision to deploy atomic bombs during the war:
As President of the United States, I had the fateful responsibility of deciding whether or not to use this weapon for the first time. It was the hardest decision I ever had to make. But the President cannot duck hard problems—he cannot pass the buck. I made the decision after discussions with the ablest men in our Government, and after long and prayerful consideration. I decided that the bomb should be used in order to end the war quickly and save countless lives—Japanese as well as American.[136]
Truman continued to strongly defend himself in his memoirs in 1955–56, stating that many lives could have been lost had the U.S. invaded mainland Japan without the atomic bombs. In 1963, he stood by his decision, telling a journalist that "it was done to save 125,000 youngsters on the U.S. side and 125,000 on the Japanese side from getting killed and that is what it did. It probably also saved a half million youngsters on both sides from being maimed for life."[137]
Strikes and economic upheaval
The end of World War II was followed by an uneasy transition from war to a peacetime economy. The costs of the war effort had been enormous, and Truman was intent on diminishing military services as quickly as possible to curtail the government's military expenditures. The effect of demobilization on the economy was unknown, proposals were met with skepticism and resistance, and fears existed that the nation would slide back into depression. In Roosevelt's final years, Congress began to reassert legislative power and Truman faced a congressional body where Republicans and conservative southern Democrats formed a powerful voting bloc.
Dormant stressors during the war emerged as polarizing issues under Truman's administration. Strikes and labor-management conflicts destabilized major industries while severe housing and consumer good shortages added to public stress over inflation which peaked at 6% in a single month. [138]
Truman's response to the widespread dissatisfaction and protest of US citizens was generally seen as ineffective.[138] The cost of consumer goods increased rapidly due to the removal of depression-era limits on the prices of everyday items while producers of the remaining price-controlled commodities struggled due to the artificially low prices of their goods. In 1945 and 1946, Farmers refused to sell grain for months even though it was desperately needed in the US and to stave off starvation in Europe.[139] Similarly, industrial laborers sought wage increases. In January 1946 a steel strike involving 800,000 laborers became the largest in the nation's history. It was followed by a coal strike in April and a rail strike in May; however, public opinion on labor action was mixed with one poll reporting a majority of the public in favor of a ban on strikes by public service workers and a year's moratorium on labor actions.

Truman with Greek American sponge divers, Florida, 1947
When a national rail strike threatened in May 1946, Truman seized the railroads in an attempt to contain the issue, but two key railway unions struck anyway. The entire national railroad system was shut down, immobilizing 24,000 freight trains and 175,000 passenger trains a day.[140] For two days public anger mounted and Truman himself drafted an irate message to Congress that called on veterans to form a lynch mob and destroy the union leaders:
Every single one of the strikers and their demagogue leaders have been living in luxury.... Now I want you who are my comrades in arms ... to come with me and eliminate the Lewises, the Whitneys, the Johnstons, the Communist Bridges [all important union officials] and the Russian Senators and Representatives ... Let's put transportation and production back to work, hang a few traitors and make our own country safe for democracy.[141]
His staff was stunned, but top aide Clark Clifford revised the original draft and Truman delivered a toned down version of the speech to Congress.
Truman called for a new law, where any railroad strikers would be drafted into the Army. As he concluded his congressional address, he received a message that the strike had been settled on presidential terms; nevertheless, a few hours later, the House voted to draft the strikers. Taft killed the bill in the Senate.[142][143]
After the settlement of the railway strike, labor action continued as an undercurrent of Truman's presidency. The President's approval rating dropped from 82% in the polls in January 1946 to 52% by June.[144] This dissatisfaction with the Truman administration's policies led to large Democratic losses in the 1946 midterm elections, and Republicans took control of Congress for the first time since 1930. The 80th Congress included Republican freshmen who would become prominent in US politics in the years to come including Wisconsin Senator Joe McCarthy and California Congressman Richard Nixon. When Truman dropped to 32% in the polls, Democratic Arkansas Senator William Fulbright suggested that Truman resign; the President said he did not care what Senator "Halfbright" said.[145][146]
Truman cooperated closely with the Republican leaders on foreign policy, but fought them bitterly on domestic issues. The power of the labor unions was significantly curtailed by the Taft–Hartley Act which was enacted over Truman's veto. Truman twice vetoed bills to lower income tax rates in 1947. Although the initial vetoes were sustained, Congress overrode his veto of a tax cut bill in 1948. In one notable instance of bipartisanship, Congress passed the Presidential Succession Act of 1947, which replaced the Secretary of State with the Speaker of the House and the President pro tempore of the Senate as successor to the President after the Vice President. [147]
As he readied for the 1948 election, Truman made clear his identity as a Democrat in the New Deal tradition, advocating for national health insurance,[148] and repeal of the Taft–Hartley Act. He broke with the New Deal by initiating an aggressive civil rights program which he termed a moral priority. His economic and social vision constituted a broad legislative agenda that came to be called the "Fair Deal."[149] Truman's proposals were not well received by Congress, even with renewed Democratic majorities in Congress after 1948. The Solid South rejected civil rights as those states still enforced segregation. Only one of the major Fair Deal bills, the Housing Act of 1949, was ever enacted.[150][151] Many of the New Deal programs that persisted during Truman's presidency have since received minor improvements and extensions.[152]
United Nations, Marshall Plan, Cold War, and China

Truman's press secretary was his old friend Charles Griffith Ross. He had great integrity but, says Alonzo L. Hamby, as a senior White House aide he was, "A better newsman than news handler, he never established a policy of coordinating news releases throughout the executive branch, frequently bumbled details, never developed...a strategy for marketing the president's image and failed to establish a strong press office."[153]
As a Wilsonian internationalist, Truman strongly supported the creation of the United Nations and included Eleanor Roosevelt on the delegation to the UN's first General Assembly.[154] With the Soviet Union expanding its sphere of influence through Eastern Europe, Truman and his foreign policy advisors took a hard line against the USSR. In this, he matched U.S. public opinion which quickly came to believe the Soviets were intent upon world domination.[155]
Although he had little personal expertise on foreign matters, Truman listened closely to his top advisors, especially George Marshall and Dean Acheson. He won bipartisan support for both the Truman Doctrine, which formalized a policy of Soviet containment, and the Marshall Plan, which aimed to help rebuild postwar Europe.[156][157] To get Congress to spend the vast sums necessary to restart the moribund European economy, Truman used an ideological argument, arguing that Communism flourishes in economically deprived areas.[158] As part of the U.S. Cold War strategy, Truman signed the National Security Act of 1947 and reorganized military forces by merging the Department of War and the Department of the Navy into the National Military Establishment (later the Department of Defense) and creating the U.S. Air Force. The act also created the CIA and the National Security Council.[159] In 1952, Truman secretly consolidated and empowered the cryptologic elements of the United States by creating the National Security Agency (NSA).
In theory, the CIA had the purview to gather, process, and analyze national security information from around the world. The CIA's legacy was not lost on Truman; he wrote a letter to the Washington Post in December 1963 calling for the CIA's responsibilities to be scaled back significantly: "For some time I have been disturbed by the way the CIA has been diverted from its original assignment. It has become an operational and at times a policy-making arm of the government. This has led to trouble and may have compounded our difficulties in several explosive areas."[160]
Truman was torn about China, where the Nationalists and Communists were fighting a large-scale civil war, because the Nationalists had been major wartime allies and had large-scale popular support in the United States, along with a powerful lobby. General George Marshall spent most of 1946 in China trying to negotiate a compromise, but failed. He convinced Truman that the Nationalists would never win on their own and that a very large-scale U.S. intervention to stop the Communists would significantly weaken U.S. opposition to the Soviets in Europe. By 1949, the Communists under Mao Zedong had won the civil war, the United States had a new enemy in Asia, and Truman came under fire from conservatives for "losing" China.[161][162][self-published source]
Berlin airlift
On June 24, 1948, the Soviet Union blocked access to the three Western-held sectors of Berlin. The Allies had not negotiated a deal to guarantee supply of the sectors deep within the Soviet-occupied zone. The commander of the U.S. occupation zone in Germany, General Lucius D. Clay, proposed sending a large armored column across the Soviet zone to West Berlin with instructions to defend itself if it were stopped or attacked. Truman believed this would entail an unacceptable risk of war. He approved Ernest Bevin's plan to supply the blockaded city by air. On June 25, the Allies initiated the Berlin Airlift, a campaign to deliver food, coal and other supplies using military aircraft on a massive scale. Nothing like it had ever been attempted before, and no single nation had the capability, either logistically or materially, to accomplish it. The airlift worked; ground access was again granted on May 11, 1949. Nevertheless, the airlift continued for several months after that. The Berlin Airlift was one of Truman's great foreign policy successes; it significantly aided his election campaign in 1948.[163]
Recognition of Israel

President Truman in the Oval Office, receiving a Hanukkah Menorah from the Prime Minister of Israel, David Ben-Gurion (center). To the right is Abba Eban, Ambassador of Israel to the U.S.
Truman had long taken an interest in the history of the Middle East, and was sympathetic to Jews who sought to re-establish their ancient homeland in Mandatory Palestine. As a senator, he announced support for Zionism; in 1943 he called for a homeland for those Jews who survived the Nazi regime. However, State Department officials were reluctant to offend the Arabs, who were opposed to the establishment of a Jewish state in the large region long populated and dominated culturally by Arabs. Secretary of Defense James Forrestal warned Truman of the importance of Saudi Arabian oil in another war; Truman replied that he would decide his policy on the basis of justice, not oil.[164] U.S. diplomats with experience in the region were opposed, but Truman told them he had few Arabs among his constituents.[165]
Palestine was secondary to the goal of protecting the "Northern Tier" of Greece, Turkey, and Iran from Communism, as promised by the Truman Doctrine.[166] Weary of both the convoluted politics of the Middle East and pressure by Jewish leaders, Truman was undecided on his policy, and skeptical about how the Jewish "underdogs" would handle power.[167][168] He later cited as decisive in his recognition of the Jewish state the advice of his former business partner, Eddie Jacobson, a non-religious Jew whom Truman absolutely trusted.[165] Truman decided to recognize Israel over the objections of Secretary of State George Marshall, who feared it would hurt relations with the populous Arab states. Marshall believed the paramount threat to the U.S. was the Soviet Union and feared that Arab oil would be lost to the United States in the event of war; he warned Truman that U.S. was "playing with fire with nothing to put it out".[169] Truman recognized the State of Israel on May 14, 1948, eleven minutes after it declared itself a nation.[170][171] Of his decision to recognize the Israeli state, Truman wrote in his memoirs: "Hitler had been murdering Jews right and left. I saw it, and I dream about it even to this day. The Jews needed some place where they could go. It is my attitude that the American government couldn't stand idly by while the victims [of] Hitler's madness are not allowed to build new lives."[172]
1948 election

Dewey during a campaign tour in New York
The 1948 presidential election is remembered for Truman's stunning come-from-behind victory.[173] In the spring of 1948, Truman's public approval rating stood at 36%,[174] and the president was nearly universally regarded as incapable of winning the general election. The "New Deal" operatives within the party—including FDR's son James—tried to swing the Democratic nomination to General Dwight D. Eisenhower, a highly popular figure whose political views and party affiliation were totally unknown. Eisenhower emphatically refused to accept, and Truman outflanked opponents to his own nomination.[173]
At the 1948 Democratic National Convention, Truman attempted to unify the party with a vague civil rights plank in the party platform. His intention was to assuage the internal conflicts between the northern and southern wings of his party. Events overtook his efforts. A sharp address given by Mayor Hubert Humphrey of Minneapolis—as well as the local political interests of a number of urban bosses—convinced the Convention to adopt a stronger civil rights plank, which Truman approved wholeheartedly. All of Alabama's delegates, and a portion of Mississippi's, walked out of the convention in protest.[175] Unfazed, Truman delivered an aggressive acceptance speech attacking the 80th Congress, which Truman called the "Do Nothing Congress,"[138] and promising to win the election and "make these Republicans like it."[176]
Republicans approve of the American farmer, but they are willing to help him go broke. They stand four-square for the American home—but not for housing. They are strong for labor—but they are stronger for restricting labor's rights. They favor minimum wage—the smaller the minimum wage the better. They endorse educational opportunity for all—but they won't spend money for teachers or for schools. They think modern medical care and hospitals are fine—for people who can afford them ... They think American standard of living is a fine thing—so long as it doesn't spread to all the people. And they admire the Government of the United States so much that they would like to buy it.
— Harry S. Truman, October 13, 1948, St. Paul, Minnesota, Radio Broadcast[177][178][179][180][181]
Within two weeks of the 1948 convention Truman issued Executive Order 9981, racially integrating the U.S. Armed Services[182][183][184] and Executive Order 9980 to integrate federal agencies. Truman took a considerable political risk in backing civil rights, and many seasoned Democrats were concerned that the loss of Dixiecrat support might destroy the Democratic Party. South Carolina Governor Strom Thurmond, a segregationist, declared his candidacy for the presidency on a Dixiecrat ticket and led a full-scale revolt of Southern "states' rights" proponents. This rebellion on the right was matched by one on the left, led by Wallace on the Progressive Party ticket. Immediately after its first post-FDR convention, the Democratic Party seemed to be disintegrating. Victory in November seemed unlikely as the party was not simply split but divided three ways.[185] For his running mate, Truman accepted Kentucky Senator Alben W. Barkley, though he really wanted Justice William O. Douglas, who turned down the nomination.[186]
Truman's political advisors described the political scene as "one unholy, confusing cacophony." They told Truman to speak directly to the people, in a personal way.[187] Campaign manager William J. Bray said Truman took this advice, and spoke personally and passionately, sometimes even setting aside his notes to talk to Americans "of everything that is in my heart and soul."[188]
The campaign was a 21,928-mile (35,290 km) presidential odyssey.[189] In a personal appeal to the nation, Truman crisscrossed the U.S. by train; his "whistle stop" speeches from the rear platform of the observation car, Ferdinand Magellan, came to represent his campaign. His combative appearances captured the popular imagination and drew huge crowds. Six stops in Michigan drew a combined half-million people;[190] a full million turned out for a New York City ticker-tape parade.[191]
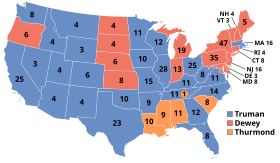
1948 electoral vote results

Truman was so widely expected to lose the 1948 election that the Chicago Tribune had printed papers with this erroneous headline when few returns were in.
The large, mostly spontaneous gatherings at Truman's whistle-stop events were an important sign of a change in momentum in the campaign, but this shift went virtually unnoticed by the national press corps. It continued reporting Republican Thomas Dewey's apparent impending victory as a certainty. One reason for the press's inaccurate projection was that polls were conducted primarily by telephone, but many people, including much of Truman's populist base, did not yet own a telephone.[192] This skewed the data to indicate a stronger support base for Dewey than existed. An unintended and undetected projection error may have contributed to the perception of Truman's bleak chances. The three major polling organizations stopped polling well before the November 2 election date—Roper in September, and Crossley and Gallup in October—thus failing to measure the period when Truman appears to have surged past Dewey.[193][194]
In the end, Truman held his progressive Midwestern base, won most of the Southern states despite the civil rights plank, and squeaked through with narrow victories in a few critical states, notably Ohio, California, and Illinois. The final tally showed the President had secured 303 electoral votes, Dewey 189, and Thurmond only 39. Henry Wallace got none. The defining image of the campaign came after Election Day, when an ecstatic Truman held aloft the erroneous front page of the Chicago Tribune with a huge headline proclaiming "Dewey Defeats Truman."[195]
Full elected term (1949–1953)
Truman's second inauguration was the first ever televised nationally.[196] His second term was grueling as his opponents controlled Congress and his policy of rollback in Korea failed. The Soviet Union's atomic bomb project progressed much faster than had been expected and they detonated their first bomb on August 29, 1949. In response, on January 7, 1953, Truman announced the detonation of the first U.S. hydrogen bomb, which was much more powerful than the Soviet Union's atomic weapons.[197]
Korean War

President Truman signing a proclamation declaring a national emergency and authorizing U.S. entry into the Korean War
On June 25, 1950, the North Korean army under Kim Il-sung invaded South Korea, starting the Korean War. In the early weeks of the war, the North Koreans easily pushed back their southern counterparts.[198] Truman called for a naval blockade of Korea, only to learn that due to budget cutbacks, the U.S. Navy could not enforce such a measure.[199] Truman promptly urged the United Nations to intervene; it did, authorizing troops under the UN flag led by U.S. General Douglas MacArthur.
Truman decided that he did not need formal authorization from Congress, believing that most legislators supported his position; this would come back to haunt him later, when the stalemated conflict was dubbed "Mr. Truman's War" by legislators.[198] However, on July 3, 1950, Truman did give Senate Majority Leader Scott W. Lucas a draft resolution titled "Joint Resolution Expressing Approval of the Action Taken in Korea". Lucas said that Congress supported the use of force, that the formal resolution would pass but was unnecessary, and that the consensus in Congress was to acquiesce. Truman responded that he did not want "to appear to be trying to get around Congress and use extra-Constitutional powers," and added that it was "up to Congress whether such a resolution should be introduced."[200]
By August 1950, U.S. troops pouring into South Korea under UN auspices were able to stabilize the situation.[201] Responding to criticism over readiness, Truman fired his Secretary of Defense, Louis A. Johnson, replacing him with the retired General Marshall. With UN approval, Truman decided on a "rollback" policy—conquest of North Korea.[202] UN forces led by General Douglas MacArthur led the counterattack, scoring a stunning surprise victory with an amphibious landing at the Battle of Inchon that nearly trapped the invaders. UN forces marched north, toward the Yalu River boundary with China, with the goal of reuniting Korea under UN auspices.[203]
However, China surprised the UN forces with a large-scale invasion in November. The UN forces were forced back to below the 38th parallel, then recovered.[204] By early 1951 the war became a fierce stalemate at about the 38th parallel where it had begun. Truman rejected MacArthur's request to attack Chinese supply bases north of the Yalu, but MacArthur promoted his plan to Republican House leader Joseph Martin, who leaked it to the press. Truman was gravely concerned that further escalation of the war might lead to open conflict with the Soviet Union, which was already supplying weapons and providing warplanes (with Korean markings and Soviet aircrew). Therefore, on April 11, 1951, Truman fired MacArthur from his commands.[205]
.mw-parser-output .quotebox{background-color:#F9F9F9;border:1px solid #aaa;box-sizing:border-box;padding:10px;font-size:88%}.mw-parser-output .quotebox.floatleft{margin:0.5em 1.4em 0.8em 0}.mw-parser-output .quotebox.floatright{margin:0.5em 0 0.8em 1.4em}.mw-parser-output .quotebox.centered{margin:0.5em auto 0.8em auto}.mw-parser-output .quotebox.floatleft p,.mw-parser-output .quotebox.floatright p{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .quotebox-title{background-color:#F9F9F9;text-align:center;font-size:larger;font-weight:bold}.mw-parser-output .quotebox-quote.quoted:before{font-family:"Times New Roman",serif;font-weight:bold;font-size:large;color:gray;content:" “ ";vertical-align:-45%;line-height:0}.mw-parser-output .quotebox-quote.quoted:after{font-family:"Times New Roman",serif;font-weight:bold;font-size:large;color:gray;content:" ” ";line-height:0}.mw-parser-output .quotebox .left-aligned{text-align:left}.mw-parser-output .quotebox .right-aligned{text-align:right}.mw-parser-output .quotebox .center-aligned{text-align:center}.mw-parser-output .quotebox cite{display:block;font-style:normal}@media screen and (max-width:360px){.mw-parser-output .quotebox{min-width:100%;margin:0 0 0.8em!important;float:none!important}}
—Harry S. Truman to biographer Merle Miller, 1972, posthumously quoted in Time magazine, 1973
The dismissal of General Douglas MacArthur was among the least politically popular decisions in presidential history. Truman's approval ratings plummeted, and he faced calls for his impeachment from, among others, Senator Robert A. Taft.[207] Fierce criticism from virtually all quarters accused Truman of refusing to shoulder the blame for a war gone sour and blaming his generals instead. Others, including Eleanor Roosevelt, supported and applauded Truman's decision. MacArthur meanwhile returned to the U.S. to a hero's welcome, and addressed a joint session of Congress, a speech the President called "a bunch of damn bullshit."[208]
Truman and his generals considered the use of nuclear weapons against the Chinese army, but ultimately chose not to escalate the war to a nuclear level.[209] The war remained a frustrating stalemate for two years, with over 30,000 Americans killed, until an armistice ended the fighting in 1953.[210] In February 1952, Truman's approval mark stood at 22% according to Gallup polls, which is the all-time lowest approval mark for an active U.S. president, though it was matched by Richard Nixon in 1974.[211][212]
Worldwide defense

Truman and Indian Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru during Nehru's visit to the United States, October 1949
The escalation of the Cold War was highlighted by Truman's approval of NSC 68, a secret statement of foreign policy. It called for tripling the defense budget, and the globalization and militarization of containment policy whereby the U.S. and its NATO allies would respond militarily to actual Soviet expansion. The document was drafted by Paul Nitze, who consulted State and Defense officials, and was formally approved by President Truman as official national strategy after the war began in Korea. It called for partial mobilization of the U.S. economy to build armaments faster than the Soviets. The plan called for strengthening Europe, weakening the Soviet Union, and building up the U.S. both militarily and economically.[213]
Early in Truman's second term, his former Secretary of Defense Forrestal died soon after retiring. Forrestal had become exhausted through years of hard labor during and after the war, and had begun to suffer depression. He retired in March 1949; soon after, he was hospitalized but committed suicide in May.[214]

Truman and Shah of Iran Mohammad Reza Pahlavi speaking at Washington National Airport, during ceremonies welcoming him to the United States
Truman was a strong supporter of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), which established a formal peacetime military alliance with Canada and democratic European nations that had not fallen under Soviet control following World War II. The treaty establishing it was widely popular and easily passed the Senate in 1949; Truman appointed General Eisenhower as commander. NATO's goals were to contain Soviet expansion in Europe and to send a clear message to communist leaders that the world's democracies were willing and able to build new security structures in support of democratic ideals. The U.S., Britain, France, Italy, the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, Norway, Denmark, Portugal, Iceland, and Canada were the original treaty signatories. The alliance resulted in the Soviets establishing a similar alliance, called the Warsaw Pact.[215][216]
General Marshall was Truman's principal adviser on foreign policy matters, influencing such decisions as the U.S. choice against offering direct military aid to Chiang Kai-shek and his Nationalist Chinese forces in the Chinese Civil War against their communist opponents. Marshall's opinion was contrary to the counsel of almost all of Truman's other advisers—Marshall thought propping up Chiang's forces would drain U.S. resources that were needed in Europe to deter the Soviets.[217] When the communists took control of the mainland, establishing the People's Republic of China and driving the Nationalists to Taiwan, Truman would have been willing to maintain some relationship between the U.S. and the new government but Mao was unwilling.[218] On June 27, 1950, after the outbreak of fighting in Korea, Truman ordered the U.S. Navy's Seventh Fleet into the Taiwan Strait to prevent further conflict between the communist government on the China mainland and the Republic of China (ROC) on Taiwan.[219][220]
Soviet espionage and McCarthyism
In August 1948, Whittaker Chambers, a former spy for the Soviets and a senior editor at Time magazine, testified before the House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC). He said that an underground communist network had worked inside the U.S. government during the 1930s, of which Chambers had been a member, along with Alger Hiss, until recently a senior State Department official. Chambers did not allege any spying during the Truman presidency. Although Hiss denied the allegations, he was convicted in January 1950 for perjury for denials under oath. The Soviet Union's success in exploding an atomic weapon in 1949 and the fall of the nationalist Chinese the same year led many Americans to conclude that subversion by Soviet spies was responsible, and to demand that communists be rooted out from the government and other places of influence.[221][222] However, Truman got himself into deeper trouble when he called the Hiss trial a "red herring".[223]
Wisconsin Senator McCarthy accused the State Department of harboring communists and rode the controversy to political fame,[224] leading to the Second Red Scare,[225] also known as McCarthyism.
Charges that Soviet agents had infiltrated the government were believed by 78% of the people in 1946, and became a major campaign issue for Eisenhower in 1952.[226] Truman was reluctant to take a more radical stance because he feared that the full disclosure of the extent of the communist infiltration would reflect badly on the Democratic Party. In 1949, Truman described American communist leaders, whom his administration was prosecuting, as "traitors", but in 1950 he vetoed the McCarran Internal Security Act. It was passed over his veto.[227] Truman would later state in private conversations with friends that his creation of a loyalty program had been a "terrible" mistake.[228]
White House renovations and assassination attempt

View of the interior shell of the White House during renovation in 1950
In 1948, Truman ordered an addition to the exterior of the White House: a second-floor balcony in the south portico, which came to be known as the Truman Balcony. The addition was unpopular. Some said it spoiled the appearance of the south facade, but it gave the First Family more living space.[229][230][231] The work uncovered structural faults that led engineering experts to conclude that the building, much of it over 130 years old, was in a dangerously dilapidated condition. That August, a section of floor collapsed, and Truman's bedroom and bathroom were closed as unsafe. No public announcement about the serious structural problems of the White House was made until after the 1948 election had been won. By then Truman had been informed that his new balcony was the only part of the building that was sound.
The Truman family moved into nearby Blair House during the renovations. As the newer West Wing, including the Oval Office, remained open, Truman walked to and from his work across the street each morning and afternoon. In due course, the decision was made to demolish and rebuild the whole interior of the main White House, as well as excavate new basement levels and underpin the foundations. The famous exterior of the structure was buttressed and retained while the extensive renovations proceeded inside. The work lasted from December 1949 until March 1952.[232]
On November 1, 1950, Puerto Rican nationalists Griselio Torresola and Oscar Collazo attempted to assassinate Truman at Blair House. On the street outside the residence, Torresola mortally wounded a White House policeman, Leslie Coffelt. Before he died, the officer shot and killed Torresola. Collazo was wounded and stopped before he entered the house. Upstairs, upon hearing gunshots, Truman had jumped up from a nap and looked out his second floor window, 31 feet (9.4 m) from the attacker. A White House guard shouted at Truman to get away from the window, which he did.[233]
Collazo was found guilty of murder and sentenced to death in 1952. Truman commuted his sentence to life in prison. To try to settle the question of Puerto Rican independence, Truman allowed a plebiscite in Puerto Rico in 1952 to determine the status of its relationship to the U.S. Nearly 82% of the people voted in favor of a new constitution for the Estado Libre Asociado, a continued 'associated free state.'[234]
Steel and coal strikes
In response to a labor/management impasse arising from bitter disagreements over wage and price controls, Truman instructed his Secretary of Commerce, Charles W. Sawyer, to take control of a number of the nation's steel mills in April 1952. Truman cited his authority as Commander in Chief and the need to maintain an uninterrupted supply of steel for munitions for the war in Korea. The Supreme Court found Truman's actions unconstitutional, however, and reversed the order in a major separation-of-powers decision, Youngstown Sheet & Tube Co. v. Sawyer (1952). The 6–3 decision, which held that Truman's assertion of authority was too vague and was not rooted in any legislative action by Congress, was delivered by a Court composed entirely of Justices appointed by either Truman or Roosevelt. The high court's reversal of Truman's order was one of the notable defeats of his presidency.[235]
Scandals and controversies

President Harry S. Truman in an official portrait
In 1950, the Senate, led by Estes Kefauver, investigated numerous charges of corruption among senior administration officials, some of whom received fur coats and deep freezers in exchange for favors. A large number of employees of the Internal Revenue Bureau (today the IRS) were accepting bribes; 166 employees either resigned or were fired in 1950,[236] with many soon facing indictment. When Attorney General J. Howard McGrath fired the special prosecutor in early 1952 for being too zealous, Truman fired McGrath.[237] Truman submitted a reorganization plan to reform the IRB; Congress passed it, but the corruption was a major issue in the 1952 presidential election.[238][239]
On December 6, 1950, Washington Post music critic Paul Hume wrote a critical review of a concert by the president's daughter Margaret Truman:
Miss Truman is a unique American phenomenon with a pleasant voice of little size and fair quality ... [she] cannot sing very well ... is flat a good deal of the time—more last night than at any time we have heard her in past years ... has not improved in the years we have heard her ... [and] still cannot sing with anything approaching professional finish.[240]
Harry Truman wrote a scathing response:
I've just read your lousy review of Margaret's concert. I've come to the conclusion that you are an "eight ulcer man on four ulcer pay." It seems to me that you are a frustrated old man who wishes he could have been successful. When you write such poppy-cock as was in the back section of the paper you work for it shows conclusively that you're off the beam and at least four of your ulcers are at work. Some day I hope to meet you. When that happens you'll need a new nose, a lot of beefsteak for black eyes, and perhaps a supporter below! Pegler, a gutter snipe, is a gentleman alongside you. I hope you'll accept that statement as a worse insult than a reflection on your ancestry.[240]
Truman was criticized by many for the letter. However, he pointed out that he wrote it as a loving father and not as the president.[241][242][243]
In 1951, William M. Boyle, Truman's longtime friend and chairman of the Democratic National Committee, was forced to resign after being charged with financial corruption.[244]
Civil rights
A 1947 report by the Truman administration titled To Secure These Rights presented a detailed ten-point agenda of civil rights reforms. Speaking about this report, international developments have to be taken into account, for with the UN-Charter being passed in 1945, the question whether international human rights law could be applicable also on an inner-land basis became crucial in the U.S. Though the report acknowledged that such a path was not free from controversy in the 1940s U.S., it nevertheless raised the distinct possibility that the UN-Charter could be used as a legal tool to combat racial discrimination in the U.S.[245]
In February 1948, the president submitted a civil rights agenda to Congress that proposed creating several federal offices devoted to issues such as voting rights and fair employment practices.[246] This provoked a storm of criticism from southern Democrats in the runup to the national nominating convention, but Truman refused to compromise, saying: "My forebears were Confederates ... but my very stomach turned over when I had learned that Negro soldiers, just back from overseas, were being dumped out of Army trucks in Mississippi and beaten."[247] Tales of the abuse, violence, and persecution suffered by many African-American veterans upon their return from World War II infuriated Truman, and were a major factor in his decision to issue Executive Order 9981, in July 1948, requiring equal opportunity in the Armed Forces.[248] In the early 1950s after several years of planning, recommendations and revisions between Truman, the Committee on Equality of Treatment and Opportunity and the various branches of the military, the services became racially integrated.[249]
Another executive order, also in 1948, made it illegal to discriminate against persons applying for civil service positions based on race. A third, in 1951, established the Committee on Government Contract Compliance (CGCC). This committee ensured defense contractors did not discriminate because of race.[250][251]
In 1950 he vetoed the McCarran Internal Security Act. It was passed over his veto.[227]
Administration and cabinet
International trips
Truman made five international trips during his presidency:[252]
1952 election

From left: President Harry S. Truman, vice presidential nominee, Alabama Senator John J. Sparkman and presidential nominee, Illinois Governor Adlai Stevenson. Oval Office, 1952
In 1951, the U.S. ratified the 22nd Amendment, making a president ineligible for election to a third term or for election to a second full term after serving more than two remaining years of a term of a previously elected president. The latter clause would have applied to Truman's situation in 1952 except that a grandfather clause in the amendment explicitly excluded the amendment from applying to the current president.[253] Nevertheless, he seriously considered running for another term in 1952, and left his name on the ballot in the New Hampshire primary. However all his close advisors, pointing to his age, his failing abilities, and his poor showing in the polls, talked him out of it.[254]
At the time of the 1952 New Hampshire primary, no candidate had won Truman's backing. His first choice, Chief Justice Fred M. Vinson, had declined to run; Illinois Governor Adlai Stevenson had also turned Truman down, Vice President Barkley was considered too old,[255][256] and Truman distrusted and disliked Senator Kefauver, who had made a name for himself by his investigations of the Truman administration scandals. Truman had hoped to recruit General Eisenhower as a Democratic candidate, but found him more interested in seeking the Republican nomination. Accordingly, Truman let his name be entered in the New Hampshire primary by supporters. The highly unpopular Truman was handily defeated by Kefauver; 18 days later the president formally announced he would not seek a second full term. Truman was eventually able to persuade Stevenson to run, and the governor gained the nomination at the 1952 Democratic National Convention.[257]
 | Harry S. Truman's Farewell Address Harry S. Truman's speech on leaving office, and returning home to Independence, Missouri. (January 15, 1953) |
Problems playing this file? See media help. | |
Eisenhower gained the Republican nomination, with Senator Nixon as his running mate, and campaigned against what he denounced as Truman's failures: "Korea, Communism and Corruption". He pledged to clean up the "mess in Washington," and promised to "go to Korea."[255][256] Eisenhower defeated Stevenson decisively in the general election, ending 20 years of Democratic presidents. While Truman and Eisenhower had previously been on good terms, Truman felt annoyed that Eisenhower did not denounce Joseph McCarthy during the campaign.[258] Similarly, Eisenhower was outraged when Truman accused the former general of disregarding "sinister forces ... Anti-Semitism, anti-Catholicism, and anti-foreignism" within the Republican Party.[259]
Post-presidency

Official White House portrait of Harry S. Truman by Greta Kempton
Upon leaving the presidency, Truman returned to Independence, Missouri, to live at the Wallace home he and Bess had shared for years with her mother.[260] Once out of office, Truman quickly decided that he did not wish to be on any corporate payroll, believing that taking advantage of such financial opportunities would diminish the integrity of the nation's highest office. He also turned down numerous offers for commercial endorsements. Since his earlier business ventures had proved unsuccessful, he had no personal savings. As a result, he faced financial challenges. Once Truman left the White House, his only income was his old army pension: $112.56 per month (equivalent to $1,030 in 2017).[261] Former members of Congress and the federal courts received a federal retirement package; President Truman himself ensured that former servants of the executive branch of government received similar support. In 1953, however, there was no such benefit package for former presidents,[262] and he received no pension for his Senate service.[263]

Truman (seated right) and his wife Bess (behind him) attend the signing of the Medicare Bill on July 30, 1965, by President Lyndon B. Johnson
Truman took out a personal loan from a Missouri bank shortly after leaving office, and then found a lucrative book deal for his memoirs. For the memoirs, Truman received only a flat payment of $670,000, and had to pay two-thirds of that in tax; he calculated he got $37,000 after he paid his assistants.[264] However, the memoirs were a commercial and critical success;[265][266] they were published in two volumes in 1955 and 1956 by Doubleday (Garden City, N.Y) and Hodder & Stoughton (London): Memoirs by Harry S. Truman: Year of Decisions and Memoirs by Harry S. Truman: Years of Trial and Hope.[267][268]
The former president was quoted in 1957 as saying to then-House Majority Leader John McCormack, "Had it not been for the fact that I was able to sell some property that my brother, sister, and I inherited from our mother, I would practically be on relief, but with the sale of that property I am not financially embarrassed."[269] The following year, Congress passed the Former Presidents Act, offering a $25,000 yearly pension to each former president, and it is likely that Truman's financial status played a role in the law's enactment.[262] The one other living former president at the time, Herbert Hoover, also took the pension, even though he did not need the money; reportedly, he did so to avoid embarrassing Truman.[270]
Truman's predecessor, Franklin D. Roosevelt, had organized his own presidential library, but legislation to enable future presidents to do something similar had not been enacted. Truman worked to garner private donations to build a presidential library, which he donated to the federal government to maintain and operate—a practice adopted by his successors.[271] He testified before Congress to have money appropriated to have presidential papers copied and organized, and was proud of the bill's passage in 1957. Max Skidmore, in his book on the life of former presidents, noted that Truman was a well-read man, especially in history. Skidmore added that the presidential papers legislation and the founding of his library "was the culmination of his interest in history. Together they constitute an enormous contribution to the United States—one of the greatest of any former president."[272]
Truman supported Adlai Stevenson's second bid for the White House in 1956, although he had initially favored Democratic Governor W. Averell Harriman of New York.[273] He continued to campaign for Democratic senatorial candidates for many years.[274] Upon turning 80 in 1964, Truman was feted in Washington, and addressed the Senate, availing himself of a new rule that allowed former presidents to be granted privilege of the floor.[275]
After a fall in his home in late 1964, his physical condition declined. In 1965, President Lyndon B. Johnson signed the Medicare bill at the Harry S. Truman Presidential Library and Museum and gave the first two Medicare cards to Truman and his wife Bess to honor the former president's fight for government health care while in office.[274] He voted in the 1972 U.S. presidential election via absentee ballot.[276]
Death

Wreath at Truman's casket on the day of his funeral, December 27, 1972, Independence, Missouri
On December 5, 1972, Truman was admitted to Kansas City's Research Hospital and Medical Center with lung congestion from pneumonia. He developed multiple organ failure and died at 7:50 am on December 26 at the age of 88 after being in a coma.[276][260] Bess Truman opted for a simple private service at the library rather than a state funeral in Washington. A week after the funeral, foreign dignitaries and Washington officials attended a memorial service at Washington National Cathedral. Bess died in 1982; they are buried at the Harry S. Truman Library and Museum in Independence.[277][278]
Tributes and legacy
Biographer Robert Donovan has tried to capture Truman's personality:
Vigorous, hard-working, simple, he had grown up close to the soil of the Midwest and understood the struggles of the people on the farms and in the small towns....After 10 years in the Senate, he had risen above the Pendergast organization. Still, he had come from a world of two-bit politicians, and its aura was one that he never was able to shed entirely. And he did retain certain characteristics one often sees in machine-bred politicians: intense partisanship, stubborn loyalty, a certain insensitivity about the transgressions of political associates, and a disinclination for the companionship of intellectuals and artists.[279]
Legacy

Truman poses in 1959 at the recreation of the Truman Oval Office at the Truman Library in 1959, with the famous "The Buck Stops Here" sign on his desk. (The reverse of the sign says, "I'm From Missouri".)

Harry S. Truman Presidential Library and Museum located in Independence, Missouri
Citing continuing divisions within the Democratic Party, the ongoing Cold War, and the boom and bust cycle, journalist Samuel Lubell in 1952 stated: "After seven years of Truman's hectic, even furious, activity the nation seemed to be about on the same general spot as when he first came to office ... Nowhere in the whole Truman record can one point to a single, decisive break-through ... All his skills and energies—and he was among our hardest-working Presidents—were directed to standing still."[280] When he left office in 1953, Truman was one of the most unpopular chief executives in history. His job approval rating of 22% in the Gallup Poll of February 1952 was lower than Richard Nixon's 24% in August 1974, the month Nixon resigned, but matched by Nixon's all-time low in January 1974.[212]
U.S. public feeling towards Truman grew steadily warmer with the passing years; as early as 1962, a poll of 75 historians conducted by Arthur M. Schlesinger, Sr. ranked Truman among the "near great" presidents. The period following his death consolidated a partial rehabilitation of his legacy among both historians and members of the public.[281] Truman died when the nation was consumed with crises in Vietnam and Watergate, and his death brought a new wave of attention to his political career.[206] In the early and mid-1970s, Truman captured the popular imagination much as he had in 1948, this time emerging as a kind of political folk hero, a president who was thought to exemplify an integrity and accountability many observers felt was lacking in the Nixon White House. This public reassessment of Truman was aided by the popularity of a book of reminiscences Truman had recounted to journalist Merle Miller beginning in 1961, with the agreement that they would not be published until after Truman's death.[282]
Truman has had his latter-day critics as well. After a review of information available to Truman about the presence of espionage activities in the U.S. government, Democratic Senator Daniel Patrick Moynihan concluded that Truman was "almost wilfully obtuse" concerning the danger of U.S. communism.[283] In 2010, historian Alonzo Hamby concluded that "Harry Truman remains a controversial president."[284] However, since leaving office, Truman has fared well in polls ranking the presidents. He has never been listed lower than ninth, and was ranked fifth in a C-SPAN poll in 2009.[285]
The fall of the Soviet Union in 1991 caused Truman advocates to claim vindication for his decisions in the postwar period. According to Truman biographer Robert Dallek, "His contribution to victory in the cold war without a devastating nuclear conflict elevated him to the stature of a great or near-great president."[286] The 1992 publication of David McCullough's favorable biography of Truman further cemented the view of Truman as a highly regarded Chief Executive.[286] According to historian Donald R. McCoy in his book on the Truman presidency:
Harry Truman himself gave a strong and far-from-incorrect impression of being a tough, concerned and direct leader. He was occasionally vulgar, often partisan, and usually nationalistic ... On his own terms, Truman can be seen as having prevented the coming of a third world war and having preserved from Communist oppression much of what he called the free world. Yet clearly he largely failed to achieve his Wilsonian aim of securing perpetual peace, making the world safe for democracy, and advancing opportunities for individual development internationally.[287]
Sites and honors

In 1953, Truman received the Solomon Bublick Award of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem.
In 1956, Truman traveled to Europe with his wife. In England, he met with Churchill and received an honorary Doctor of Civil Law degree from Oxford University. Across Britain he was hailed; London's Daily Telegraph characterized Truman as the "Living and kicking symbol of everything that everybody likes best about the United States."[289] In 1959, he was given a 50-year award by the Masons, recognizing his longstanding involvement: he was initiated on February 9, 1909, into the Belton Masonic Lodge in Missouri. In 1911, he helped establish the Grandview Lodge, and he served as its first Worshipful Master. In September 1940, during his Senate re-election campaign, Truman was elected Grand Master of the Missouri Grand Lodge of Freemasonry; Truman said later that the Masonic election assured his victory in the general election. In 1945, he was made a 33° Sovereign Grand Inspector General and an Honorary Member of the supreme council at the Supreme Council A.A.S.R. Southern Jurisdiction Headquarters in Washington D.C.[290][291] Truman was also a member of Sons of the American Revolution (SAR)[292] and a card-carrying member of the Sons of Confederate Veterans.[293] Two of his relatives were Confederate soldiers.[293][294]
In 1975, the Truman Scholarship was created as a federal program to honor U.S. college students who exemplified dedication to public service and leadership in public policy.[295] In 2004, the President Harry S. Truman Fellowship in National Security Science and Engineering was created as a distinguished postdoctoral three-year appointment at Sandia National Laboratories.[296] In 2001, the University of Missouri established the Harry S. Truman School of Public Affairs to advance the study and practice of governance.[297] The University of Missouri's Missouri Tigers athletic programs have an official mascot named Truman the Tiger. On July 1, 1996, Northeast Missouri State University became Truman State University—to mark its transformation from a teachers' college to a highly selective liberal arts university and to honor the only Missourian to become president. A member institution of the City Colleges of Chicago, Harry S Truman College in Chicago, Illinois, is named in his honor for his dedication to public colleges and universities. In 2000, the headquarters for the State Department, built in the 1930s but never officially named, was dedicated as the Harry S Truman Building.[298]
Despite Truman's attempt to curtail the naval carrier arm, which led to the 1949 Revolt of the Admirals,[299] an aircraft carrier is named after him. The USS Harry S. Truman (CVN-75) was christened on September 7, 1996. [300] The 129th Field Artillery Regiment is designated "Truman's Own" in recognition of Truman's service as commander of its D Battery during World War I.[301]
In 1984, Truman was posthumously awarded the United States Congressional Gold Medal.[302] In 1991, he was inducted into the Hall of Famous Missourians, and a bronze bust depicting him is on permanent display in the rotunda of the Missouri State Capitol.[303]
Other sites associated with Truman include:
Harry S. Truman National Historic Site includes the Wallace House at 219 N. Delaware in Independence and the family farmhouse at Grandview, Missouri (Truman sold most of the farm for Kansas City suburban development including the Truman Corners Shopping Center).
Harry S Truman Birthplace State Historic Site is the house where Truman was born and spent 11 months in Lamar, Missouri.[304]
Harry S. Truman Presidential Library and Museum – The Presidential library in Independence
Harry S. Truman Little White House – Truman's winter getaway at Key West, Florida
In Athens, Greece, a 12-foot-tall bronze statue of President Harry S. Truman, was erected in 1963 with donations from Greek-Americans.[305]
See also
- Electoral history of Harry S. Truman
Truman (film)- Truman Day
- List of Presidents of the United States
Harry Truman, a song by the band Chicago
Notes
^ Truman was Vice President under President Franklin D. Roosevelt and became President upon Roosevelt's death on April 12, 1945. As this was prior to the adoption of the Twenty-Fifth Amendment in 1967, a vacancy in the office of Vice President was not filled.
^ ab Truman was not given a middle name, only the initial S. There is controversy over whether this initial should be followed by a period, although Truman's own archived correspondence suggests that he regularly used the period when writing his name.[6]
^ For example, see Fussell, Paul (1988). "Thank God for the Atomic Bomb". Thank God for the Atomic Bomb and Other Essays. New York Summit Books..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
References
^ ab Ferrell 1994, p. 108.
^ "County Judges 1923-1972". County History: County Judges. Kansas City, MO: Jackson County, Missouri. 2018. Retrieved April 20, 2018.
^ ab "County Judges 1923-1972".
^ ab Ferrell 1994, p. 99.
^ "County Judges 1826-1922". County History: County Judges. Kansas City, MO: Jackson County, Missouri. 2018. Retrieved April 20, 2018.
^ "Use of the Period After the "S" in Harry S. Truman's Name". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved March 5, 2016.
^ Richard Conley (2016). Presidential Relations with Congress. Transaction Publishers. pp. 35–.
^ Miller 2012.
^ "BBC - History - World Wars: Nuclear Power: The End of the War Against Japan". bbc.co.uk. Retrieved June 8, 2018.
^ https://elpais.com/internacional/2016/05/24/actualidad/1464089684_484295.html
^ United Nations Security Council Resolutions 82, 83, 84, 85 and 88
^ McCullough 1992, p. 37.
^ Truman Library 2012.
^ McCullough 1992, pp. 27, 37.
^ Niel Johnson; Verna Gail Johnson (1999). "Rooted in History: The Genealogy of Harry S. Truman". Harry S. Truman Library – Genealogy. Retrieved May 6, 2018..
^ "Ulster-Scots and the United States Presidents" (PDF). Ulter Scots Agency. Retrieved 12 July 2010.
^ Truman Library, Birth 2012.
^ McCullough 1992, pp. 37, 77, 1112.
^ Devine, Michael J. (2009). Harry S. Truman, the State of Israel, and the Quest for Peace in the Middle East. Truman State Univ Press. p. 93. ISBN 978-1-935503-80-4.
^ Schultz, Joseph P. (1982). Mid-America's Promise: A Profile of Kansas City Jewry. Jewish Community Foundation of Greater Kansas City. p. 33.
^ "San Francisco Jewish Bulletin, Volume 129". Jewish Community Publications. 1979. p. v.
^ abc Oshinsky 2004, pp. 365–380.
^ McCullough 1992, p. 38.
^ Ferrell 1994, p. 87.
^ Truman Library & 2012aa.
^ Ferrell, Robert H. (1994). Harry S. Truman: A Life. Columbia, MO: University of Missouri Press. pp. 25–26. ISBN 978-0-8262-1050-0.
^ Truman Library, Job 2012.
^ Gies, Joseph (1968). Harry S. Truman: A Pictorial Biography. New York, NY: Doubleday. p. 5.
^ McCullough 1992, pp. 67, 99.
^ McCullough 1992, pp. 78–79.
^ Ferrell, Robert H. (1994). Harry S. Truman: A Life. Columbia, MO: University of Missouri Press. p. 52. ISBN 978-0-8262-1050-0.
^ Ferrell, Robert H. (1994). Harry S. Truman: A Life. Columbia, MO: University of Missouri Press. p. 53. ISBN 978-0-8262-1050-0.
^ Ferrell, Robert H. (1994). Harry S. Truman: A Life. Columbia, MO: University of Missouri Press. p. 79. ISBN 978-0-8262-1050-0.
^ KirKendall, Richard Stewart (1989). The Harry S. Truman Encyclopedia. Boston, MA: G. K. Hall. p. 40.
^ Danilov, Victor J. (2013). Famous Americans: A Directory of Museums, Historic Sites, and Memorials. Lanham, MD: Scarecrow Press. p. 268. ISBN 978-0-8108-9185-2.
^ ab Hamby 1995, pp. 17–18, 135.
^ Miller, Richard Lawrence (1986). Truman: The Rise to Power. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill. p. 206. ISBN 978-0-07-042185-1.
^ Gross, Norman (2004). America's Lawyer-Presidents: From Law Office to Oval Office. Evanston, IL: Northwestern University Press. p. 260. ISBN 978-0-8101-1218-6.
^ Jackman, Tom (Kansas City Star) (September 20, 1996). "49 Years Later, Truman Gets His Law License". Tuscaloosa News. Tuscaloosa, AL. p. 1D.
^ abcdef Gilwee 2000.
^ McCullough 1992, p. 105.
^ Truman Library, Eye 2012.
^ Ferrell, Robert H., ed. (1998). Dear Bess: The Letters from Harry to Bess Truman, 1910–1959. Columbia, MO: University of Missouri Press. p. 219. ISBN 978-0-8262-1203-0.
^ Offner, Arnold A. (2002). Another Such Victory: President Truman and the Cold War, 1945-1953. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press. p. 6. ISBN 978-0-8047-4254-2.
^ ab Another Such Victory, p. 6.
^ McCullough 1992, pp. 105–10.
^ Giangreco 2012.
^ Current, Freidel & Williams 1971, p. 594.
^ McCullough 1992, p. 115.
^ Burnes 2003, p. 49.
^ Farinacci, Donald J. (2017). Truman and MacArthur: Adversaries for a Common Cause. Hoosick Falls, NY: Merriam Press. pp. 71–72. ISBN 978-1-57638-630-9.
^ abcde Farinacci, pp. 71-72.
^ McCullough 1992, pp. 130, 531.
^ Giangreco 2002, p. 192.
^ Giangreco 2002, pp. 181–86.
^ Daniels, Roger (2010). Immigration and the Legacy of Harry S. Truman. Kirksville, MO: Truman State University Press. p. 1. ISBN 978-1-931112-99-4.
^ Espinosa, Gastón (2009). Religion and the American Presidency. New York: Columbia University Press. p. 220. ISBN 978-0-231-14333-2.
^ Nielsen, Niels C. (2009). God In The Obama Era. New York, NY: Morgan James Publishing. pp. 152–153, 156. ISBN 978-1-60037-646-7.
^ Tiernan, L. Curtis. "Biographical Sketch, L. Curtis Tiernan". Monsignor L. Curtis Tiernan Papers. Independence, MO: Harry S. Truman Presidential Library & Museum. Retrieved May 21, 2018.
^ "Biographical Sketch, L. Curtis Tiernan".
^ "FAQ: Was President Truman the first Baptist president?". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved March 5, 2016..
^ Spalding, Elizabeth Edwards (2009), "Religion and the presidency of Harry S. Truman", in Espinosa, Gastón, Religion and the American Presidency: George Washington to George W. Bush, pp. 219–49.
^ Sobel, Robert (1990). Biographical Directory of the United States Executive Branch, 1774–1989. Westport, CT: Greenwood Press. p. 358. ISBN 978-0-313-26593-8.
^ Pullen, Randy (1999). "Twice the Citizen -- And Then Some". Army Reserve magazine. Washington, DC: U.S. Army Reserve: 12.
^ Clay, Steven E. (2010). US Army Order of Battle, 1919–1941. Ft. Leavenworth, KS: Combat Studies Institute Press. p. 878.
^ Tucker, Frank (December 1, 2010). "Army History: Truman, you're too old...". Gateway Today. St. Louis, MO: Association of the United States Army, St. Louis Chapter. pp. 5–8.
^ ab Army History: Truman, you're too old
^ Maddox, Robert James (2007). Hiroshima in History: The Myths of Revisionism. Columbia, MO: University of Missouri Press. p. 77. ISBN 978-0-8262-1732-5.
^ "Biographical Sketch: Harry S. Truman, 33rd President of the United States". Trumanlibrary.org. Harry S. Truman Library and Museum. Retrieved May 27, 2016.
^ Pullen, Twice the Citizen
^ Truman Library 1919.
^ Goldstein 2008.
^ McCullough 1992, pp. 63–64, 68.
^ ab Ferrell 1994, p. 88.
^ Ferrell 1994, p. 86.
^ Hamby 1995, pp. 410–12.
^ ab Dallek 2008, p. 6.
^ Barr 2004.
^ Savage 1991, p. 65.
^ ab United States Senate 2012.
^ Kirkendall, Richard Stewart (1989). The Harry S. Truman Encyclopedia. Boston, MA: G. K. Hall. p. 27. ISBN 978-0-8161-8915-1.
^ Dallek 2008, pp. 7–9.
^ abc Winn 2000.
^ Time & January 8, 1973.
^ McCullough 1992, p. 232.
^ McCullough 1992, p. 230.
^ Dallek 2008, pp. 11–12.
^ Hamby 1995, pp. 236–47.
^ Alexrod, Alan. The Real History of the Cold War: A New Look at the Past. Sterling. p. 44.
^ Michael James Lacey (1991). The Truman Presidency. pp. 35–36.
^ Dallek 2008, pp. 12–14.
^ Herman, Arthur (2012), Freedom's Forge: How American Business Produced Victory in World War II, New York, NY: Random House, pp. 103, 118, 194, 198–9, 235–6, 275, 281, 303, 312, ISBN 978-1-4000-6964-4.
^ Life & November 30, 1942.
^ McCullough 1992, pp. 337–38: "Later estimates were that the Truman Committee saved the country as much as $15 billion."
^ McDonald 1984: "This committee saved billions in taxpayers' money by helping eliminate waste and fraud."
^ Daniels 1998, p. 228: Jonathan W. Daniels quotes journalist Marquis Childs who wrote in November 1942 that the Truman Committee had "saved billions—yes, billions—of dollars."
^ Hamilton 2009, p. 301: "Over seven years (1941–1948) the committee heard from 1,798 witnesses during 432 public hearings. It published nearly two thousand pages of documents and saved perhaps $15 billion and thousands of lives by exposing faulty airplane and munitions production."
^ Time 2012.
^ Senate Truman Committee 2012.
^ McCullough 1992, pp. 373–378.
^ Dallek 2008, pp. 14–16.
^ Dallek 2008, pp. 15–17.
^ Occasions When Vice Presidents Have Voted to Break Tie Votes in the Senate, Senate Historical Office, United States Senate.
^ Harold Foote Gosnell, Truman's Crises: A Political Biography of Harry S. Truman (Greenwood Press, 1980), p. 212: "On only one occasion did [Truman] break a tie, and this was when his negative vote defeated a Taft amendment to the Lend-Lease Act which would have prevented postwar delivery of lend-lease goods contracted for during the war."
^ Robert C. Byrd, Senate, 1789–1989, Vol. 1: Addresses on the History of the United States Senate (Government Printing Office, 1988), p. 534: "In his eighty-two days as vice president, he had the opportunity to vote only once--on an amendment to limit the Lend-Lease extension bill. The vote was tied, and Truman voted no, which, in a sense, was unnecessary since the bill would have died even without his vote."
^ Dallek 2008, p. 16.
^ ab U.S. History 2012.
^ Schwab, Nick (August 13, 2014). "Lauren Bacall and Harry Truman's Piano Moment Led to Bigger Things". US News. Retrieved December 17, 2016.
^ Truman Library 2012h.
^ McCullough 1992, p. 425.
^ Goodwin 1994, p. 478.
^ McCullough 1992, p. 366.
^ Hamby 1995, pp. 301-02, 472.
^ Hamby 1995, pp. 474.
^ McCullough 1992, p. 511.
^ McCullough 1992, p. 436.
^ McCullough 1992, p. 348.
^ McCoy 1984, pp. 21–22.
^ Dallek 2008, pp. 19–20.
^ Reynolds 2005.
^ Alexrod, Alan. The Real History of the Cold War: A New Look at the Past. Sterling. p. 56.
^ PBS 2012.
^ Truman 1955, p. 416.
^ McCoy 1984, p. 37.
^ "Total Casualties – The Atomic Bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki". atomicarchive.com. Retrieved December 16, 2016.
^ Miller 1974, pp. 227–31.
^ Dallek 2008, pp. 24–28.
^ Kramer, Ronald C; Kauzlarich, David (2011), Rothe, Dawn; Mullins, Christopher W, eds., "Nuclear weapons, international law, and the normalization of state crime", State crime: Current perspectives, pp. 94–121, ISBN 978-0-8135-4901-9.
^ "Hiroshima und Nagasaki: Wessen Schuld?". zeit.de. Retrieved June 8, 2018.
^ "Hiroshima, crimen imperdonable". elespectador.com. August 13, 2008. Retrieved June 8, 2018.
^ "Rezension: Sachbuch: Gefügige Russen, tote Japaner". Retrieved June 8, 2018 – via www.faz.net.
^ Ryall, Julian (June 4, 2015). "US museum must call Hiroshima and Nagasaki 'war crimes', say Japanese". Retrieved June 8, 2018 – via www.telegraph.co.uk.
^ Scherer, Klaus (2015). Nagasaki - Der Mythos der zweiten Bombe. Munich: Hanser Verlag. ISBN 978-3446249479.
^ Mitchell, Greg (August 9, 2016). "71 Years Ago: When Truman Failed To Pause – And The Nagasaki War Crime Followed". huffingtonpost.com. Retrieved June 8, 2018.
^ "「なんであんな殺され方をしたのか、私は知りたい。あの世で、ちゃんとお兄ちゃんに説明できるように」――原爆投下から70年。広島の被爆者が語った原爆被害と戦争への思い - IWJ Independent Web Journal". iwj.co.jp. August 6, 2015. Retrieved June 8, 2018.
^ "Harry S. Truman: Address in Milwaukee, Wisconsin". www.presidency.ucsb.edu. Retrieved June 8, 2018.
^ Lambers, William (May 30, 2006). Nuclear Weapons. William K Lambers. p. 11. ISBN 0-9724629-4-5.
^ abc Miller Center 2012.
^ McCoy 1984, pp. 54–55.
^ View a contemporary newsreel report
^ McCullough 1992, pp. 498-501.
^ McCullough 1992, pp. 501-6.
^ Acacia, John (2009). Clark Clifford: The Wise Man of Washington. p. 22.
^ McCoy 1984, pp. 64–65.
^ Dallek 2008, pp. 48–50.
^ McCoy 1984, p. 91.
^ McCoy 1984, pp. 96–102.
^ Markel, Howard (2015), "'Give 'Em Health, Harry'", Milbank Quarterly, 93 (1): 1–7, doi:10.1111/1468-0009.12096, PMC 4364422.
^ Dallek 2008, pp. 84–86.
^ Binning, Esterly & Sracic 1999, p. 417.
^ Lamb, Charles M; Nye, Adam W (2012), "Do Presidents Control Bureaucracy? The Federal Housing Administration during the Truman‐Eisenhower Era", Political Science Quarterly, 127 (3): 445–67, doi:10.1002/j.1538-165x.2012.tb00734.x, JSTOR 23563185.
^ Neustadt 1954, pp. 349–81.
^ Hamby 1995, p. 310.
^ Roosevelt 1961.
^ Dallek 2008, pp. 56–57.
^ Freeland 1970, p. 90.
^ Roberts 2000.
^ Holsti 1996, p. 214.
^ Dallek 2008, pp. 62–63.
^ Limit CIA Role To Intelligence by Harry S Truman, The Washington Post,
December 22, 1963
^ May, Ernest R. (2002) "1947-48: When Marshall Kept the U.S. out of War in China." Journal of Military History 66#4: 1001–1010. online
^ Stern, Bert (2014). Winter in China. Xlibris Corporation. p. 232.
^ Truman Library 1988a.
^ McCullough 1992, pp. 595–97.
^ ab McCullough 1992, p. 599.
^ Ottolenghi 2004, pp. 963–88.
^ Baylis, Thomas. How Israel was Won: A Concise History of the Arab-Israeli Conflict, p. 55 (Lexington Books, Rowman and Littlefield, 1999).
^ Holmes, David. The Faiths of the Postwar Presidents: From Truman to Obama, pp. 16-17 (U. Georgia Press, 2012).
^ McCullough 1992, pp. 604–5.
^ Lenczowski 1990, p. 26.
^ Truman Library 1948.
^ Berdichevsky 2012.
^ ab Hechler & Elsey 2006.
^ Burnes 2003, p. 137.
^ McCullough 1992, p. 640.
^ Hamby 2008.
^ "Harry S. Truman: Address in St. Paul at the Municipal Auditorium". www.presidency.ucsb.edu.
^ "A quote by Harry Truman". www.goodreads.com.
^ "President Harry Truman on Republicans". October 5, 2012.
^ "Ten Quotes About Republicans From Harry Truman". November 22, 2014.
^ Board, The Editorial (November 24, 2017). "Opinion - When a Tax Cut Costs Millions Their Medical Coverage" – via NYTimes.com.
^ Center of Military History 2012.
^ Federal Register 1948.
^ Truman Library 1998.
^ McCoy 1984, pp. 153–158.
^ Pietrusza 2011, pp. 226–232.
^ "Footnotes on Political Battles of 1948". Truman's Library. Truman's Library. Retrieved January 28, 2016.
^ Bray, William J. "Recollections of the 1948 Campaign". Truman's Library. Truman's Library. Retrieved January 28, 2016.
^ McCullough 1992, p. 654.
^ McCullough 1992, p. 657.
^ McCullough 1992, p. 701.
^ Curran & Takata 2002.
^ Bennett 2012.
^ Truman Library 1971.
^ Jones 1948.
^ United States Senate 2005.
^ Atomic Archive 1953.
^ ab McCoy 1984, pp. 222–27.
^ Truman Library, Memo 1950.
^ Dean, John (2007), Broken Government: How Republican Rule Destroyed the Legislative, Executive, and Judicial Branches, Penguin, pp. 257, 315.
^ Dallek 2008, p. 107.
^ Matray 1979, pp. 314–33.
^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 81–90.
^ Cohen & Gooch 2006, pp. 165–95.
^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 123–29.
^ ab Time & December 3, 1973.
^ Strout 1999.
^ Weintraub 2000.
^ "How the Korean War Almost Went Nuclear".
^ Chambers II 1999, p. 849.
^ Roper 2010.
^ ab Presidential Job Approval for Richard Nixon at the American Presidency Project.
^ Wells, Jr. 1979, pp. 116–58.
^ Mitchell 1998, pp. 223–28.
^ McCoy 1984, pp. 197–99, 232.
^ Dallek 2008, pp. 89–91.
^ May 2002, pp. 1001–10.
^ Ferrell 1994, pp. 217–18, 224.
^ Donovan 1983, pp. 198–199.
^ Marolda, Edward J. "The Seventh Fleet in Chinese Waters". Archived from the original on May 26, 2014. Retrieved December 5, 2014.
^ Dallek 2008, pp. 87–88.
^ McCoy 1984, pp. 194, 217–18.
^ Richard S. Kirkendall (2012). The Civil Liberties Legacy of Harry S. Truman. Truman State UP. p. 124.
^ Weinstein 1997, pp. 450–51.
^ Evans, p. 324.
^ Troy 2008, p. 128.
^ ab McCoy 1984, pp. 216–17, 234–35.
^ McCullough 1992, p. 553.
^ White House Museum 1952.
^ Truman Library, Balcony 2012.
^ Truman Library, Balcony II 2012.
^ McCullough 1992, pp. 593, 652, 725, 875ff.
^ "FAQ: Assassination Attempt on President Truman's Life". Harry S. Truman Library and Museum.
^ Nohlen, Dieter (2005), Elections in the Americas: A Data Handbook, I, p. 556, ISBN 978-0-19-928357-6.
^ Higgs 2004.
^ Smaltz 1998.
^ Smaltz 1996.
^ McCoy 1984, p. 299.
^ Donovan 1983, pp. 116–17.
^ ab Truman Library, FAQ 1950.
^ Barnes 2008.
^ Giglio 2001, p. 112.
^ Smith 2001.
^ Eleonora W. Schoenebaum, ed. Political Profiles: The Truman Years (1978) pp 48-49.
^ Christopher N.J.Roberts. "William H. Fitzpatrick's Editorials on Human Rights (1949)". Quellen zur Geschichte der Menschenrechte. Retrieved November 4, 2017.
^ Truman Library, Special Message 1948.
^ Truman 1973, p. 429.
^ Kirkendall 1989, pp. 10–11.
^ MacGregor 1981, pp. 312–15, 376–78, 457–59.
^ National Archives 1948.
^ National Archives 1953.
^ "Travels of President Harry S. Truman". U.S. Department of State Office of the Historian.
^ Find Law 2012.
^ Alonzo L. Hamby. Man of the People: A Life of Harry S. Truman (1995) pp 602-5.
^ ab McCullough 1992, p. 887.
^ ab Ambrose 1983, p. 515.
^ Dallek 2008, pp. 139–142.
^ Time & November 10, 2008.
^ Dallek 2008, p. 144.
^ ab Truman Library 2012i.
^ Vaccaro 1953.
^ ab Smith 2008.
^ Dallek 2008, p. 150.
^ Ferrell 1994, p. 387.
^ Time & August 13, 1956.
^ McCullough 1992, p. 949; quoting Nevins 1955.
^ Truman 1955, title page.
^ Truman 1956, title page.
^ McCullough 1992, p. 963.
^ Martin 1960, p. 249.
^ Burnes 2003, pp. 217–18.
^ Skidmore 2004, pp. 123–124.
^ Ohio State 2012.
^ ab Truman Library 1965.
^ McCullough 1992, p. 983.
^ ab "6:00 p.m." CBS Radio News. CBS. December 25, 1972. Retrieved December 27, 2017 – via YouTube.
^ Washington National Cathedral 2012.
^ Wooten 1973, p. 1.
^ Donovan, Robert J. (1977). Conflict and Crisis: The Presidency of Harry S. Truman, 1945–1948. p. xv.
^ Lubell, Samuel (1956). The Future of American Politics (2nd ed.). Anchor Press. pp. 9–10.
^ Wisconsin Magazine of History & Autumn 1975.
^ Dallek 2008, pp. 149, 152.
^ Moynihan 1997.
^ Hamby 2002.
^ CSPAN 2009.
^ ab Dallek 2008, p. 152.
^ McCoy 1984, pp. 318–19.
^ Kloetzel & Charles 2012, pp. 50, 61, 71, 91, 99.
^ McCullough 1992, pp. 952–59, quote on p. 959.
^ Grand Lodge-Pennsylvania 2011.
^ Time & March 24, 1952.
^ Truman Library, SAR 2012.
^ ab Missouri Partisan Ranger 1995.
^ Eakin & Hale 1995, p. 71.
^ Truman Scholarship 2012.
^ Truman Fellowship 2012.
^ Truman School of Public Affairs 2010.
^ CNN 2000.
^ Time & October 17, 1949.
^ Army National Guard 2012.
^ "Congressional Gold Medal Recipients". Office of the Clerk. House of Representatives. Archived from the original on July 23, 2011. Retrieved August 20, 2014.
^ Hall of Famous Missourians 2012.
^ Truman Birthplace 2012.
^ "Statue of Truman in Athens, Bombed in 1986, Is Restored". Retrieved 2018-04-27.
Bibliography
Books
Ambrose, Stephen E. (1983). Eisenhower: 1890–1952. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0-671-44069-5.
Binning, William C.; Esterly, Larry E.; Sracic, Paul A. (1999). Encyclopedia of American Parties, Campaigns, and Elections. Westport, CT: Greenwood. ISBN 978-0-8131-1755-3.
Burnes, Brian (2003). Harry S. Truman: His Life and Times. Kansas City, MS: Kansas City Star Books. ISBN 978-0-9740009-3-0.
Chambers II, John W. (1999). The Oxford Companion to American Military History. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-507198-0.
Cohen, Eliot A.; Gooch, John (2006). Military Misfortunes: The Anatomy of Failure in War. New York: Free Press. ISBN 978-0-7432-8082-2.
Current, Richard Nelson; Freidel, Frank Burt; Williams, Thomas Harry (1971). American History: A Survey. II. New York: Knopf.
Dallek, Robert (2008). Harry S. Truman. New York: Times Books. ISBN 978-0-8050-6938-9.
Daniels, Jonathan (1998). The Man of Independence. University of Missouri Press. ISBN 0-8262-1190-9.
Donovan, Robert J. (1983). Tumultuous Years: 1949–1953. New York: W. W. Norton. ISBN 978-0-393-01619-2.
Eakin, Joanne C.; Hale, Donald R., eds. (1995). Branded as Rebels. Madison, WI: University of Wisconsin Press. ASIN B003GWL8J6.
Eisler, Kim Isaac (1993). A Justice for All: William J. Brennan, Jr., and the Decisions that Transformed America. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0-671-76787-7.
Evans, M Stanton, Blacklisted by History.
Ferrell, Robert Hugh (1994). Harry S. Truman: A Life. Columbia, Missouri: University of Missouri Press. ISBN 978-0-8262-1050-0.
Freeland, Richard M. (1970). The Truman Doctrine and the Origins of McCarthyism. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 978-0-8147-2576-4.
Giglio, James N. (2001). Truman in cartoon and caricature. Kirksville, MI: Truman State University Press. ISBN 978-0-8138-1806-1.
Goodwin, Doris Kearns (1994). No Ordinary Time: Franklin and Eleanor Roosevelt: The Home Front in World War II. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0-671-64240-2.
Hamby, Alonzo L., ed. (1974). Harry S. Truman and the Fair Deal. Lexington, MA: D. C. Heath & Co. ISBN 978-0-669-87080-0.
Hamby, Alonzo L. (1995). Man of the People: A Life of Harry S. Truman. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-504546-8.
Hamilton, Lee H. (2009). "Relations between the President and Congress in Wartime". In James A. Thurber. Rivals for Power: Presidential–Congressional Relations. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 0-7425-6142-9.
Holsti, Ole (1996). Public Opinion and American Foreign Policy. Ann Arbor, MI: The University of Michigan Press. ISBN 978-0-472-06619-3.
Judis, John B. (2014). Genesis: Truman, American Jews, and the Origins of the Arab/Israeli Conflict. New York: Farrar, Straus & Giroux. ISBN 978-0-374-16109-5.
Kirkendall, Richard S. (1989). Harry S. Truman Encyclopedia. Boston: G. K. Hall Publishing. ISBN 978-0-8161-8915-1.
Kloetzel, James E.; Charles, Steve, eds. (April 2012). Scott Standard Postage Stamp Catalog. 1. Sidney, OH: Scott Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-89487-460-4.
Lenczowski, George (1990). American Presidents and the Middle East. Durham, NC: Duke University Press. ISBN 978-0-8223-0972-7.
McCoy, Donald R. (1984). The Presidency of Harry S. Truman. Lawrence, KS: University Press of Kansas. ISBN 978-0-7006-0252-0.
McCullough, David (1992). Truman. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0-671-86920-5.
MacGregor, Morris J., Jr. (1981). Integration of the Armed Services 1940–1965. Washington, D.C.: Center of Military History. ISBN 978-0-16-001925-8.
- Margolies, Daniel S. ed. A Companion to Harry S. Truman (2012); 614pp; emphasis on historiography; see Sean J. Savage, "Truman in Historical, Popular, and Political Memory," pp 9–25. excerpt
Martin, Joseph William (1960). My First Fifty Years in Politics as Told to Robert J. Donovan. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Miller, Merle (1974). Plain Speaking: An Oral Biography of Harry S. Truman. New York: Putnam Publishing. ISBN 978-0-399-11261-4.
Mitchell, Franklin D. (1998). Harry S. Truman and the News Media: Contentious Relations, Belated Respect. Columbia, MO: University of Missouri Press. ISBN 0-8262-1180-1.
Oshinsky, David M. (2004). "Harry Truman". In Brinkley, Alan; Dyer, Davis. The American Presidency. Boston: Houghton Mifflin. ISBN 978-0-618-38273-6.
Pietrusza, David (2011). 1948: Harry Truman's Improbable Victory and the Year That Transformed America. New York: Union Square Press. ISBN 978-1-4027-6748-7.
Savage, Sean J. (1991). Roosevelt: The Party Leader, 1932–1945. Lexington, KY: The University Press of Kentucky. ISBN 978-0-8131-1755-3.
Skidmore, Max J. (2004). After the White House: Former Presidents as Private Citizens (rev ed.). New York: Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-312-29559-2.
Stohl, Michael (1988). "National Interest and State Terrorism". The Politics of Terrorism. New York: CRC Press.
Stokesbury, James L. (1990). A Short History of the Korean War. New York: Harper Perennial. ISBN 978-0-688-09513-0.
Troy, Gil (2008). Leading from the Center: Why Moderates Make the Best Presidents. New York: Basic Books. ISBN 978-0-465-00293-1.
Weinstein, Allen (1997). Perjury: The Hiss-Chambers Case (revised ed.). New York: Random House. ISBN 0-679-77338-X.
Primary sources
Truman, Harry S. (2002). Ferrell, Robert H., ed. The Autobiography of Harry S. Truman. Columbia, Missouri: University of Missouri Press. ISBN 0-8262-1445-2.
Truman, Harry S. (1955). Memoirs: Year of Decisions. 1. Garden City, NY: Doubleday.
online
——— (1956). Memoirs: Years of Trial and Hope. 2. Garden City, NY: Doubleday.
online v 2
Truman, Margaret (1973). Harry S. Truman. New York: William Morrow. ISBN 978-0-688-00005-9.
Journals
Griffith, Robert, ed. (Autumn 1975). "Truman and the Historians: The Reconstruction of Postwar American history". The Wisconsin Magazine of History. 59 (1).
Hamby, Alonzo L (August 2008). "1948 Democratic Convention The South Secedes Again". Smithsonian.
Hechler, Ken; Elsey, George M. (2006). "The Greatest Upset in American Political History: Harry Truman and the 1948 Election". White House Studies (Winter).
Matray, James I. (September 1, 1979). "Truman's Plan for Victory: National Self-determination and the Thirty-eighth Parallel Decision in Korea". Journal of American History. 66 (2): 314. doi:10.2307/1900879. ISSN 0021-8723. JSTOR 1900879.
May, Ernest R. (2002). "1947–48: When Marshall Kept the U.S. Out of War in China". The Journal of Military History (October 2002). JSTOR 3093261.
Neustadt, Richard E. (1954). "Congress and the Fair Deal: A Legislative Balance Sheet". Public Policy. Boston. 5. reprinted in Hamby 1974, pp. 15–42
Ottolenghi, Michael (December 2004). "Harry Truman's Recognition of Israel". Historical Journal. 47 (4).
Smaltz, Donald C. (July 1998). "Independent Counsel: A View from Inside". The Georgetown Law Journal. 86 (6).
Strout, Lawrence N. (1999). "Covering McCarthyism: How the Christian Science Monitor Handled Joseph R. McCarthy, 1950–1954". Journal of Political and Military Sociology. 2001 (Summer).
Wells, Samuel F., Jr. (Autumn 1979). "Sounding the Tocsin: NSC 68 and the Soviet Threat". International Security. 4 (2): 116. doi:10.2307/2626746. JSTOR 2626746.
"Truman Committee Exposes Housing Mess". Life. November 30, 1942. pp. 45–46, 48, 50, 52. Retrieved October 10, 2012.
Time
Gibbs, Nancy (November 10, 2008). "When New President Meets Old, It's Not Always Pretty". Time. Retrieved September 4, 2012.
"Armed Forces: Revolt of the Admirals". Time. October 17, 1949. Retrieved July 25, 2012. (Subscription required (help)).
"The Art of the Possible". Time. June 6, 1949. Retrieved July 25, 2012. (Subscription required (help)).
"Historical Notes: Giving Them More Hell". Time. December 3, 1973. Retrieved July 25, 2012. (Subscription required (help)).
"The Man of Spirit". Time. August 13, 1956. Retrieved July 25, 2012. (Subscription required (help)).
"National Affairs: Taft–Hartley: How It Works and How It Has Worked". Time. October 19, 1959. Retrieved July 25, 2012. (Subscription required (help)).
"The Presidency: The World of Harry Truman". Time. January 8, 1973. Retrieved July 25, 2012. (Subscription required (help)).
"Truman on Time Magazine Covers". Time. 2012. Retrieved July 25, 2012.
[permanent dead link]
"The Wonderful Wastebasket". Time. March 24, 1952. p. 3. Retrieved July 25, 2012. (Subscription required (help)).
The Washington Post
Barnes, Bart (January 29, 2008). "Margaret Truman Daniel Dies at Age 83". The Washington Post. Retrieved April 2, 2010.
Barr, Cameron W. (December 11, 2004). "Listing Madonna Rescued in Bethesda". The Washington Post. Retrieved April 4, 2010.
Smith, J. Y. (November 28, 2001). "Paul Hume: Music Critic Who Panned Truman Daughter's Singing and Drew Presidential Wrath". The Washington Post. Pittsburgh Post-Gazette. Retrieved July 22, 2012.
The New York Times
Nevins, Allan (November 6, 1955). "Year of Decisions a 'volume of distinction'". The New York Times Book Review.
Weintraub, Stanley (2000). "MacArthur's War Korea and the Undoing of an American Hero". The New York Times. Retrieved September 3, 2012.
Harry S. Truman Library & Museum
Giangreco, D. M.; Griffin, Robert E (1988). "The Airlift Begins: Airbridge to Berlin – The Berlin Crisis of 1948, its Origins and Aftermath". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved July 28, 2012.
Marks, Ted (1962). "Oral History Interview with Ted Marks". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved July 27, 2012.
Southern, Mrs. William (June 28, 1919). "Wedding of Bess Wallace and Capt. Harry S. Truman". The Examiner. Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved July 29, 2012.
Strout, Richard L. (February 5, 1971). "Oral History Interview with Richard L. Strout". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved July 27, 2012.
Truman, Harry (May 14, 1948). "Memo recognizing the state of Israel". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved July 28, 2012.
Truman, Harry (November 11, 1918). "WWI Letter from Harry to Bess". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved July 24, 2012.
Vest, Kathleen. "Truman's First Democratic Convention". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
"Background Information". The Truman Balcony. Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved October 16, 2012.
"Background Information (Continued)". The Truman Balcony. Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved October 16, 2012.
"Biographical sketch of Mrs. Harry S. Truman". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved July 29, 2012.
"Birthplace of Harry S. Truman". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. 1988. Retrieved July 25, 2012.
"Chronological Record of the 129th Field Artillery 1917–1919". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved July 27, 2012.
"Desegregation of the Armed Forces". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved July 28, 2012.
"Drugstore Clerk at 14 His First Job". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved July 25, 2012.
"Eleanor and Harry: The Correspondence of Eleanor Roosevelt and Harry S. Truman". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved July 28, 2012.
"FAQ: Is the letter on display that Truman wrote in defense of his daughter's singing?". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. December 6, 1950. Retrieved July 29, 2012.
"Harry S. Truman Post-Presidential Papers". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved July 28, 2012.
"Harry Truman joins Battery B of the Missouri National Guard". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved July 27, 2012.
"Memorandum of Information for the Secretary – Blockade of Korea". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. July 6, 1950. Archived from the original on August 9, 2007. Retrieved July 28, 2012.
"Military Personnel File of Harry S. Truman". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved July 27, 2012.
"President Lyndon B. Johnson Signs Medicare Bill". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. July 30, 1965. Retrieved July 29, 2012.
"President Truman Addresses Congress on Proposed Health Program, Washington, D.C". This Day in Truman History. Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. November 19, 1945. Retrieved July 27, 2012.
McDonald, John W. (May 1984). "10 of Truman's Happiest Years Spent in Senate". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved May 10, 2014. Originally published in the Independence Examiner, Truman Centennial Edition.
"Special Message to the Congress on Civil Rights". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved December 2, 2012.
"Use of the Period After the "S" in Harry S. Truman's Name". Harry S. Truman Library & Museum. Retrieved July 24, 2012.
Online sources
- Roberts, Christopher N.J.: William H. Fitzpatrick’s Editorials on Human Rights (1949), published by Arbeitskreis Menschenrechte im 20. Jahrhundert, published at "Quellen zur Geschichte der Menschenrechte". Retrieved November 4, 2017.
"Special Designation Liting". Army National Guard, United States Army. Retrieved September 8, 2012.
""Mike" Device is Tested". Atomic Archive. Retrieved September 7, 2012.
Bennett, Stephen Earl (May 2012). "Restoration of Confidence: Polling's Comeback from 1948". Public Opinion Pros. Archived from the original on March 5, 2012. Retrieved November 1, 2012.
Berdichevsky, Norman (May 2012). "Israel: From Darling of the Left to Pariah State". New English Review. Retrieved September 3, 2012.
Curran, Jeanne; Takata, Susan R. (2002). "Getting a Sample Isn't Always Easy". Dear Habermas. California State University—Dominguez Hills. Retrieved September 6, 2012.
"U.S. Constitution: Twenty-second Amendment". Find Law. Retrieved September 7, 2012.
Giangreco, D. M. "Capt. Harry Truman & Battery D, 129th Field Artillery In Action in the Argonne". Doughboy Center: The Story of the American Expeditionary Forces. WorldWar1.com. Retrieved July 29, 2012.
——— (April 7, 2002). "Soldier from Independence: Harry S. Truman and the Great War". U.S. Army Command and General Staff College. Retrieved July 29, 2012.
Gilwee, William J. (2000). "Capt. Harry Truman, Artilleryman and Future President". Doughboy Center: The Story of the American Expeditionary Forces. Worldwar1.com. Archived from the original on June 14, 2008. Retrieved July 29, 2012.
Goldstein, Steve (January 31, 2008). "First Daughter". Obit mag. Archived from the original on May 10, 2012. Retrieved July 29, 2012.
Hamby, Alonzo. "Presidency: How Do Historians Evaluate the Administration of Harry Truman?". History News Network. George Mason University. Retrieved September 8, 2012.
Higgs, Robert (March 1, 2004). "Truman's Attempt to Seize the Steel Industry". The Freeman. The Independent Institute. Retrieved September 7, 2012.
Jones, Tim. "Dewey defeats Truman". Chicago Tribune. p. 1. Retrieved September 7, 2012.
Miller, Henry I. (August 1, 2012). "The Nuking of Japan was a Tactical and Moral Imperative". Forbes. Retrieved May 10, 2017.
Moynihan, Daniel Patrick (1997). "Chairman's Forward" (PDF). Moynihan Commission on Government Secrecy. Government Printing Office. Retrieved September 3, 2012.
"Reading 2: Goodwill Ambassador to the World". National Park Service. 1961. Retrieved September 1, 2012.
Reynolds, Paul (August 3, 2005). "Hiroshima arguments rage 60 years on". BBC News. Retrieved July 30, 2012.
Roberts, Geoffrey (December 2000). "Historians and the Cold War". History Today. Retrieved April 4, 2010.
Smaltz, Donald C. (January 29, 1996). "Speech Delivered by Donald C. Smaltz". University of North Texas Libraries. Retrieved September 3, 2012.
Smith, Stephanie (March 18, 2008). "Former Presidents: Federal Pension and Retirement Benefits" (PDF). U.S. Senate Congressional Research Service. Retrieved September 3, 2012.
Truman, Harry S. (August 5, 1963). "Letter from Harry S. Truman to Irv Kupcinet (unsent), 08/05/1963". National Archives – Online Public Access. Retrieved September 2, 2012.
"America in the Second World War: The Manhattan Project". U.S. History. 2012. Retrieved July 30, 2012.
Vaccaro, Ernest B. (January 15, 1953). "Truman Puts in Busy Day as Term Comes to Close". The Victoria Advocate. Retrieved September 8, 2012.
"Presidential Funerals: Services Following Deaths of American Presidents". Washington National Cathedral. 2012. Archived from the original on August 13, 2012. Retrieved September 3, 2012.
Winn, Kenneth H. "It All Adds Up: Reform and the Erosion of Representative Government in Missouri, 1900–2000". Missouri Secretary of State. Retrieved July 30, 2012.
Wooten, James T. (January 6, 1973). "Truman Honored By World Notables At Cathedral Rites". The New York Times. p. 1. Retrieved November 1, 2012.
"American President: A Reference Resource". Miller Center, University of Virginia. Archived from the original on October 30, 2012. Retrieved September 9, 2012.
"Biographical Dictionary of the Federal Judiciary". Washington, D.C.: Federal Judicial Center. Archived from the original on July 30, 2016. Retrieved March 4, 2012. searches run from page, "select research categories" then check "court type" and "nominating president", then select U.S. District Courts (or U.S. Circuit Courts) and also Harry Truman.
"C-SPAN Survey of Presidential Leadership". Archived from the original on February 17, 2009. Retrieved April 5, 2010.
"Chapter 12: The President Intervenes". U.S. Army Center of Military History. 2012. Archived from the original on August 24, 2012. Retrieved September 3, 2012.
"Executive Order 9981, Establishing the President's Committee on Equality of Treatment and Opportunity in the Armed Services, Harry S. Truman". Federal Register. National Archives. 1948. Retrieved September 6, 2012.
"Hall of Famous Missourians". Missouri House of Representatives. Retrieved September 7, 2012.
"Harry S. Truman: 2nd Confederate President". The Missouri Partisan Ranger. 1995. Retrieved July 29, 2012.
"Harry S Truman – 1948". United States Federal Archives. Retrieved September 7, 2012.
"Harry S Truman (1884–1972) Thirty-third President (1945–1952)". The Grand Lodge of Free and Accepted Masons of Pennsylvania. 2011. Archived from the original on July 17, 2012. Retrieved July 29, 2012.
"Harry S. Truman, 34th Vice President (1945)". United States Senate. 2012. Retrieved July 30, 2012.
"Harry S. Truman Birthplace State Historic Site". Missouri State Parks and Historic Sites. 2012. Archived from the original on November 25, 2010. Retrieved July 30, 2012.
"Inauguration of the President: Fact & Firsts". United States Senate. 2005. Retrieved September 3, 2012.
"Interview Transcripts: The Potsdam Conference". The American Experience. PBS. 2012. Retrieved July 31, 2012.
"Job Performance Ratings for President Truman". Public Opinion Archives. Roper Center. 2010. Archived from the original on February 8, 2013. Retrieved September 7, 2012.
"Truman Fellowship". Sandia National Laboratories. Retrieved September 8, 2012.
"Our History: A Living Memorial". Harry S. Truman Scholarship Foundation. Archived from the original on November 3, 2012. Retrieved September 8, 2012.
"Harry S Truman School of Public Affairs". Truman School of Public Affairs, University of Missouri. Retrieved June 18, 2008.
"March 1, 1941: The Truman Committee". United States Senate. Retrieved November 18, 2012.
"Records of the Committee on Government Contract Compliance". United States Federal Archives. Retrieved September 7, 2012.
"State Department headquarters named for Harry S. Truman". CNN. Associated Press. September 22, 2000. Archived from the original on December 8, 2004. Retrieved April 4, 2010.
"Truman Reconstruction: 1948–1952". White House Museum. 1952. Retrieved September 3, 2012.
"U.S. Domestic Politics in the Early Cold War Era, 1947–1961". The Ohio State University. Archived from the original on June 5, 2011. Retrieved September 7, 2012.
"USS Harry S. Truman (CVN-75)". NavSource Online. July 10, 2012. Retrieved September 8, 2012.
External links
Official
- Harry S. Truman Library & Museum
- Harry S Truman National Historic Site
- White House biography
Media coverage
"Harry S. Truman collected news and commentary". The New York Times.
Newspaper clippings about Harry S. Truman in the 20th Century Press Archives of the German National Library of Economics (ZBW)
Other
United States Congress. "Harry S. Truman (id: T000387)". Biographical Directory of the United States Congress.
Harry S. Truman: A Resource Guide from the Library of Congress- Federal Bureau of Investigation Records: The Vault – Harry S. Truman
Essays on Harry S. Truman, each member of his cabinet and First Lady from the Miller Center of Public Affairs
The Presidents: Truman, an American Experience documentary
Works by or about Harry S. Truman at Internet Archive
Works by Harry S. Truman at LibriVox (public domain audiobooks)
"Life Portrait of Harry S. Truman", from C-SPAN's American Presidents: Life Portraits, October 18, 1999
Appearances on C-SPAN
- Harry S. Truman Personal Manuscripts
Harry S. Truman on IMDb




