German Americans
 German Americans % of population by state | |
| Total population | |
|---|---|
44,754,050[1] 14.4% of the U.S. population (2016) | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
Plurality in New York,[2] Pennsylvania,[3]Colorado and the Midwest.[4] | |
| Languages | |
English (American English dialects, Pennsylvania Dutch English) German (American German dialects, Standard German, Bavarian German, Swabian German, Colognian German, Alsatian German, Bernese German, Hutterite German, Pennsylvania German, Plautdietsch, Texas German) | |
| Religion | |
| |
| Related ethnic groups | |
|
German Americans (German: Deutschamerikaner) are Americans who have full or partial German ancestry. With an estimated size of approximately 44 million in 2016, German Americans are the largest of the ancestry groups reported by the US Census Bureau in its American Community Survey.[1] The group accounts for about one third of the total ethnic German population in the world.[6][7][8]
None of the German states had American colonies. In the 1670s, the first significant groups of German immigrants arrived in the British colonies, settling primarily in Pennsylvania, New York, and Virginia. Immigration continued in very large numbers during the 19th century, with eight million arrivals from Germany. Between 1820 and 1870 over seven and a half million German immigrants came to the United States—more than doubling the entire population of the country. By 2010, their population grew to 49.8 million immigrants, reflecting a jump of 6 million people since 2000.
There is a "German belt" that extends all the way across the United States, from eastern Pennsylvania to the Oregon coast. Pennsylvania has the largest population of German-Americans in the U.S. and is home to one of the group's original settlements, Germantown (Philadelphia), founded in 1683 and the birthplace of the American antislavery movement in 1688, as well as the revolutionary Battle of Germantown. The state of Pennsylvania has 3.5 million people of German ancestry.
They were pulled by the attractions of land and religious freedom, and pushed out of Germany by shortages of land and religious or political oppression.[9] Many arrived seeking religious or political freedom, others for economic opportunities greater than those in Europe, and others for the chance to start fresh in the New World. The arrivals before 1850 were mostly farmers who sought out the most productive land, where their intensive farming techniques would pay off. After 1840, many came to cities, where "Germania"—German-speaking districts—soon emerged.[10][11][12]
German Americans established the first kindergartens in the United States,[13] introduced the Christmas tree tradition,[14][15] and introduced popular foods such as hot dogs and hamburgers to America.[16]
The great majority of people with some German ancestry have become Americanized and hardly can be distinguished; fewer than 5% speak German. German-American societies abound, as do celebrations that are held throughout the country to celebrate German heritage of which the German-American Steuben Parade in New York City is one of the most well-known and is held every third Saturday in September. Traditional Oktoberfest celebrations and the German-American Day are popular festivities. There are major annual events in cities with German heritage including Chicago, Cincinnati, Milwaukee, Pittsburgh, San Antonio, and St. Louis.
Contents
1 History
1.1 Colonial era
1.1.1 Palatines
1.1.2 Louisiana
1.1.3 Southeast
1.1.4 New England
1.1.5 Pennsylvania
1.2 American Revolution
1.3 19th century
1.3.1 Jews
1.3.2 Northeastern cities
1.3.3 Cities of the Midwest
1.3.4 Deep South
1.3.5 Texas
1.3.6 Germans from Russia
1.3.7 Civil War
1.3.8 Farmers
1.3.9 Politics
1.4 World Wars
1.4.1 Intellectuals
1.4.2 World War I anti-German sentiment
1.4.3 World War II
1.5 Contemporary period
2 Demographics
2.1 German-American communities
2.1.1 Communities with high percentages of people of German ancestry
2.1.2 Large communities[definition needed] with high percentages of people of German ancestry
2.1.3 Communities with the most residents born in Germany
3 Counties by percentages of Germans
4 Culture
4.1 Music
4.2 Turners
4.3 Media
4.4 Athletics
4.5 Religion
4.6 Language
5 Assimilation
6 German-American influence
7 Education
8 Notable people
8.1 German-American presidents
9 See also
10 Notes
11 References
12 Further reading
12.1 Historiography
12.2 Primary sources
12.3 In German
13 External links
13.1 German-American history and culture
13.2 German-American organizations
13.3 Local German-American history and culture
History
The Germans included many quite distinct subgroups with differing religious and cultural values.[17] Lutherans and Catholics typically opposed Yankee moralizing programs such as the prohibition of beer, and favored paternalistic families with the husband deciding the family position on public affairs.[18][19] They generally opposed women's suffrage but this was used as argument in favor of suffrage when German Americans became pariahs during World War I.[20] On the other hand, there were Protestant groups that emerged from European pietism such as the German Methodist and United Brethren; they more closely resembled the Yankee Methodists in their moralism.[21]
Colonial era
The first English settlers arrived at Jamestown, Virginia in 1607, and were accompanied by the first German American, Dr. Johannes Fleischer. He was followed in 1608 by five glassmakers and three carpenters or house builders.[22] The first permanent German settlement in what became the United States was Germantown, Pennsylvania, founded near Philadelphia on October 6, 1683.[23]

John Jacob Astor, in an oil painting by Gilbert Stuart, 1794, was the first of the Astor family dynasty and the first millionaire in the United States, making his fortune in the fur trade and New York City real estate.
Large numbers of Germans migrated from the 1680s to 1760s, with Pennsylvania the favored destination. They migrated to America for a variety of reasons.[23]Push factors involved worsening opportunities for farm ownership in central Europe, persecution of some religious groups, and military conscription; pull factors were better economic conditions, especially the opportunity to own land, and religious freedom. Often immigrants paid for their passage by selling their labor for a period of years as indentured servants.[24]
Large sections of Pennsylvania, Upstate New York, and the Shenandoah valley of Virginia attracted Germans. Most were Lutheran or German Reformed; many belonged to small religious sects such as the Moravians and Mennonites. German Catholics did not arrive in number until after the War of 1812.[25]
Palatines
In 1709, Protestant Germans from the Pfalz or Palatine region of Germany escaped conditions of poverty, traveling first to Rotterdam and then to London. Anne, Queen of Great Britain, helped them get to her colonies in America. The trip was long and difficult to survive because of the poor quality of food and water aboard ships and the infectious disease typhus. Many immigrants, particularly children, died before reaching America in June 1710.[26]
The Palatine immigration of about 2100 people who survived was the largest single immigration to America in the colonial period. Most were first settled along the Hudson River in work camps, to pay off their passage. By 1711, seven villages had been established in New York on the Robert Livingston manor. In 1723 Germans became the first Europeans allowed to buy land in the Mohawk Valley west of Little Falls. One hundred homesteads were allocated in the Burnetsfield Patent. By 1750, the Germans occupied a strip some 12 miles (19 km) long along both sides of the Mohawk River. The soil was excellent; some 500 houses were built, mostly of stone, and the region prospered in spite of Indian raids. Herkimer was the best-known of the German settlements in a region long known as the "German Flats".[26]
They kept to themselves, married their own, spoke German, attended Lutheran churches, and retained their own customs and foods. They emphasized farm ownership. Some mastered English to become conversant with local legal and business opportunities. They tolerated slavery (although few were rich enough to own a slave).[27]
The most famous of the early German Palatine immigrants was editor John Peter Zenger, who led the fight in colonial New York City for freedom of the press in America. A later immigrant, John Jacob Astor, who came from Baden after the Revolutionary War, became the richest man in America from his fur trading empire and real estate investments in New York.[28]
Louisiana
John Law organized the first colonization of Louisiana with German immigrants. Of the over 5,000 Germans initially immigrating primarily from the Alsace Region as few as 500 made up the first wave of immigrants to leave France en route to the Americas. Less than 150 of those first indentured German farmers made it to Louisiana and settled along what became known as the German Coast. With tenacity, determination and the leadership of D'arensburg these Germans felled trees, cleared land, and cultivated the soil with simple hand tools as draft animals were not available. The German coast settlers supplied the budding City of New Orleans with corn, rice, eggs. and meat for many years following.
The Mississippi Company settled thousands of German pioneers in French Louisiana during 1721. It encouraged Germans, particularly Germans of the Alsatian region who had recently fallen under French rule, and the Swiss to immigrate. Alsace was sold to France within the greater context of the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648).
The Jesuit Charlevoix traveled New France (Canada and Louisiana) in the early 1700s. His letter said "these 9,000 Germans, who were raised in the Palatinate (Alsace part of France) were in Arkansas. The Germans left Arkansas en masse. They went to New Orleans and demanded passage to Europe. The Mississippi Company gave the Germans rich lands on the right bank of the Mississippi River about 25 miles (40 km) above New Orleans. The area is now known as 'the German Coast'."
A thriving population of Germans lived upriver from New Orleans, Louisiana, known as the German Coast. They were attracted to the area through pamphlets such as J. Hanno Deiler's "Louisiana: A Home for German Settlers".[29]

Carl Schurz was the first German born US Senator (Missouri, 1868) and later US Secretary of the Interior
Southeast
Two waves of German colonists in 1714 and 1717 founded a large colony in Virginia called Germanna,[30] located near modern-day Culpeper, Virginia. Virginia Lieutenant Governor Alexander Spotswood, taking advantage of the headright system, had bought land in present-day Spotsylvania and encouraged German immigration by advertising in Germany for miners to move to Virginia and establish a mining industry in the colony. The name "Germanna", selected by Governor Alexander Spotswood, reflected both the German immigrants who sailed across the Atlantic to Virginia and the British Queen, Anne, who was in power at the time of the first settlement at Germanna.
In North Carolina, German Moravians living around Bethlehem, Pennsylvania purchased nearly 100,000 acres (400 km2) from Lord Granville (one of the British Lords Proprietor) in the Piedmont of North Carolina in 1753. They established German settlements on that tract, especially in the area around what is now Winston-Salem.[31] They also founded the transitional settlement of Bethabara, North Carolina, translated as House of Passage, the first planned Moravian community in North Carolina, in 1759. Soon after, the German Moravians founded the town of Salem in 1766 (now a historical section in the center of Winston-Salem) and Salem College (an early female college) in 1772.
In the Georgia Colony, Germans mainly from the Swabia region settled in Savannah, St. Simon's Island and Fort Frederica in the 1730s and 1740s. They were actively recruited by James Oglethorpe and quickly distinguished themselves through improved farming, advanced tabby (cement)-construction, and leading joint Lutheran-Anglican-Reformed religious services for the colonists.
German immigrants also settled in other areas of the American South, including around the Dutch (Deutsch) Fork area of South Carolina,[25] and Texas, especially in the Austin area.
New England
Between 1742 and 1753, roughly 1,000 Germans settled in Broad Bay, Massachusetts (now Waldoboro, Maine). Many of the colonists fled to Boston, Maine, Nova Scotia, and North Carolina after their houses were burned and their neighbors killed or carried into captivity by Native Americans. The Germans who remained found it difficult to survive on farming, and eventually turned to the shipping and fishing industries.[32]
Pennsylvania
The tide of German immigration to Pennsylvania swelled between 1725 and 1775, with immigrants arriving as redemptioners or indentured servants. By 1775, Germans constituted about one-third of the population of the state. German farmers were renowned for their highly productive animal husbandry and agricultural practices. Politically, they were generally inactive until 1740, when they joined a Quaker-led coalition that took control of the legislature, which later supported the American Revolution. Despite this, many of the German settlers were loyalists during the Revolution, possibly because they feared their royal land grants would be taken away by a new republican government, or because of loyalty to a British German monarchy who had provided the opportunity to live in a liberal society.[33] The Germans, comprising Lutherans, Reformed, Mennonites, Amish, and other sects, developed a rich religious life with a strong musical culture. Collectively, they came to be known as the Pennsylvania Dutch (from Deutsch).[34][35]
Etymologically, the word Dutch originates from the Old High German word "diutisc" (from "diot" "people"), referring to the Germanic "language of the people" as opposed to Latin, the language of the learned (see also theodiscus). Only later did the word come to refer to the people who spoke a Germanic language, and only in the last 1-2 centuries to refer only to the people of the Netherlands. Other Germanic language variants for "deutsch/deitsch/dutch" are: Dutch "Duits" and "Diets", Yiddish "daytsh", Danish/Norwegian "tysk", or Swedish "tyska." The Japanese "doitzu" also derives from the aforementioned "Dutch" variations. There were few German Catholics in Pennsylvania before the 1810s.[36]
The Studebaker brothers, forefathers of the wagon and automobile makers, arrived in Pennsylvania in 1736 from the famous blade town of Solingen. With their skills, they made wagons that carried the frontiersmen westward; their cannons provided the Union Army with artillery in the American Civil War, and their automobile company became one of the largest in America, although never eclipsing the "Big Three", and was a factor in the war effort and in the industrial foundations of the Army.[37]
From names in the 1790 U.S. census, historians estimate Germans constituted nearly 9% of the white population in the United States.[38]
American Revolution
The King of Great Britain, whose King George III was also the Elector of Hanover in Germany, hired 18,000 Hessians (career soldiers from small German states) to support British forces. Many were captured; they remained as prisoners during the war but some stayed and became U.S. citizens.[39] German Americans served on both sides of the American Revolution. The religious minorities were neutral. The Lutherans were split. In New York, many were neutral or supported the Loyalist cause. In Pennsylvania most were on the patriot side.[40] The Muhlenberg family, led by Rev. Henry Muhlenberg was especially influential on the Patriot side.[41] His son Peter Muhlenberg, a Lutheran clergyman in Virginia became a major general and later a Congressman.[42][43]
The brief Fries's Rebellion was an anti-tax movement among Germans in Pennsylvania in 1799-1800.[44]
19th century
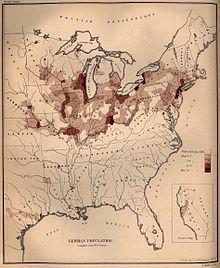
German population density in the United States, 1872
| German Immigration to United States (1820–2004)[45] | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Immigration period | Number of Immigrants | Immigration period | Number of Immigrants |
| 1820–1840 | 160,335 | 1921–1930 | 412,202 |
| 1841–1850 | 434,626 | 1931–1940 | 114,058 |
| 1851–1860 | 951,667 | 1941–1950 | 226,578 |
| 1861–1870 | 787,468 | 1951–1960 | 477,765 |
| 1871–1880 | 718,182 | 1961–1970 | 190,796 |
| 1881–1890 | 1,452,970 | 1971–1980 | 74,414 |
| 1891–1900 | 505,152 | 1981–1990 | 91,961 |
| 1901–1910 | 341,498 | 1991–2000 | 92,606 |
| 1911–1920 | 143,945 | 2001–2004 | 61,253 |
| Total : 7,237,594 | |||
The largest flow of German immigration to America occurred between 1820 and World War I, during which time nearly six million Germans immigrated to the United States. From 1840 to 1880, they were the largest group of immigrants. Following the Revolutions of 1848 in the German states, a wave of political refugees fled to America, who became known as Forty-Eighters. They included professionals, journalists, and politicians. Prominent Forty-Eighters included Carl Schurz and Henry Villard.[46]

"From the Old to the New World" shows German emigrants boarding a steamer in Hamburg, to New York. Harper's Weekly, (New York) November 7, 1874
"Latin farmer" or Latin Settlement is the designation of several settlements founded by some of the Dreissiger and other refugees from Europe after rebellions like the Frankfurter Wachensturm beginning in the 1830s—predominantly in Texas and Missouri, but also in other US states—in which German intellectuals (freethinkers, German: Freidenker, and Latinists) met together to devote themselves to the German literature, philosophy, science, classical music, and the Latin language. A prominent representative of this generation of immigrants was Gustav Koerner who lived most of the time in Belleville, Illinois until his death.
Jews
A few German Jews came in the colonial era. The largest numbers arrived after 1820, especially in the mid-19th century.[47] They spread across the North and South (and California, where Levi Strauss arrived in 1853). They formed small German-Jewish communities in cities and towns. They typically were local and regional merchants selling clothing; others were livestock dealers, agricultural commodity traders, bankers, and operators of local businesses. Henry Lehman, who founded Lehman Brothers in Alabama, was a particularly prominent example of such a German-Jewish immigrant. They formed Reform synagogues[48] and sponsored numerous local and national philanthropic organizations, such as B'nai B'rith.[49] This German-speaking group is quite distinct from the Yiddish-speaking East-European Jews who arrived in much larger numbers starting in the late 19th century and concentrated in New York.
Northeastern cities
The port cities of New York, and Baltimore had large populations. As did Hoboken, New Jersey.
Cities of the Midwest
Cities along the Great Lakes, the Ohio River, and the Mississippi and Missouri Rivers attracted a large German element. The Midwestern cities of Milwaukee, Cincinnati, St. Louis, Chicago were favored destinations of German immigrants. Also, the Northern Kentucky and Louisville area along the Ohio River was a favored destination. By 1900, the populations of the cities of Cleveland, Milwaukee, and Cincinnati were all more than 40% German American. Dubuque and Davenport, Iowa had even larger proportions, as did Omaha, Nebraska, where the proportion of German Americans was 57% in 1910. In many other cities of the Midwest, such as Fort Wayne, Indiana, German Americans were at least 30% of the population.[32][50] By 1850 there were 5,000 Germans, mostly Schwabians living in, and around, Ann Arbor, Michigan.[51]
Many concentrations acquired distinctive names suggesting their heritage, such as the "Over-the-Rhine" district in Cincinnati and "German Village" in Columbus, Ohio.[52]
A favorite destination was Milwaukee, known as "the German Athens". Radical Germans trained in politics in the old country dominated the city's Socialists. Skilled workers dominated many crafts, while entrepreneurs created the brewing industry; the most famous brands included Pabst, Schlitz, Miller, and Blatz.[53]
Whereas half of German immigrants settled in cities, the other half established farms in the Midwest. From Ohio to the Plains states, a heavy presence persists in rural areas into the 21st century.[25][54]
Deep South
Few German immigrants settled in the Deep South, apart from New Orleans, the German Coast, and Texas.[55]
Texas

The Wahrenberger House in Austin served as a German-American school.[56]
Texas attracted many Germans who entered through Galveston and Indianola, both those who came to farm, and later immigrants who more rapidly took industrial jobs in cities such as Houston. As in Milwaukee, Germans in Houston built the brewing industry. By the 1920s, the first generation of college-educated German Americans were moving into the chemical and oil industries.[25]
Texas had about 20,000 German Americans in the 1850s. They did not form a uniform bloc, but were highly diverse and drew from geographic areas and all sectors of European society, except that very few aristocrats or upper middle class businessmen arrived. In this regard, Texas Germania was a microcosm of the Germania nationwide.
The Germans who settled Texas were diverse in many ways. They included peasant farmers and intellectuals; Protestants, Catholics, Jews, and atheists; Prussians, Saxons, and Hessians; abolitionists and slave owners; farmers and townsfolk; frugal, honest folk and ax murderers. They differed in dialect, customs, and physical features. A majority had been farmers in Germany, and most arrived seeking economic opportunities. A few dissident intellectuals fleeing the 1848 revolutions sought political freedom, but few, save perhaps the Wends, went for religious freedom. The German settlements in Texas reflected their diversity. Even in the confined area of the Hill Country, each valley offered a different kind of German. The Llano valley had stern, teetotaling German Methodists, who renounced dancing and fraternal organizations; the Pedernales valley had fun-loving, hardworking Lutherans and Catholics who enjoyed drinking and dancing; and the Guadalupe valley had freethinking Germans descended from intellectual political refugees. The scattered German ethnic islands were also diverse. These small enclaves included Lindsay in Cooke County, largely Westphalian Catholic; Waka in Ochiltree County, Midwestern Mennonite; Hurnville in Clay County, Russian German Baptist; and Lockett in Wilbarger County, Wendish Lutheran.[57]
Germans from Russia

Temporary quarters for Volga Germans in central Kansas, 1875
Germans from Russia were the most traditional of German-speaking arrivals.[citation needed] They were Germans who had lived for generations throughout the Russian Empire, but especially along the Volga River in Russia and near the Crimea. Their ancestors had come from all over the German-speaking world, invited by Catherine the Great in 1762 and 1763 to settle and introduce more advanced German agriculture methods to rural Russia. They had been promised by the manifesto of their settlement the ability to practice their respective Christian denominations, retain their culture and language, and retain immunity from conscription for them and their descendants. As time passed, the Russian monarchy gradually eroded the ethnic German population's relative autonomy. Conscription eventually was reinstated; this was especially harmful to the Mennonites, who practice pacifism. Throughout the 19th century, pressure increased from the Russian government to culturally assimilate. Many Germans from Russia found it necessary to emigrate to avoid conscription and preserve their culture. About 100,000 immigrated by 1900, settling primarily in the Dakotas, Kansas and Nebraska. The southern central part of North Dakota was known as "the German-Russian triangle". A smaller number moved farther west, finding employment as ranchers and cowboys.
Negatively influenced by the violation of their rights and cultural persecution by the Tsar, the Germans from Russia who settled in the northern Midwest saw themselves a downtrodden ethnic group separate from Russian Americans and having an entirely different experience from the German Americans who had emigrated from German lands; they settled in tight-knit communities that retained their German language and culture. They raised large families, built German-style churches, buried their dead in distinctive cemeteries using cast iron grave markers, and created choir groups that sang German church hymns. Many farmers specialized in sugar beets—still a major crop in the upper Great Plains. During World War I, their identity was challenged by anti-German sentiment. By the end of World War II, the German language, which had always been used with English for public and official matters, was in serious decline. Today, German is preserved mainly through singing groups and recipes, with the Germans from Russia in the northern Great Plains states speaking predominantly English. German remains the second most spoken language in North and South Dakota, and Germans from Russia often use loanwords, such as Kuchen for cake. Despite the loss of their language, the ethnic group remains distinct, and has left a lasting impression on the American West.[58]
Civil War
Sentiment among German Americans was largely anti-slavery, especially among Forty-Eighters.[46] Notable Forty-Eighter Hermann Raster wrote passionately against slavery and was very pro-Lincoln. Raster published anti-slavery pamphlets and was the editor of the most influential German language newspaper in America at the time.[59] He helped secure the votes of German-Americans across the United States for Abraham Lincoln. When Raster died the Chicago Tribune published an article regarding his service as a correspondent for America to the German states saying, "His writings during and after the Civil War did more to create understanding and appreciation of the American situation in Germany and to float U.S. bonds in Europe than the combined efforts of all the U.S. ministers and consuls."[60] Hundreds of thousands of German Americans volunteered to fight for the Union in the American Civil War (1861–1865).[61] The Germans were the largest immigrant group to participate in the Civil War; over 176,000 U.S. soldiers were born in Germany.[62] A popular Union commander among Germans, Major General Franz Sigel was the highest-ranking German officer in the Union Army, with many German immigrants claiming to enlist to "fight mit Sigel".[63]

The German vote in 1900 was in doubt; they opposed the "repudiation" policy of Bryan (right poster), but also disliked the overseas expansion McKinley had delivered (left poster)
Although only one in four Germans fought in all-German regiments, they created the public image of the German soldier. Pennsylvania fielded five German regiments, New York eleven, and Ohio six.[61]
Farmers
Western railroads, with large land grants available to attract farmers, set up agencies in Hamburg and other German cities, promising cheap transportation, and sales of farmland on easy terms. For example, the Santa Fe railroad hired its own commissioner for immigration, and sold over 300,000 acres (1,200 km2) to German-speaking farmers.[64]
Throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, the German Americans showed a high interest in becoming farmers, and keeping their children and grandchildren on the land. While they needed profits to stay in operation, they used profits as a tool "to maintain continuity of the family."[65] They used risk averse strategies, and carefully planned their inheritances to keep the land in the family. Their communities showed smaller average farm size, greater equality, less absentee ownership and greater geographic persistence. As one farmer explained, "To protect your family has turned out to be the same thing as protecting your land."[66]
Germany was a large country with many diverse subregions which contributed immigrants. Dubuque was the base of the Ostfriesische Nachrichten ("East Fresian News") from 1881 to 1971. It connected the 20,000 immigrants from East Friesland (Ostfriesland), Germany, to each other across the Midwest, and to their old homeland. In Germany East Friesland was often a topic of ridicule regarding backward rustics, but editor Leupke Hündling shrewdly combined stories of proud memories of Ostfriesland. The editor enlisted a network of local correspondents. By mixing local American and local German news, letters, poetry, fiction, and dialogue, the German-language newspaper allowed immigrants to honor their origins and celebrate their new life as highly prosperous farmers with much larger farms than were possible back in impoverished Ostfriesland. During the world wars, when Germania came under heavy attack, the paper stressed its humanitarian role, mobilizing readers to help the people of East Friesland with relief funds. Younger generations could usually speak German but not read it, so the subscription based dwindled away as the target audience Americanized itself.[67]
Politics
Relatively few German Americans held office, but the men voted once they became citizens. In general during the Third party System (1850s–1890s), the Protestants and Jews leaned toward the Republican party and the Catholics were strongly Democratic. When prohibition was on the ballot, the Germans voted solidly against it. They strongly distrusted moralistic crusaders, whom they called "Puritans", including the temperance reformers and many Populists. The German community strongly opposed Free Silver, and voted heavily against crusader William Jennings Bryan in 1896. In 1900, however, many German Democrats returned to their party and voted for Bryan, perhaps because of President William McKinley's foreign policy.[68]
At the local level, historians have explored the changing voting behavior of the German-American community and one of its major strongholds, St. Louis, Missouri. The German Americans had voted 80 percent for Lincoln in 1860, and strongly supported the war effort. They were a bastion of the Republican Party in St. Louis and nearby immigrant strongholds in Missouri and southern Illinois. The German Americans were angered by a proposed Missouri state constitution that discriminated against Catholics and freethinkers. The requirement of a special loyalty oath for priests and ministers was troublesome. Despite their strong opposition the constitution was ratified in 1865. Racial tensions with the blacks began to emerge, especially in terms of competition for unskilled labor jobs. Germania was nervous about black suffrage in 1868, fearing that blacks would support puritanical laws Especially regarding the prohibition of beer gardens on Sundays. The tensions split off a large German element in 1872, led by Carl Schurz. They supported the Liberal Republican party led by Benjamin Gratz Brown for governor in 1870 and Horace Greeley for president in 1872.[69]
Many Germans in late 19th century cities were communists; Germans played a significant role in the labor union movement.[70][71] A few were anarchists.[72] Eight of the forty-two anarchist defendants in the Haymarket Affair of 1886 in Chicago were German.
World Wars
Intellectuals

Hugo Münsterberg, Harvard professor of psychology
Hugo Münsterberg (1863–1916), a German psychologist, moved to Harvard in the 1890s and became a leader in the new profession. He was president of the American Psychological Association in 1898, and the American Philosophical Association in 1908, and played a major role in many other American and international organizations.[73]
Arthur Preuss (1871–1934) was a leading journalist, and theologian. A layman in St Louis. His Fortnightly Review (in English) was a major conservative voice read closely by church leaders and intellectuals from 1894 until 1934. He was intensely loyal to the Vatican. Preuss upheld the German Catholic community, denounced the "Americanism" heresy, promoted the Catholic University of America, and anguished over the anti-German America hysteria during World War I. He provided lengthy commentary regarding the National Catholic Welfare Conference, the anti-Catholic factor in the presidential campaign of 1928, the hardships of the Great Depression, and the liberalism of the New Deal.[74][75]
World War I anti-German sentiment
During World War I (1914–18, American involvement 1917-18), German Americans were often accused of being too sympathetic to Imperial Germany. Former president Theodore Roosevelt denounced "hyphenated Americanism", insisting that dual loyalties were impossible in wartime. A small minority came out for Germany, or ridiculed the British (as did H. L. Mencken). Similarly, Harvard psychology professor Hugo Münsterberg dropped his efforts to mediate between America and Germany, and threw his efforts behind the German cause.[76][77]
The Justice Department prepared a list of all German aliens, counting approximately 480,000 of them, more than 4,000 of whom were imprisoned in 1917–18. The allegations included spying for Germany, or endorsing the German war effort.[78] Thousands were forced to buy war bonds to show their loyalty.[79] The Red Cross barred individuals with German last names from joining in fear of sabotage. One person was killed by a mob; in Collinsville, Illinois, German-born Robert Prager was dragged from jail as a suspected spy and lynched.[80] A Minnesota minister was tarred and feathered when he was overheard praying in German with a dying woman.[81]
In Chicago, Frederick Stock temporarily stepped down as conductor of the Chicago Symphony Orchestra until he finalized his naturalization papers. Orchestras replaced music by German composer Wagner with French composer Berlioz. In Cincinnati, the public library was asked to withdraw all German books from its shelves.[82] German-named streets were renamed. The town, Berlin, Michigan, was changed to Marne, Michigan (honoring those who fought in the Battle of Marne). In Iowa, in the 1918 Babel Proclamation, the governor prohibited all foreign languages in schools and public places. Nebraska banned instruction in any language except English, but the U.S. Supreme Court ruled the ban illegal in 1923 (Meyer v. Nebraska).[83] The response of German Americans to these tactics was often to "Americanize" names (e.g., Schmidt to Smith, Müller to Miller) and limit the use of the German language in public places, especially churches.[84]

American wartime propaganda depicted the bloodthirsty German "Hun" soldier as an enemy of civilization, with his eyes on America from across the Atlantic

German-American farmer John Meints of Minnesota was tarred and feathered in August 1918 for allegedly not supporting war bond drives.
World War II

Marlene Dietrich signing a soldier's cast (Belgium, 1944).
Between 1931 and 1940, 114,000 Germans moved to the United States, many of whom—including Nobel prize winner Albert Einstein and author Erich Maria Remarque—were Jewish Germans or anti-Nazis fleeing government oppression.[85] About 25,000 people became paying members of the pro-Nazi German American Bund during the years before the war.[86] German aliens were the subject of suspicion and discrimination during the war, although prejudice and sheer numbers meant they suffered as a group generally less than Japanese Americans. The Alien Registration Act of 1940 required 300,000 German-born resident aliens who had German citizenship to register with the Federal government and restricted their travel and property ownership rights.[87][88] Under the still active Alien Enemy Act of 1798, the United States government interned nearly 11,000 German citizens between 1940 and 1948. Civil rights violations occurred.[89] An unknown number of "voluntary internees" joined their spouses and parents in the camps and were not permitted to leave.[90][91][92]
President Franklin D. Roosevelt sought out Americans of German ancestry for top war jobs, including General Dwight D. Eisenhower, Admiral Chester W. Nimitz, and USAAF General Carl Andrew Spaatz. He appointed Republican Wendell Willkie (who ironically ran against Roosevelt in the 1940 presidential election) as a personal representative. German Americans who had fluent German language skills were an important asset to wartime intelligence, and they served as translators and as spies for the United States.[93] The war evoked strong pro-American patriotic sentiments among German Americans, few of whom by then had contacts with distant relatives in the old country.[25][94]
| Year | Number |
|---|---|
| 1980[95] | 49,224,146 |
| 1990[96] | 57,947,374 |
| 2000[97] | 42,885,162 |
| 2010[98] | 47,911,129 |
Contemporary period

Parking meter checker stands by his police vehicle which is imprinted with the German word for police (Polizei). It is part of the town's highlighting its German ethnic origins. New Ulm, Minnesota, July 1974.
In the aftermath of World War II, millions of ethnic Germans were forcibly expelled from their homes within the redrawn borders of Central and Eastern Europe, including the Soviet Union, Poland, Czechoslovakia, Romania, Hungary and Yugoslavia. Most resettled in Germany, but others came as refugees to the United States in the late 1940s, and established cultural centers in their new homes. Some Danube Swabians, for instance, ethnic Germans who had maintained language and customs after settlement along the Danube in Hungary, later Yugoslavia (now Serbia), immigrated to the U.S. after the war.
After 1970, anti-German sentiment aroused by World War II faded away.[99] Today, German Americans who immigrated after World War II share the same characteristics as any other Western European immigrant group in the U.S. They are mostly professionals and academics who have come for professional reasons. Since the collapse of the Soviet Union and reunification, Germany has become a preferred destination for immigrants rather than a source of migrating peoples.[100]

US Ancestries by County, Germany in light blue, as of 2000[update] census
In the 1990 U.S. Census, 58 million Americans claimed to be solely or partially of German descent.[101] According to the 2005 American Community Survey, 50 million Americans have German ancestry. German Americans represent 17% of the total U.S. population and 26% of the non-Hispanic white population.[102]
The Economist magazine in 2015 interviewed Petra Schürmann, the director of the German-American Heritage Museum in Washington for a major article on German-Americans. She notes that all over the United States celebrations such as German fests and Oktoberfests have been appearing.
Demographics

Distribution of German Americans according to the 2000 Census
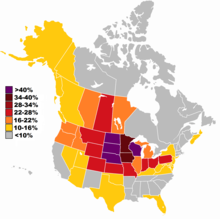
States with the highest proportions of German Americans tend to be those of the upper Midwest, including Iowa, Minnesota, Nebraska, Wisconsin, and the Dakotas; all at over one-third.[103]
Of the four major US regions, German was the most-reported ancestry in the Midwest, second in the West, and third in both the Northeast and the South. German was the top reported ancestry in 23 states, and it was one of the top five reported ancestries in every state except Maine and Rhode Island.[104]
At the 2000 census, this was the breakdown of German Americans by state, including the District of Columbia:
| State | German American Population | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 354,259 | 5.7 | |
| 121,832 | 14.2 | |
| 977,613 | 15.6 | |
| 358,764 | 9.3 | |
| 6,517,470 | 9.8 | |
| 1,090,983 | 22.0 | |
| 365,727 | 9.8 | |
| 133,757 | 14.3 | |
| 27,450 | 4.8 | |
| 2,270,456 | 11.8 | |
| 757,769 | 7.0 | |
| 83,967 | 5.8 | |
| 317,536 | 18.8 | |
| 2,668,955 | 19.6 | |
| 1,629,766 | 22.6 | |
| 1,169,638 | 35.7 | |
| 856,348 | 25.8 | |
| 638,231 | 12.7 | |
| 403,222 | 7.0 | |
| 109,401 | 8.6 | |
| 937,887 | 15.7 | |
| 402,176 | 5.9 | |
| 2,271,091 | 20.4 | |
| 1,949,346 | 38.4 | |
| 172,456 | 4.5 | |
| 1,576,813 | 23.5 | |
| 282,130 | 27.0 | |
| 738,894 | 42.7 | |
| 338,717 | 14.1 | |
| 124,430 | 8.6 | |
| 1,092,054 | 12.6 | |
| 219,278 | 9.8 | |
| 2,250,309 | 11.2 | |
| 1,020,432 | 9.5 | |
| 290,452 | 46.8 | |
| 3,231,788 | 26.5 | |
| 531,375 | 12.6 | |
| 811,780 | 20.5 | |
| 4,491,269 | 25.4 | |
| 60,634 | 5.7 | |
| 425,455 | 8.4 | |
| 334,068 | 44.5 | |
| 612,669 | 8.3 | |
| 2,542,996 | 9.9 | |
| 313,733 | 11.5 | |
| 67,706 | 9.1 | |
| 973,438 | 11.7 | |
| 1,319,975 | 18.8 | |
| 354,704 | 14.0 | |
| 2,455,980 | 43.8 | |
| 144,972 | 25.9 | |
| Total US | 42,902,103 | 15.2 |
[105][not in citation given]
German-American communities
Today, most German Americans have assimilated to the point that they no longer have readily identifiable ethnic communities, though there are still many metropolitan areas where German is the most reported ethnicity, such as Cincinnati, Northern Kentucky, Cleveland, Columbus, Indianapolis, Milwaukee, Minneapolis – Saint Paul, Pittsburgh, and St. Louis.[106][107]
Communities with high percentages of people of German ancestry
The 25 U.S. communities with the highest percentage of residents claiming German ancestry are:[108]
Monterey, Ohio 83.6%
Granville, Ohio 79.6%
St. Henry, Ohio 78.5%
Germantown Township, Illinois 77.6%
Jackson, Indiana 77.3%
Washington, Ohio 77.2%
St. Rose, Illinois 77.1%
Butler, Ohio 76.4%
Marion, Ohio 76.3%
Jennings, Ohio and Germantown, Illinois (village) 75.6%
Coldwater, Ohio 74.9%
Jackson, Ohio 74.6%
Union, Ohio 74.1%
Minster, Ohio and Kalida, Ohio 73.5%
Greensburg, Ohio 73.4%
Aviston, Illinois 72.5%
Teutopolis, Illinois (village) 72.4%
Teutopolis, Illinois (township) and Cottonwood, Minnesota 72.3%
Dallas, Michigan 71.7%
Gibson, Ohio 71.6%
Town of Marshfield, Fond du Lac County, Wisconsin 71.5%
Santa Fe, Illinois 70.8%
Recovery, Ohio 70.4%
Town of Brothertown, Wisconsin 69.9%
Town of Herman, Dodge County, Wisconsin 69.8%
Large communities[definition needed] with high percentages of people of German ancestry
U.S. communities with the highest percentage of residents claiming German ancestry are:[109][not in citation given]
Bismarck, North Dakota 56,1%
Dubuque, Iowa 43%
Fargo, North Dakota 31%
Madison, Wisconsin 29%
Green Bay, Wisconsin 29%
Levittown, Pennsylvania 22%
Erie, Pennsylvania 22%
Cincinnati, Ohio 19.8%
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 19.7%
Columbus, Ohio 19.4%
Beaverton, Oregon 17%
Communities with the most residents born in Germany
The 25 U.S. communities with the most residents born in Germany are:[110]
Lely Resort, Florida 6.8%
Pemberton Heights, New Jersey 5.0%
Kempner, Texas 4.8%
Cedar Glen Lakes, New Jersey 4.5%
Alamogordo, New Mexico 4.3%
Sunshine Acres, Florida and Leisureville, Florida 4.2%
Wakefield, Kansas 4.1%
Quantico, Virginia 4.0%
Crestwood Village, New Jersey 3.8%
Shandaken, New York 3.5%
Vine Grove, Kentucky 3.4%
Burnt Store Marina, Florida and Boles Acres, New Mexico 3.2%
Allenhurst, Georgia, Security-Widefield, Colorado, Grandview Plaza, Kansas, and Fairbanks Ranch, California 3.0%
Standing Pine, Mississippi 2.9%
Millers Falls, Massachusetts, Marco Island, Florida, Daytona Beach Shores, Florida, Radcliff, Kentucky, Beverly Hills, Florida, Davilla, Texas, Annandale, New Jersey, and Holiday Heights, New Jersey 2.8%
Fort Riley North, Kansas, Copperas Cove, Texas, and Cedar Glen West, New Jersey 2.7%
Pelican Bay, Florida, Masaryktown, Florida, Highland Beach, Florida, Milford, Kansas, and Langdon, New Hampshire 2.6%
Forest Home, New York, Southwest Bell, Texas, Vineyards, Florida, South Palm Beach, Florida, and Basye-Bryce Mountain, Virginia 2.5%
Sausalito, California, Bovina, New York, Fanwood, New Jersey, Fountain, Colorado, Rye Brook, New York and Desoto Lakes, Florida 2.4%
Ogden, Kansas, Blue Berry Hill, Texas, Lauderdale-by-the-Sea, Florida, Sherman, Connecticut, Leisuretowne, New Jersey, Killeen, Texas, White House Station, New Jersey, Junction City, Kansas, Ocean Ridge, Florida, Viola, New York, Waynesville, Missouri and Mill Neck, New York 2.3%
Level Plains, Alabama, Kingsbury, Nevada, Tega Cay, South Carolina, Margaretville, New York, White Sands, New Mexico, Stamford, New York, Point Lookout, New York, and Terra Mar, Florida 2.2%
Rifton, Manasota Key, Florida, Del Mar, California, Yuba Foothills, California, Daleville, Alabama. Tesuque, New Mexico, Plainsboro Center, New Jersey, Silver Ridge, New Jersey and Palm Beach, Florida 2.1%
Oriental, North Carolina, Holiday City-Berkeley, New Jersey, North Sea, New York, Ponce Inlet, Florida, Woodlawn-Dotsonville, Tennessee, West Hurley, New York, Littlerock, California, Felton, California, Laguna Woods, California, Leisure Village, New Jersey, Readsboro, Vermont, Nolanville, Texas, and Groveland-Big Oak Flat, California 2.0%
Rotonda, Florida, Grayson, California, Shokan, New York, The Meadows, Florida, Southeast Comanche, Oklahoma, Lincolndale, New York, Fort Polk South, Louisiana, and Townsend, Massachusetts 1.9%
Pine Ridge, Florida, Boca Pointe, Florida, Rodney Village, Delaware, Palenville, New York, and Topsfield, Massachusetts 1.8%
Counties by percentages of Germans
Emmons County, North Dakota 72.5%
McIntosh County, North Dakota 71.6%
Logan County, North Dakota 71.5%
Hutchinson County, South Dakota 67.6%
Faulk County, South Dakota 66.9%
Oliver County, North Dakota 66.6%
McPherson County, South Dakota 66.4%
Grant County, North Dakota 66.1%
Campbell County, South Dakota 66.0%
Cedar County, Nebraska 65.9%
Sheridan County, North Dakota 65.9%
Edmunds County, South Dakota 64.9%
Pierce County, Nebraska 64.7%
Brown County, Minnesota 63.8%
Morton County, North Dakota 63.7%
Hettinger County, North Dakota 63.0%
Kidder County, North Dakota 62.9%
Sibley County, Minnesota 62.7%
LaMoure County, North Dakota 61.9%
Washington County, Wisconsin 60.7%
Osage County, Missouri 60.5%
Calumet County, Wisconsin 60.5%
Wayne County, Nebraska 60.5%
Putnam County, Ohio 60.0%
Carroll County, Iowa 59.5%
Boone County, Nebraska 59.3%
Rush County, Kansas 59.0%
Slope County, North Dakota 58.4%
Sheridan County, Kansas 58.4%
Wells County, North Dakota 58.3%
Golden Valley County, North Dakota 58.1%
Walworth County, South Dakota 58.1%
Potter County, South Dakota 58.1%
Nemaha County, Kansas 58.1%
Stanton County, Nebraska 57.9%
Trego County, Kansas 57.8%
Burleigh County, North Dakota 57.8%
Taylor County, Wisconsin 57.7%
Lincoln County, Wisconsin 57.7%
Butler County, Iowa 57.6%
Ida County, Iowa 57.6%
Fond du Lac County, Wisconsin 57.3%
Cuming County, Nebraska 57.2%
McCook County, South Dakota 57.1%
Dodge County, Wisconsin 57.0%
Mercer County, Ohio 56.8%
Traverse County, Minnesota 56.5%
Stutsman County, North Dakota 56.3%
Dubois County, Indiana 56.3%
Sac County, Iowa 56.3%
Clayton County, Iowa 56.0%
Grundy County, Iowa 56.0%
Harlan County, Nebraska 55.9%
Hanson County, South Dakota 55.8%
Stark County, North Dakota 55.7%
Delaware County, Iowa 55.6%
Mercer County, North Dakota 55.5%
Wheeler County, Nebraska 55.5%
Webster County, Nebraska 55.4%
Manitowoc County, Wisconsin 55.4%
Renville County, Minnesota 55.3%
Chickasaw County, Iowa 55.2%
Brown County, South Dakota 55.2%
Grant County, South Dakota 54.9%
McLeod County, Minnesota 54.8%
Martin County, Minnesota 54.6%
Sully County, South Dakota 54.5%
Wabasha County, Minnesota 54.5%
Dubuque County, Iowa 54.5%
Jackson County, Minnesota 54.4%
Bremer County, Iowa 54.4%
Pierce County, North Dakota 54.3%
Dickey County, North Dakota 54.3%
Ellis County, Kansas 54.3%
Antelope County, Nebraska 54.3%
Thomas County, Nebraska 54.2%
Ness County, Kansas 53.9%
Waupaca County, Wisconsin 53.7%
Winnebago County, Wisconsin 53.6%
Jefferson County, Wisconsin 53.4%
Sheboygan County, Wisconsin 53.4%
Big Stone County, Minnesota 53.3%
Gregory County, South Dakota 53.3%
Stearns County, Minnesota 52.9%
Seward County, Nebraska 52.9%
Clinton County, Illinois 52.7%
Calhoun County, Illinois 52.4%
Spink County, South Dakota 52.4%
Liberty County, Montana 52.4%
Fillmore County, Nebraska 52.2%
Waseca County, Minnesota 52.1%
Blue Earth County, Minnesota 52.0%
Otoe County, Nebraska 52.0%
Thayer County, Nebraska 52.0%
Franklin County, Nebraska 52.0%
Miner County, South Dakota 51.9%
McHenry County, North Dakota 51.9%
Aurora County, South Dakota 51.9%
Auglaize County, Ohio 51.9%
Wood County, Wisconsin 51.9%
Washington County, Kansas 51.8%
Jones County, Iowa 51.8%
Hand County, South Dakota 51.8%
Holt County, Nebraska 51.6%
Knox County, Nebraska 51.5%
Washington County, Illinois 51.5%
Morrison County, Minnesota 51.5%
Faribault County, Minnesota 51.4%
Marshall County, Kansas 51.4%
Hamilton County, Nebraska 51.3%
Jackson County, Iowa 51.0%
Henry County, Ohio 51.0%
Howard County, Nebraska 51.0%
Hayes County, Nebraska 50.9%
Johnson County, Nebraska 50.9%
Iowa County, Iowa 50.9%
Frontier County, Nebraska 50.7%
York County, Nebraska 50.7%
Turner County, South Dakota 50.6%
Foster County, North Dakota 50.5%
Richland County, North Dakota 50.5%
Grant County, Wisconsin 50.5%
Fayette County, Iowa 50.5%
Benton County, Minnesota 50.4%
Murray County, Minnesota 50.3%
Marquette County, Wisconsin 50.3%
Buffalo County, Wisconsin 50.2%
Dunn County, North Dakota 50.1%
Langlade County, Wisconsin 50.1%
Clark County, Wisconsin 50.1%
Waukesha County, Wisconsin 50.1%
Wilkin County, Minnesota 50.0%
Sioux County, Nebraska 49.8%
Nuckolls County, Nebraska 49.8%
Platte County, Nebraska 49.7%
Sauk County, Wisconsin 49.7%
Monroe County, Illinois 49.7%
Hooker County, Nebraska 49.6%
Gove County, Kansas 49.5%
Franklin County, Iowa 49.5%
Ransom County, North Dakota 49.3%
Ozaukee County, Wisconsin 49.3%
Benton County, Iowa 49.3%
Price County, Wisconsin 49.2%
Elk County, Pennsylvania 49.2%
Russell County, Kansas 49.2%
Madison County, Nebraska 49.2%
Sanborn County, South Dakota 49.1%
Cottonwood County, Minnesota 49.1%
Allamakee County, Iowa 48.9%
Stevens County, Minnesota 48.9%
Adams County, Nebraska 48.9%
Merrick County, Nebraska 48.8%
Clay County, Nebraska 48.7%
Outagamie County, Wisconsin 48.6%
Cedar County, Iowa 48.6%
Mitchell County, Kansas 48.6%
Blaine County, Nebraska 48.6%
Meeker County, Minnesota 48.6%
Kossuth County, Iowa 48.6%
Bowman County, North Dakota 48.5%
Deuel County, South Dakota 48.5%
Floyd County, Iowa 48.3%
Cheyenne County, Kansas 48.3%
Stanley County, South Dakota 48.3%
Ste. Genevieve County, Missouri 48.2%
Barnes County, North Dakota 48.2%
Shelby County, Iowa 48.1%
Rock County, Minnesota 48.0%
Perkins County, Nebraska 47.9%
Calhoun County, Iowa 47.9%
Todd County, Minnesota 47.9%
Pawnee County, Nebraska 47.8%
Eddy County, North Dakota 47.8%
Oconto County, Wisconsin 47.8%
Codington County, South Dakota 47.6%
Davison County, South Dakota 47.6%
Cherokee County, Iowa 47.6%
Gosper County, Nebraska 47.6%
Boyd County, Nebraska 47.4%
Hardin County, Iowa 47.3%
Douglas County, Minnesota 47.2%
Greeley County, Nebraska 47.2%
Towner County, North Dakota 47.1%
Dixon County, Nebraska 47.1%
Red Willow County, Nebraska 47.1%
Cheyenne County, Nebraska 47.1%
McLean County, North Dakota 46.9%
Pocahontas County, Iowa 46.9%
Sargent County, North Dakota 46.8%
Jefferson County, Nebraska 46.8%
Lyon County, Iowa 46.7%
Plymouth County, Iowa 46.7%
Houston County, Minnesota 46.6%
Dodge County, Nebraska 46.5%
Hitchcock County, Nebraska 46.5%
Gage County, Nebraska 46.5%
Lincoln County, Kansas 46.5%
Thomas County, Kansas 46.4%
Mitchell County, Iowa 46.4%
Winona County, Minnesota 46.4%
Clinton County, Iowa 46.4%
Lake County, South Dakota 46.3%
Wabaunsee County, Kansas 46.3%
Crawford County, Iowa 46.3%
La Crosse County, Wisconsin 46.2%
Yankton County, South Dakota 46.1%
Chippewa County, Minnesota 46.1%
Hodgeman County, Kansas 45.8%
Billings County, North Dakota 45.7%
Jerauld County, South Dakota 45.7%
Buchanan County, Iowa 45.7%
Dearborn County, Indiana 45.7%
Seneca County, Ohio 45.7%
Perry County, Missouri 45.4%
Furnas County, Nebraska 45.4%
Kingsbury County, South Dakota 45.3%
Richardson County, Nebraska 45.3%
Gasconade County, Missouri 45.3%
Jo Daviess County, Illinois 45.3%
Butte County, South Dakota 45.2%
Hyde County, South Dakota 45.2%
Swift County, Minnesota 45.2%
Carver County, Minnesota 45.1%
Fallon County, Montana 45.1%
Clark County, South Dakota 45.1%
Buffalo County, Nebraska 45.1%
Dunn County, Wisconsin 45.1%
Chippewa County, Wisconsin 45.1%
O'Brien County, Iowa 45.0%
Snyder County, Pennsylvania 45.0%
Pierce County, Wisconsin 45.0%
St. Croix County, Wisconsin 44.9%
Phelps County, Nebraska 44.9%
Door County, Wisconsin 44.9%
Clay County, Iowa 44.8%
Box Butte County, Nebraska 44.7%
Nance County, Nebraska 44.7%
Clay County, South Dakota 44.7%
Huron County, Michigan 44.6%
Woodford County, Illinois 44.6%
Oneida County, Wisconsin 44.5%
Nemaha County, Nebraska 44.4%
Gray County, Kansas 44.4%
Palo Alto County, Iowa 44.4%
Dickinson County, Iowa 44.3%
Harding County, South Dakota 44.3%
Brule County, South Dakota 44.3%
McPherson County, Nebraska 44.2%
Wright County, Minnesota 44.2%
Adams County, North Dakota 44.0%
Wibaux County, Montana 44.0%
Deuel County, Nebraska 44.0%
Logan County, Kansas 43.9%
Cavalier County, North Dakota 43.9%
Perkins County, South Dakota 43.9%
Lincoln County, Minnesota 43.9%
Eau Claire County, Wisconsin 43.9%
Kewaunee County, Wisconsin 43.9%
Wyandot County, Ohio 43.9%
Lac qui Parle County, Minnesota 43.8%
Brookings County, South Dakota 43.7%
Iowa County, Wisconsin 43.5%
Fulton County, Ohio 43.5%
Wallace County, Kansas 43.4%
Monroe County, Wisconsin 43.4%
Winneshiek County, Iowa 43.4%
Barton County, Kansas 43.3%
Warren County, Missouri 43.3%
Perry County, Pennsylvania 43.3%
Cass County, North Dakota 43.2%
Otter Tail County, Minnesota 43.2%
Valley County, Nebraska 43.2%
Bon Homme County, South Dakota 43.1%
Lawrence County, South Dakota 43.0%
Smith County, Kansas 43.0%
Audubon County, Iowa 43.0%
Portage County, Wisconsin 43.0%
Cass County, Nebraska 42.9%
Cheyenne County, Colorado 42.9%
Stephenson County, Illinois 42.9%
Washington County, Nebraska 42.8%
Effingham County, Illinois 42.8%
Polk County, Nebraska 42.8%
Goodhue County, Minnesota 42.8%
Lafayette County, Wisconsin 42.8%
Van Wert County, Ohio 42.7%
Graham County, Kansas 42.6%
Saunders County, Nebraska 42.4%
Juneau County, Wisconsin 42.4%
Pope County, Minnesota 42.3%
Hancock County, Iowa 42.3%
Howard County, Iowa 42.3%
Barron County, Wisconsin 42.2%
Adams County, Illinois 42.1%
Adair County, Iowa 42.1%
Moody County, South Dakota 42.1%
Golden Valley County, Montana 42.0%
Beadle County, South Dakota 42.0%
Lancaster County, Nebraska 42.0%
Lancaster County, Nebraska 42.0%
Ottawa County, Ohio 41.7%
Ward County, North Dakota 41.6%
Rock County, Nebraska 41.6%
Rooks County, Kansas 41.6%
Somerset County, Pennsylvania 41.5%
Garfield County, Nebraska 41.3%
Marshall County, South Dakota 41.2%
Burt County, Nebraska 41.2%
Fillmore County, Minnesota 41.2%
Putnam County, Illinois 41.2%
Jersey County, Illinois 41.1%
Sherburne County, Minnesota 41.1%
Harrison County, Iowa 41.1%
Butler County, Pennsylvania 41.0%
Steele County, Minnesota 41.0%
Richland County, Wisconsin 41.0%
Day County, South Dakota 41.0%
Goshen County, Wyoming 41.0%
Chase County, Nebraska 40.9%
Phillips County, Kansas 40.9%
Greeley County, Kansas 40.9%
Williams County, Ohio 40.9%
Crawford County, Ohio 40.9%
Posey County, Indiana 40.9%
Gillespie County, Texas 40.8%
Washburn County, Wisconsin 40.8%
Morrill County, Nebraska 40.7%
Kingman County, Kansas 40.7%
Clarion County, Pennsylvania 40.7%
Wichita County, Kansas 40.6%
Dawson County, Montana 40.6%
Haakon County, South Dakota 40.6%
Pottawatomie County, Kansas 40.5%
Spencer County, Indiana 40.5%
Keya Paha County, Nebraska 40.4%
Logan County, Nebraska 40.4%
Minnehaha County, South Dakota 40.4%
Cass County, Iowa 40.3%
Culture
The Germans worked hard to maintain and cultivate their language, especially through newspapers and classes in elementary and high schools. German Americans in many cities, such as Milwaukee, brought their strong support of education, establishing German-language schools and teacher training seminaries (Töchter-Institut) to prepare students and teachers in German language training. By the late 19th century, the Germania Publishing Company was established in Milwaukee, a publisher of books, magazines, and newspapers in German.[111]
"Germania" was the common term for German American neighborhoods and their organizations.[112]Deutschtum was the term for transplanted German nationalism, both culturally and politically. Between 1875 and 1915, the German American population in the United States doubled, and many of its members insisted on maintaining their culture. German was used in local schools and churches, while numerous Vereine, associations dedicated to literature, humor, gymnastics, and singing, sprang up in German American communities. German Americans tended to support the German government's actions, and, even after the United States entered World War I, they often voted for antidraft and antiwar candidates. 'Deutschtum' in the United States disintegrated after 1918.[113]
Music
Beginning in 1741, the German-speaking Moravian Church Settlements of Bethlehem, Nazareth and Lititz, Pennsylvania, and Wachovia in North Carolina had highly developed musical cultures. Choral music, Brass and String Music and Congregational singing were highly cultivated. The Moravian Church produced many composers and musicians. Haydn's Creation had its American debut in Bethlehem in the early 19th century.
The spiritual beliefs of Johann Conrad Beissel (1690–1768) and the Ephrata Cloister—such as the asceticism and mysticism of this Lancaster County, Pennsylvania, group - are reflected in Beissel's treatises on music and hymns, which have been considered the beginning of America's musical heritage.[114]
In most major cities, Germans took the lead in creating a musical culture, with popular bands, singing societies, operas and symphonic orchestras.[115]
A small city, Wheeling, West Virginia could boast of 11 singing societies—Maennerchor, Harmonie, Liedertafel, Beethoven, Concordia, Liederkranz, Germania, Teutonia, Harmonie-Maennerchor, Arion, and Mozart. The first began in 1855; the last folded in 1961. An important aspect of Wheeling social life, these societies reflected various social classes and enjoyed great popularity until anti-German sentiments during World War I and changing social values dealt them a death blow.[116]
The Liederkranz, a German-American music society, played an important role in the integration of the German community into the life of Louisville, Kentucky. Started in 1848, the organization was strengthened by the arrival of German liberals after the failure of the revolution of that year. By the mid-1850s the Germans formed one-third of Louisville's population and faced nativist hostility organized in the Know-Nothing movement. Violent demonstrations forced the chorus to suppress publicity of its performances that included works by composer Richard Wagner. The Liederkranz suspended operations during the Civil War, but afterward grew rapidly, and was able to build a large auditorium by 1873. An audience of 8,000 that attended a performance in 1877 demonstrated that the Germans were an accepted part of Louisville life.[117]
The Imperial government in Berlin promoted German culture in the U.S., especially music. A steady influx of German-born conductors, including Arthur Nikisch and Karl Muck, spurred the reception of German music in the United States, while German musicians seized on Victorian Americans' growing concern with 'emotion'. The performance of pieces such as Beethoven's Ninth Symphony established German serious music as the superior language of feeling.[118]
Turners
Turner societies in the United States were first organized during the mid-19th century so German American immigrants could visit with one another and become involved in social and sports activities. The National Turnerbund, the head organization of the Turnvereine, started drilling members as in militia units in 1854. Nearly half of all Turners fought in the Civil War, mostly on the Union side, and a special group served as bodyguards for President Lincoln.
By the 1890s, Turners numbered nearly 65,000. At the turn of the 21st century, however, with the ethnic identity of European Americans in flux and Americanization a key element of immigrant life, there were few Turner groups, athletic events were limited, and non-Germans were members. A survey of surviving groups and members reflects these radical changes in the role of Turner societies and their marginalization in 21st-century American society, as younger German Americans tended not to belong, even in strongholds of German heritage in the Midwest.[119]
Media

German newspapers in North America, 1922
As for any immigrant population, the development of a foreign-language press helped immigrants more easily learn about their new home, maintain connections to their native land, and unite immigrant communities.[120] By the late 19th century, Germania published over 800 regular publications. The most prestigious daily newspapers, such as the New Yorker Staats-Zeitung, the Anzeiger des Westens in St. Louis, and the Illinois Staats-Zeitung in Chicago, promoted middle-class values and encouraged German ethnic loyalty among their readership.[121] The Germans were proud of their language, supported many German-language public and private schools, and conducted their church services in German.[122] They published at least two-thirds of all foreign language newspapers in the U.S. The papers were owned and operated in the U.S., with no control from Germany. As Wittke emphasizes, press. it was "essentially an American press published in a foreign tongue." The papers reported on major political and diplomatic events involving Germany, with pride but from the viewpoint of its American readers.[123][124] For example, during the latter half of the 19th century, at least 176 different German-language publications began operations in the city of Cincinnati alone. Many of these publications folded within a year, while a select few, such as the Cincinnati Freie Presse, lasted nearly a century.[125] Other cities experienced similar turnover among immigrant publications, especially from opinion press, which published little news and focused instead on editorial commentary.[126]
By the end of the 19th century, there were over 800 German-language publications in the United States.[127] German immigration was on the decline, however, and with subsequent generations integrating into English-speaking society, the German language press began to struggle.[128] The periodicals that managed to survive in immigrant communities faced an additional challenge with anti-German sentiment during World War I[129] and with the Espionage and Sedition Acts, which authorized censorship of foreign language newspapers.[130]Prohibition also had a destabilizing impact on the German immigrant communities upon which the German-language publications relied.[128] By 1920, there were only 278 German language publications remaining in the country.[131] After 1945, only a few publications have been started. One example is Hiwwe wie Driwwe (Kutztown, PA), the nation's only Pennsylvania German newspaper, which was established in 1997.
Athletics
Germans brought organized gymnastics to America, and were strong supporters of sports programs. They used sport both to promote ethnic identity and pride and to facilitate integration into American society. Beginning in the mid-19th century, the Turner movement offered exercise and sports programs, while also providing a social haven for the thousands of new German immigrants arriving in the United States each year. Another highly successful German sports organization was the Buffalo Germans basketball team, winners of 762 games (against only 85 losses) in the early years of the 20th century. These examples, and others, reflect the evolving place of sport in the assimilation and socialization of much of the German-American population.[132]
Religion

This 1850 census map shows the Lutheran population. Nearly all were German, since few Scandinavians had arrived yet.
German immigrants who arrived before the 19th century tended to have been members of the Evangelical Lutheran Churches in Germany, and created the Lutheran Synods of Pennsylvania, North Carolina and New York. The largest Lutheran denominations in the U.S. today—the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America, the Lutheran Church–Missouri Synod, and the Wisconsin Evangelical Lutheran Synod—are all descended from churches started by German immigrants among others. Calvinist Germans founded the Reformed Church in the United States (especially in New York and Pennsylvania), and the Evangelical Synod of North America (strongest in the Midwest), which is now part of the United Church of Christ. Many immigrants joined different churches from those that existed in Germany. Protestants often joined the Methodist church.[25] In the 1740s, Count Nicolas von Zinzendorf tried to unite all the German-speaking Christians—(Lutheran, Reformed, and Separatists)—into one "Church of God in the Spirit". The Moravian Church in America is one of the results of this effort, as are the many "Union" churches in rural Pennsylvania.
Before 1800, communities of Amish, Mennonites, Schwarzenau Brethren and Moravians had formed and are still in existence today. The Old Order Amish and a majority of the Old Order Mennonites still speak dialects of German, including Pennsylvania German, informally known as Pennsylvania Dutch. The Amish, who were originally from southern Germany and Switzerland, arrived in Pennsylvania during the early 18th century. Amish immigration to the United States reached its peak between the years 1727 and 1770. Religious freedom was perhaps the most pressing cause for Amish immigration to Pennsylvania, which became known as a haven for persecuted religious groups.[133]
The Hutterites are another example of a group of German Americans who continue a lifestyle similar to that of their ancestors. Like the Amish, they fled persecution for their religious beliefs, and came to the United States between 1874 and 1879. Today, Hutterites mostly reside in Montana, the Dakotas, and Minnesota, and the western provinces of Canada. Hutterites continue to speak Hutterite German. Most are able to understand Standard German in addition to their dialect.[134] The German speaking "Russian" Mennonites migrated during the same time as the Hutterites, but assimilated relatively quickly in the United States, whereas groups of "Russian" Mennonites in Canada resisted assimilation.[135]
Immigrants from Germany in the mid-to-late-19th century brought many different religions with them. The most numerous were Lutheran or Catholic, although the Lutherans were themselves split among different groups. The more conservative Lutherans comprised the Lutheran Church–Missouri Synod and the Wisconsin Evangelical Lutheran Synod. Other Lutherans formed various synods, most of which merged with Scandinavian-based synods in 1988, forming the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America.[136]Catholic Germans started immigrating in large numbers in the mid to latter 19th century, spurred in particular by the Kulturkampf.
Some 19th-century immigrants, especially the "Forty-Eighters", were secular, rejecting formal religion. About 250,000 German Jews had arrived by the 1870s, and they sponsored reform synagogues in many small cities across the country. About 2 million Central and Eastern European Jews arrived from the 1880s to 1924, bringing more traditional religious practices.[137]
Language
German speakers in the US | |
Year | Speakers |
|---|---|
| 1910a | 2,759,032 |
| 1920a | 2,267,128 |
| 1930a | 2,188,006 |
| 1940a | 1,589,040 |
| 1960a | 1,332,399 |
| 1970a | 1,201,535 |
| 1980[138] | 1,586,593 |
| 1990[139] | 1,547,987 |
| 2000[140] | 1,383,442 |
| 2007[141] | 1,104,354 |
^a Foreign-born population only[142] | |
After two or three generations, most German Americans adopted mainstream American customs — some of which they heavily influenced — and switched their language to English. As one scholar concludes, "The overwhelming evidence ... indicates that the German-American school was a bilingual one much (perhaps a whole generation or more) earlier than 1917, and that the majority of the pupils may have been English-dominant bilinguals from the early 1880s on."[143] By 1914, the older members attended German-language church services, while younger ones attended English services (in Lutheran, Evangelical and Catholic churches). In German parochial schools, the children spoke English among themselves, though some of their classes were in German. In 1917–18, after the US entry into World War I on the side of the British, nearly all German language instruction ended, as did most German-language church services.[84]
About 1.5 million Americans speak German at home, according to the 2000 census. From 1860–1917, German was widely spoken in German neighborhoods; see German in the United States. There is a false belief, called the Muhlenberg legend, that German was almost the official language of the U.S. There was never any such proposal. The U.S. has no official language, but use of German was strongly discouraged during World War I and fell out of daily use in many places.[144]
There were fierce battles in Wisconsin and Illinois around 1890 regarding proposals to stop the use of German as the primary language in public and parochial schools. The Bennett Law was a highly controversial state law passed in Wisconsin in 1889 that required the use of English to teach major subjects in all public and private elementary and high schools. It affected the state's many German-language private schools (and some Norwegian schools), and was bitterly resented by German American communities. The German Catholics and Lutherans each operated large networks of parochial schools in the state. Because the language used in the classroom was German, the law meant the teachers would have to be replaced with bilingual teachers, and in most cases shut down. The Germans formed a coalition between Catholics and Lutherans, under the leadership of the Democratic Party, and the language issue produced a landslide for the Democrats, as Republicans dropped the issue until World War I. By 1917, almost all schools taught in English, but courses in German were common in areas with large German populations. These courses were permanently dropped.[145]
Assimilation
"Assimilation" in this context means the steady loss of distinctive characteristics (especially language), as the Germans melted into a common American nationality.
German Americans are no longer a conspicuous ethnic group.[146] As Melvin G. Holli puts it, "Public expression of German ethnicity is nowhere proportionate to the number of German Americans in the nation's population. Almost nowhere are German Americans as a group as visible as many smaller groups. Two examples suffice to illustrate this point: when one surveys the popular television scene of the past decade, one hears Yiddish humor done by comedians; one sees Polish, Greek, and East European detective heroes; Italian-Americans in situation comedies; and blacks such as the Jeffersons and Huxtables. But one searches in vain for quintessentially German-American characters or melodramas patterned after German-American experiences. ... A second example of the virtual invisibility is that, though German Americans have been one of the largest ethnic groups in the Chicago area (numbering near one-half million between 1900 and 1910), no museum or archive exists to memorialize that fact. On the other hand, many smaller groups such as Lithuanians, Poles, Swedes, Jews, and others have museums, archives, and exhibit halls dedicated to their immigrant forefathers".[147]:93 - 94[a]
But this inconspicuousness was not always the case. By 1910 German Americans had created their own distinctive, vibrant, prosperous German-language communities, referred to collectively as "Germania". According to historian Walter Kamphoefner, a "number of big cities introduced German into their public school programs".[149]Indianapolis, Cincinnati, Cleveland and other cities "had what we now call two-way immersion programs: school taught half in German, half in English".[149] This was a tradition which continued "all the way down to World War I."[149] According to Kamphoefner, German "was in a similar position as the Spanish language is in the 20th and 21st century"; it "was by far the most widespread foreign language, and whoever was the largest group was at a definite advantage in getting its language into the public sphere."[149] Kamphoefner has come across evidence that as late as 1917, a German version of "The Star-Spangled Banner" was still being sung in public schools in Indianapolis.[149] Cynthia Moothart O'Bannon, writing about Fort Wayne, Indiana, states that before World War One, "German was the primary language in the homes, churches and parochial schools"[150] of German American settlers. She states that "Many street signs were in German. (Main Street, for instance, was Haupt Strasse.) A large portion of local industry and commercial enterprises had at its roots German tooling and emigres. (An entire German town was moved to Fort Wayne when Wayne Knitting Mills opened.) Mayors, judges, firefighters and other community leaders had strong German ties. Social and sporting clubs and Germania Park in St. Joseph Township provided outlets to engage in traditional German activities".[150] She goes on to state that "The cultural influences were so strong, in fact, that the Chicago Tribune in 1893 declared Fort Wayne a "most German town.""[150] Melvin G. Holli states that "No continental foreign-born group had been so widely and favorably received in the United States, or had won such high marks from its hosts as had the Germans before World War I. Some public opinion surveys conducted before the war showed German Americans were even more highly regarded than immigrants from the mother culture, England".[147]:106 Holli states that the Chicago Symphony Orchestra once "had so many German-American musicians that the conductor often addressed them in the German language"[147]:101, and he states that "No ethnic theater in Chicago glittered with such a classy repertory as did the German-American theater, or served to introduce so many European classical works to American audiences".[147]:102
The transition to the English language was abrupt, forced by federal, state and local governments, and by public opinion, when the U.S. was at war with Germany in 1917-18. After 1917 the German language was seldom heard in public; most newspapers and magazines closed; churches and parochial schools switched to English. Melvin G. Holli states that "In 1917 the Missouri Synod's Lutheran Church conference minutes appeared in English for the first time, and the synod's new constitution dropped its insistence on using the language of Luther only and instead suggested bilingualism. Dozens of Lutheran schools also dropped instruction in the German language. English-language services also intruded themselves into parishes where German had been the lingua franca. Whereas only 471 congregations nationwide held English services in 1910, the number preaching in the tongue of Albion in the synod skyrocketed to 2,492 by 1919. The German Evangelical Synod of Missouri, Ohio, and other states also anglicized its name by dropping German from the title".[147]:106 Writing about Fort Wayne, Indiana, Cynthia Moothart O'Bannon states that, in the First World War, "Local churches were forced to discontinue sermons in German, schools were pressured to stop teaching in German, and the local library director was ordered to purchase no more books written in German. The library shelves also were purged of English-language materials deemed sympathetic to or neutral on Germany. Anti-German sentiment forced the renaming of several local institutions. Teutonia Building, Loan & Savings became Home Loan & Savings, and The German-American bank became Lincoln National Bank & Trust Co."[150] She continues that "in perhaps the most obvious bend to prevailing trends, Berghoff Brewery changed its motto from "A very German brew" to "A very good brew," according to "Fort Wayne: A Most German Town," a documentary produced by local public television station WFWA, Channel 39".[150] Film critic Roger Ebert wrote how "I could hear the pain in my German-American father's voice as he recalled being yanked out of Lutheran school during World War I and forbidden by his immigrant parents ever to speak German again".[151]
Melvin G. Holli states, regarding Chicago, that "After the Great War it became clear that no ethnic group was so de-ethnicized in its public expression by a single historic event as German Americans. While Polish Americans, Lithuanian Americans, and other subject nationalities underwent a great consciousness raising, German ethnicity fell into a protracted and permanent slump. The war damaged public expression of German ethnic, linguistic, and cultural institutions almost beyond repair".[147]:106 He states that, after the war, German ethnicity "would never regain its prewar public acclaim, its larger-than-life public presence, with its symbols, rituals, and, above all, its large numbers of people who took pride in their Teutonic ancestry and enjoyed the role of Uncle Sam's favored adopted son".[147]:107 He states "A key indicator of the decline of "Deutschtum" in Chicago was the census: the number identifying themselves to the census-taker as German-born plummeted from 191,000 in 1910 to 112,000 in 1920. This drop far exceeds the natural mortality rate or the number who might be expected to move. Self-identifiers had found it prudent to claim some nationality other than German. To claim German nationality had become too painful an experience".[147]:106 Along similar lines, Terrence G. Wiley states that, in Nebraska, "around 14 percent of the population had identified itself as being of German-origin in 1910; however, only 4.4 percent made comparable assertions in 1920. In Wisconsin, the decline in percentage of those identifying themselves as Germans was even more obvious. The 1920 census reported only 6.6. percent of the population as being of German-origin, as opposed to nearly 29 percent ten years earlier ... These statistics led Burnell ... to conclude that: "No other North American ethnic group, past or present, has attempted so forcefully to officially conceal their ... ethnic origins. One must attribute this reaction to the wave of repression that swept the Continent and enveloped anyone with a German past"".[152]
The Catholic high schools were deliberately structured to commingle ethnic groups so as to promote ethnic (but not interreligious) intermarriage.[153] German-speaking taverns, beer gardens and saloons were all shut down by prohibition; those that reopened in 1933 spoke English.
While its impact appears to be less well-known and studied than the impact which World War One had on German Americans, World War Two was likewise difficult for them and likewise had the impact of forcing them to drop distinctive German characteristics and assimilate into the general US culture.[154][155] According to Melvin G. Holli, "By 1930, some German American leaders in Chicago felt, as Dr. Leslie Tischauser put it, "the damage done by the wartime experience had been largely repaired." The German language was being taught in the schools again; the German theater still survived; and German Day celebrations were drawing larger and larger crowds. Although the assimilation process had taken its toll of pre-1914 German immigrants, a smaller group of newer postwar arrivals had developed a vocal if not impolitic interest in the rebuilding process in Germany under National Socialism. As the 1930s moved on, Hitler's brutality and Nazi excesses made Germanism once again suspect. The rise of Nazism, as Luebke notes, "transformed German ethnicity in America into a source of social and psychological discomfort, if not distress. The overt expression of German-American opinion consequently declined, and in more recent years, virtually disappeared as a reliable index of political attitudes. . . .""[147]:108 Holli goes on to state that "The pain increased during the late 1930s and early 1940s, when Congressman Martin Dies held public hearings about the menace of Nazi subversives and spies among the German Americans. In 1940 the Democratic party's attack on anti-war elements as disloyal and pro-Nazi, and the advent of the war itself, made German ethnicity too heavy a burden to bear. As Professor Tischauser wrote, "The notoriety gained by those who supported the German government between 1933 and 1941 cast a pall over German-Americans everywhere. Leaders of the German-American community would have great difficulty rebuilding an ethnic consciousness. . . . Few German-Americans, however, could defend what Hitler . . . had done to millions of people in pursuit of the 'final solution,' and the wisest course for German-Americans was to forget any attachment to the German half of their heritage.""[147]:108 - 109 Jennifer Hansler has stated that "Fred Trump sought to pass himself off as Swedish amid anti-German sentiment sparked by World War II";[156]Donald reaffirmed this myth in The Art of the Deal.[156][157][158]
By the 1940s Germania had largely vanished outside some rural areas and the Germans were thoroughly assimilated.[159] According to Melvin G. Holli, by the end of World War Two, German Americans "were ethnics without any visible national or local leaders. Not even politicians would think of addressing them explicitly as an ethnic constituency as they would say, Polish Americans, Jewish Americans, or African Americans".[147]:109 Holli states that "Being on the wrong side in two wars had a devastating and long-term negative impact on the public celebration of German-American ethnicity".[147]:106
Historians have tried to explain what became of the German Americans and their descendants. Kazal (2004) looks at Germans in Philadelphia, focusing on four ethnic subcultures: middle-class Vereinsdeutsche, working-class socialists, Lutherans, and Catholics. Each group followed a somewhat distinctive path toward assimilation. Lutherans, and the better situated Vereinsdeutsche with whom they often overlapped, after World War I abandoned the last major German characteristics and redefined themselves as old stock or as "Nordic" Americans, stressing their colonial roots in Pennsylvania and distancing themselves from more recent immigrants. On the other hand, working-class and Catholic Germans, groups that heavily overlapped, lived and worked with Irish and other European ethnics; they also gave up German characteristics but came to identify themselves as white ethnics, distancing themselves above all from African American recent arrivals in nearby neighborhoods. Well before World War I, women in particular were becoming more and more involved in a mass consumer culture that lured them out of their German-language neighborhood shops and into English language downtown department stores. The 1920s and 1930s brought English language popular culture via movies and radio that drowned out the few surviving German language venues.[160]
Kazal points out that German Americans have not had an experience that is especially typical of immigrant groups. "Certainly, in a number of ways, the German-American experience was idiosyncratic. No other large immigrant group was subjected to such strong, sustained pressure to abandon its ethnic identity for an American one. None was so divided internally, a characteristic that made German Americans especially vulnerable to such pressure. Among the larger groups that immigrated in the country after 1830, none - despite regional variations - appears to have muted its ethnic identity to so great an extent."[160]:273 This quote from Kazal identifies both external pressures on German Americans and internal dividedness among them as reasons for their high level of assimilation.
Regarding the external pressures, Kazal writes: "The pressure imposed on German Americans to forsake their ethnic identity was extreme in both nature and duration. No other ethnic group saw its "adoptive fatherland" twice enter a world war against its country of origin. To this stigma, the Third Reich added the lasting one of the Holocaust. In her study of ethnic identity in the 1980s, sociologist Mary Waters noted that the "effect of the Nazi movement and World War II was still quite strong" in shaping "popular perceptions of the German-American character," enough so that some individuals of mixed background often would acknowledge only the non-German part of their ancestry".[160]:273[b] Kazal contrasts this experience with the experiences of the Japanese, Poles, Czechs, Lithuanians, Italians, east European Jews, and Irish. "Japanese Americans, of course, suffered far more during the Second World War",[160]:273 but until at least the 1950s, the pressure on Japanese Americans "ran toward exclusion from, rather than inclusion in, the nation".[160]:273 "The state and many ordinary European Americans refused to recognize Asians as potentially American. In contrast, they pressured Germans to accept precisely that American identity in place of a German one".[160]:273 Kazal goes on to state "The burden of "enemy" status made those pressures far greater for Germans than for other European ethnic groups. To some extent, American intervention in World War I actually helped fuel ethnic nationalism in the United States among Poles, Czechs, Lithuanians, Italians, and east European Jews, who felt their desires for existing or prospective homelands stood to gain from an Allied victory. Indeed, some historians have depicted the following decade as one when immigrants transcended local or regional homeland affiliations to craft or further consolidate national identities as Poles, Czechs, and Italians. Such groups escaped the fury of "100 percent Americanism" during the war, in part because of their obvious stake in the defeat of the Central Powers".[160]:273 - 274 As for Irish Americans, Kazal states that the lack of enthusiasm of many of them for helping England made them "vulnerable to the wartime "antihyphen" climate",[160]:274, but that "Irish nationalist activity intensified during and immediately after that war, as many Irish Americans became swept up in the events leading to the creation of the Irish Free State",[160]:274 and that "It made a difference for the long-term viability of Irish-American identity that the Irish homeland not only did not go to war with the United States but, in fact, emerged during the interwar years as a sovereign nation".[160]:274
Kazal then goes on to discuss the internal dividedness. He writes: "German-American identity fell victim not only to a peculiar set of events, but also to an extraordinarily high level of internal diversity. All ethnic groups have internal divides, whether of class, religion, gender, politics, or homeland region. What distinguished German America was that it incorporated not just some but all of these divisions. Irish Americans, for example, had lost their status as primarily a proletarian group by 1900, yet they were united by religion and politics. "Irish American" had come to mean Irish Catholic; the vast majority of Irish Americans subscribed to some form of Irish nationalism conflated with American patriotism; and Irish-American voters were overwhelmingly Democrats. The power of this synthesis, Kerby Miller argued, explains the survival of Irish-American identity despite the ebbing of organised Irish-American nationalism after the Free State's founding. For German Americans, however, religion and party politics were sources of division rather than of unity".[160]:274 Kazal goes on to state that "The subcultures of German America, meanwhile, had ample opportunity for contact, however testy, with non-German counterparts. The latter beckoned as destinations when the cost of being German-American rose too high".[160]:274 It is not just Kazal who has pointed out the internal dividedness of the German American community. David Peterson highlights the internal dividedness when he states that Kathleen Neils Conzen, "along with many others, concludes that German-Americans' heterogeneity, particularly in religion, hampered their ability to build socially and politically stable ethnic communities",[162]:27 and that Conzen "stresses that German Americans assimilated relatively rapidly and that their diversity played a key role in that assimilation".[162]:47 (Conzen is also drawn upon by Joy Kristina Adams, who cites Conzen when she (Adams) states that "The diversity and size of the German settlements made them susceptible to long-term Americanization by fostering factionalism, increasing contacts between Germans and non-Germans, and weakening unified leadership".)[163] The Encyclopedia of the Great Plains also stresses the internal dividedness, stating "One of the distinguishing characteristics of the German population in North America (especially in comparison to other immigrant groups) has been its relative degree of cultural diversity, reflected especially in the number of Christian denominations to which Germans belonged. In part this reflects patterns that had developed over centuries in Germany, whose population came to include nearly every variety of Christianity–from Catholics, Lutherans, and Reformed groups to more radical Anabaptist pietistic movements such as Amish, Mennonites, Schwenkfelders, and the Moravian church. It is not surprising, then, that nearly all of these denominations were represented among the German immigrant population in North America."[164] Robert Paul McCaffery points out that "Despite their numbers ... and unlike many immigrant groups, Germans never united as a powerful ethnic block. Religious disputes brought from the old country prevented them from uniting in the new. The two strongest denominations, Catholics and Lutherans, could not come together; and the Free Thinkers distrusted and shunned them both."[165]:4 "These divisions ran so deep that German-Americans could neither unite to fend off attacks engendered by World War I, nor elect German candidates for political office".[165]:4 McCaffery states that "Discussions of the disunity of the Germans are many",[165]:15 giving a work by Nathan Glazer and Daniel Patrick Moynihan and a work by Kathleen Neils Conzen as examples,[165]:15 and he states that Leslie V. Tischauser "maintains that neither World War I, political questions of importance to Germans, nor German candidates could unite the German-Americans of Chicago".[165]:16 Jason Todd Baker, meanwhile, writes that "Divided by imported regional prejudices, religious differences, political affiliations, and spread in pockets across the city, the Germans in nineteenth-century St. Louis comprised the city's largest immigrant ethnicity and possibly its least cohesive".[166]:95 He goes on to state that German Americans in St. Louis "could not be relied upon to do much of anything as a group. St. Louis served (and still does) as the seat of the Lutheran Church Missouri Synod, a conservative American Lutheran confession, and their local strength led to friction with Germans of other faiths. These Lutherans did not traffic much with the sizable German Catholic population of the city, who often shared their houses of worship and political stances with the Irish. The small rabbinical German Jewish community remained insular. The Freethinkers, atheists, socialists, et al., had little use for any of these groups. In addition, the Germans, while heavily concentrated in a few pockets of north and south St. Louis, were spread across the city proper and into the larger countryside".[166]:99 And according to the Max Kade Institute for German-American Studies, "The diversity of religious expression among German-speaking immigrants was paralleled by a high degree of heterogeneity stemming from differences in regional and linguistic origins. This situation differed from that of other nineteenth-century immigrant groups, notably the Irish, but also Italians and people of other European backgrounds. The resulting lack of a unified and clearly definable German-American community explains in part why only few Americans, including those of German descent, have any idea when Steuben Day or German-American Day falls, whereas the Irish St. Patrick’s Day is one of America’s most popular celebrations, and Columbus Day, named after the Italian explorer, is a federal holiday".[167][c]
Despite the remarkable level of assimilation reached by German Americans, it is worth noting that a distinct German American ethnicity survived well into the mid/late-20th century in some places. Writing about the town of Hustisford, Wisconsin, Jennifer Ludden discusses Mel Grulke, who was born in 1941, with German his first language at home; "Grulke's great-grandparents immigrated to the U.S. in the late 1880s, yet three generations later, his farmer parents still spoke German at home, attended German language church services and chatted in German with shopkeepers when they brought their farm eggs into town to sell".[149] Bethany Lutheran Church in Hustisford offered German-language services into the 1970s;[149] Zum Kripplein Christi, in the same county as Hustisford (Dodge County), "offered a Sunday service in German as recently as the 1990s";[167] St. Luke Lutheran Church, in Wishek, North Dakota, still held German-language services until as recently as about 1994.[170] Homer Rudolf, a man from North Dakota of German Russian descent, stated in 2004 that his maternal grandmother, who died in 1980 at the age of 90, "did not learn English".[171] As recently as 1990, one quarter of North Dakota's households included a German speaker.[172]
To this day, relatively unassimilated people of German-speaking heritage can be found in the United States among different Anabaptist groups - the Old Order Amish and most Old Order Mennonites speak Pennsylvania Dutch (or Bernese German or Alsatian by a minority of Amish) along with High German to various degrees (though they are generally fluent in English).[173] All Hutterites speak Hutterite German and many "Russian" Mennonites speak Plautdietsch, a German dialect coming originally from the area around Danzig. The three Amish dialects as well as Hutterite German are still learned by all children of the group, whereas Plautdietsch-speakers tend much more to assimilate. Another group of relatively unassimilated people of German-speaking heritage can be found in the Amana Colonies in Iowa; according to the website Statistical Atlas, all of the residents of East Amana speak German at home, and only 67.7% can speak English 'Very Well'.[174]
German-American influence
@media all and (max-width:720px){.mw-parser-output .tmulti>.thumbinner{width:100%!important;max-width:none!important}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsingle{float:none!important;max-width:none!important;width:100%!important;text-align:center}}

Freie Bibliothek und Lesehalle (Free Library and Reading Hall) and Deutsches Dispensary (German Dispensary), both by William Schickel (1883–1884) on Second Avenue at St Mark's Place in the East Village

Deutsch-Amerikanische Schützen Gesellschaft (German-American Shooting Society) by William C. Frohne (1885) on St. Mark's Place in the East Village

Germans have contributed to a vast number of areas in American culture and technology. Baron von Steuben, a former Prussian officer, led the reorganization of the U.S. Army during the War for Independence and helped make the victory against British troops possible. The Steinway & Sons piano manufacturing firm was founded by immigrant Henry E. Steinway in 1853. German settlers brought the Christmas tree custom and other German Christmas traditions to the United States. The Studebakers built large numbers of wagons used during the Western migration; Studebaker, like the Duesenberg brothers, later became an important early automobile manufacturer. Carl Schurz, a refugee from the unsuccessful first German democratic revolution of 1848 became an influential politician first in the Republican then in the Democratic party, and served as U.S. Secretary of the Interior.[175]
After World War II, Wernher von Braun, and most of the leading engineers from the former German V-2 rocket base at Peenemünde, were brought to the U.S. They contributed decisively to the development of U.S. military rockets, as well as rockets for the NASA space program and the initiation of the Apollo program to land on the Moon.[176] Similarly, fellow German aviation technologist Siegfried Knemeyer, the former top aviation technologist within Reichsmarschall Hermann Göring's Reich Air Ministry during World War II, was brought to the United States through a similar path to von Braun, and served as a civilian employee of the USAF for over twenty years.
The influence of German cuisine is seen in the cuisine of the United States throughout the country, especially regarding pastries, meats and sausages, and above all, beer. Frankfurters (or "wieners", originating from Frankfurt am Main and Vienna, respectively), hamburgers, bratwurst, sauerkraut, and strudel are common dishes. German bakers introduced the pretzel, which is popular across the United States. Germans introduced America to lager, the most-produced beer style in the United States, and have been the dominant ethnic group in the beer industry since 1850.[25][177]
The oldest extant brewery in the United States is D. G. Yuengling & Son of Pottsville, Pennsylvania (approximately 80 miles northwest of Philadelphia), founded in 1829 by an immigrant from Aldingen in what is today Baden-Württemberg; the brewery's flagship product remains a 19th-century German-style amber lager.[178] By the late 19th century, Milwaukee, with a large population of German origin, was once the home to four of the world's largest breweries owned by ethnic Germans (Schlitz, Blatz, Pabst, and Miller) and was the number one beer producing city in the world for many years. Almost half of all current beer sales in the United States can be attributed to German immigrants, Capt. A. Pabst, Eberhard Anheuser, and Adolphus Busch, who founded Anheuser-Busch in St. Louis in 1860.[179] Later German immigrants figured prominently in the rebirth of craft brews following Prohibition, culminating in the microbrew movement that swept the U.S. beginning in the late 1980s.
German and German-American celebrations, such as Oktoberfest, Rhenish Carnival, German-American Day and Von Steuben Day are held regularly throughout the country. One of the largest is the German-American Steuben Parade in New York City, held every third Saturday in September. There are also major annual events in Chicago's Lincoln Square neighborhood, a traditional a center of the city's German population, in Cincinnati, where its annual Oktoberfest Zinzinnati[180] is the largest Oktoberfest outside of Germany[181] and in Milwaukee, which celebrates its German heritage with an annual German Fest.[106] Many of the immigrants from Germany and other German-speaking countries came to Pennsylvania to what was then "Allegheny City" (now part of the North Side of the City of Pittsburgh). So many German speakers arrived, the area became known as "Deutschtown" and has been revived as such.[182][183] Within Deutschtown and since 1854, The Teutonia Männerchor has been promoting and furthering German cultural traditions.[184]
Skat, the most popular card game in Germany, is also played in areas of the United States with large German American populations, such as Wisconsin and Texas.[106]
Education
The following German international schools are in operation in the United States, serving German citizens, Americans, and other U.S. residents:
- German International School Boston
- German School New York
- German American School of Portland
- German International School of Silicon Valley
- German School Washington, D.C.
Notable people
German Americans have been influential in almost every field in American society, including science, architecture, business, sports, entertainment, theology, politics, and the military. Many of these individuals were of German Jewish descent or anti-Nazis who fled Nazi oppression.[185]
German American general/flag military officers Baron von Steuben, George Armstrong Custer, John Pershing, Dwight D. Eisenhower, Chester W. Nimitz, Carl Andrew Spaatz and Norman Schwarzkopf commanded the United States Army in the American Revolutionary War, American Civil War, Indian Wars, World War I, World War II, and the Persian Gulf War, respectively.
German Americans were famous American politicians, including Carl Schurz, Friedrich Hecker, Frederick Muhlenberg, Henry Morgenthau, Sr., Henry Morgenthau, Jr., Dwight D. Eisenhower, Herbert Hoover, Henry Kissinger, John Boehner and Donald Trump.
Many German Americans have played a prominent role in American industry and business, including Henry J. Heinz (H. J. Heinz Company), Frank Seiberling (Goodyear Tire and Rubber Company), Walt Disney (Disney), John D. Rockefeller (Standard Oil), William Boeing (The Boeing Company) and (United Airlines), Walter Chrysler (Chrysler Corporation), Frederick and August Duesenberg (Duesenberg Automobile Corporation), Studebaker brothers (Studebaker Automobile Corporation), George Westinghouse (Westinghouse Electric Corporation), Levi Strauss (Levi Strauss & Co.), Charles Guth (PepsiCo Inc.), Bill Gates (Microsoft Corporation), Jawed Karim (YouTube), Elon Musk (SolarCity), (SpaceX) and (Tesla Motors), James L. Kraft (Kraft Foods Inc.), Henry E. Steinway (Steinway & Sons), Charles Pfizer (Pfizer, Inc.), John Jacob Astor (Waldorf Astoria Hotels and Resorts), Conrad Hilton (Hilton Hotels & Resorts), Guggenheim family (Solomon R. Guggenheim Foundation), (Guggenheim Partners), Marcus Goldman and Samuel Sachs (The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc.), Lehman Brothers (Lehman Brothers Holdings Inc.), Carl Laemmle (Universal Studios), Marcus Loew (Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer Studios Inc.), Harry Cohn (Columbia Pictures Industries, Inc.), Herman Hollerith (International Business Machines Corporation (IBM)), Steve Jobs (Apple Inc.),[186]Michael Dell (Dell Inc.), Eric Schmidt (Google Inc.) and (Alphabet Inc.), Peter Thiel (PayPal Inc.), Adolph Simon Ochs and Arthur Ochs Sulzberger (The New York Times), Charles Bergstresser (The Wall Street Journal), Al Neuharth (USA Today), Eugene Meyer (The Washington Post) etc.
German Americans were pioneers and dominated beer brewing for much of American history, beginning with breweries founded in the 19th century by German immigrants August Schell (August Schell Brewing Company), Christian Moerlein (Christian Moerlein Brewing Co.), Eberhard Anheuser (Anheuser-Busch InBev), Adolphus Busch (Anheuser-Busch InBev), Adolph Coors (Molson Coors Brewing Company), Frederick Miller (Miller Brewing Company), Frederick Pabst (Pabst Brewing Company), Bernhard Stroh (Stroh Brewery Company) and Joseph Schlitz (Joseph Schlitz Brewing Company).[179]
Some, such as Brooklyn Bridge engineer John A. Roebling and architects Walter Gropius and Ludwig Mies van der Rohe, left behind visible landmarks.
Others, including Albert Einstein, J. Robert Oppenheimer, Wernher von Braun, John Peter Zenger, John Steinbeck, Kurt Vonnegut, Joseph Weizenbaum set intellectual landmarks while Neil Armstrong was the first human to land on the moon.
Still others, such as Bruce Willis, George Eyser, Babe Ruth, Lou Gehrig, Jack Nicklaus, Dale Earnhardt, Doris Mary Ann Kappelhoff (Doris Day), Grace Kelly, Clark Gable, Marlene Dietrich, Johnny Weissmuller, Ernst Lubitsch, Walter Damrosch, Henry John Deutschendorf (John Denver), John Kay, Heidi Klum, Meryl Streep, Marlon Brando, Kim Basinger, Sandra Bullock, David Hasselhoff, Leonardo DiCaprio, Kirsten Dunst, and Kevin George Knipfing (Kevin James) became prominent athletes, actors, film directors or artists.[187]
German-American presidents
There have been three presidents whose fathers were of German descent: Dwight D. Eisenhower (original family name Eisenhauer and maternal side is also German/Swiss), Herbert Hoover (original family name Huber), and Donald Trump (whose paternal grandparents were Bavarian immigrants). Presidents with maternal German ancestry include Richard Milhous Nixon (Nixon's maternal ancestors were Germans who anglicized Melhausen to Milhous)[188] and Barack Obama, whose maternal family's ancestry includes German immigrants from the South German town of Besigheim[189] and from Bischwiller in the Alsace region that is nowadays part of France; both families came to America around 1750.[190]
See also
- Distinguished German-American of the Year
- Hyphenated American
Notes
^ Similarly, W. Bruce Leslie has written that "German American invisibility in contemporary society and in history is an anomaly deserving attention. By standard statistical measurement, the Germans were the largest immigrant group. Yet historians have been far more interested in Italian, Irish, Polish, and Eastern European Jewish immigration and culture. Irish bars, Italian restaurants, and Jewish humor abound. German language is rarely studied in high schools or colleges and German restaurants are an endagered culinary species. The blending of so many millions into the American mainstream with barely a trace is one of the major untold stories in American history".[148]:294
^ In the book that Kazal appears to be quoting here, Waters states "Many people cited various political or social events as having an effect on their consciousness and degree of ethnic identity. I have already noted Laurie Jablonski's stronger identification with her Polish than with her German ancestry, a fact she attributed to the influence her surname had on how others reacted to her. When I asked about times when the relative influence of one or the other side might be stronger, however, she revealed that political events in Germany and Poland had a lot to do with how she chose to identify herself".[161]:83 Waters goes on to state that "The association of being German with being a Nazi is still strong for Laurie, forty years after World War II. A similar story to Laurie's is related in a description by Hinda Winawer-Steiner and Norbert Wetzel of a workshop for family therapists on ethnicity and family therapy. The therapists were supposed to talk about their ethnicity and how it might influence their work. A discussion of a German-American family revealed that two of the therapists who had identified themselves as Polish-American at the beginning of the workshop were, in fact, half German. It turned out that they were suppressing their German identity because of the negative connotations associated with being German. "When asked, one explained that she simply considered herself Polish. The other, after some reflection, said that in a group that was half Jewish, she had been reluctant to acknowledge her German heritage" (Winawer-Steiner and Wetzel 1982, 253)".[161]:84
^ A similar statement about the diversity of German Americans has been made by Andrew R. L. Cayton: "In the process of participating in the public culture of Ohio, some Germans struggled to keep connections with their birthplaces. A coherent community was difficult to maintain, however. Proud as they were of "Deutschthum," or the sum of Germanness, it became increasingly vague. Germans were too diverse in terms of religion and politics. "Wherever four Germans gathered," observed the Deutsche Pionier in 1879, "they will find four different ideas.""[168]:155 Another similar statement about the diversity of German Americans has been made by by Randall M. Miller. Writing about New Orleans, Miller states "During the nineteenth century, the Irish and Germans provided the largest numbers of mmigrants and gave the city its immigrant cast. The Irish and Germans differed, however, in their ethnic cohesiveness and interactions with the host culture(s)".[169]:129 Miller then states that "German immigrants ... lacked sufficient cultural and social unity to impose a single powerful German imprint on the city. They were widely dispersed throughout the Second and Third Municipalities, and in Carrollton and Lafayette, and they were fragmented by differences in religion, region of origin, and class. The proliferation of German clubs, associations, and institutions bespoke the Germans' numerical significance in the city, but it also attested to their divisions, for such organizations tended to cater to very specific groups rather than bind the various German strands together. To be sure, distinct concentrations of Germans existed in various parts of the city, wherein various German cultural values survived and influenced the culture of non-Germans in their midst, and German Gemütlichkeit was easily accommodated in the city's genial public culture. But, overall, Germans were too diverse and divided to dominate the city".[169]:129 Miller contrasts this situation with the situation of Irish Americans in New Orleans: "Irish immigrants had greater cohesion and wider influence than the Germans. In the great waves of late antebellum immigration, the vast majority of Irish immigrants entering New Orleans came from a few select counties in Ireland. They shared a common faith, poverty, and national identity. ... New Orleans was small enough so that dispersal did not diminish Irish power; in fact, Irish immigrants everywhere shared so many common cultural and class interests that dispersion served to broaden Irish influence on the city's culture".[169]:129
References
^ ab "People reporting ancestry". 2016 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates. US Census Bureau. Retrieved 8 July 2016..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em} Margin of error is +/-117,093.
^ ab "6 Maps That Show How Ethnic Groups Are Divided Across America". 2013-09-08. Retrieved 2016-03-10.
^ "The Germans in America". 2014-04-24. Retrieved 2015-06-12.
^ "Ancestry of the Population by State: 1980 - Table 3" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-11-11.
^ One Nation Under God: Religion in Contemporary American Society, p. 120.
^ Germans and foreigners with an immigrant background Archived May 4, 2009, at the Wayback Machine.. 156 is the estimate which counts all people claiming ethnic German ancestry in the U.S., Brazil, Argentina, and elsewhere.
^ "Ethnic Groups of Europe: An Encyclopedia" by Jeffrey Cole (2011), page 171.
^ "Report on German population". Histclo.com. 4 February 2010. Retrieved 2013-01-07.
^ Robert C. Nesbit (2004). Wisconsin: A History. University of Wisconsin Press. pp. 155–57.
^ Zane L. Miller, "Cincinnati Germans and the Invention of an Ethnic Group", Queen City Heritage: The Journal of the Cincinnati Historical Society 42 (Fall 1984): 13-22
^ Bayrd Still, Milwaukee, the History of a City (1948) pp. 260–63, 299
^ On Illinois see, Raymond Lohne, "Team of Friends: A New Lincoln Theory and Legacy", Journal of the Illinois State Historical Society Fall/Winter2008, Vol. 101 Issue 3/4, pp 285–314
^ "Schurz, Margarethe [Meyer] (Mrs. Carl Schurz) 1833 - 1876". 11 June 2011. Archived from the original on 11 June 2011.CS1 maint: BOT: original-url status unknown (link)
^ "The History of Christmas", Gareth Marples, retrieved December 2, 2006
^ Harvard Office of News and Public Affairs. "Professor Brought Christmas Tree to New England". News.harvard.edu. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2009-08-05. Retrieved 2010-03-18.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ Paul Kleppner, The Third Electoral System, 1853-1892: Parties, Voters, and Political Cultures (1979) pp 147-58 maps out the political beliefs of key subgroups.
^ Richardson, Belinda (2007). Christian Clergy Response to Intimate Partner Violence: Attitudes, Training, Or Religious Views?. ProQuest. p. 55.
^ Michael A. Lerner (2009). Dry Manhattan: Prohibition in New York City. Harvard UP. pp. 31–32.
^ Rose, Kenneth D. (1997). American Women and the Repeal of Prohibition. NYU Press. pp. 34–35.
^ Philip R. VanderMeer, "Religion, society, and politics: a classification of American religious groups." Social Science History (1981): 3-24 in JSTOR.
^ Grassl, Gary Carl (June–July 2008), "Tour of German-American Sites at James Fort, Historic Jamestown" (PDF), German-American Journal, 56 (3): 10,About 1% of the more than 700,000 objects catalogued by archaeologists at Jamestown so far bear words. More than 90% of these words are in German
[permanent dead link]; Where it All Began - Celebrating 400 Years of Germans in America, German Information Center, archived from the original on 2008-11-16, retrieved 2009-05-26; Celebration of the 400th Anniversary of the First Germans in America, April 18, Reuters, March 25, 2008, retrieved 2009-05-26
[permanent dead link];Jabs, Albert E. (June–July 2008), "400 Years of Germans In Jamestown" (PDF), German-American Journal, 56 (3): 1, 11
[permanent dead link]
^ ab First German-Americans, retrieved 2006-10-05
^ Gottlieb Mittleberger on Indentured Servitude Archived 2009-02-01 at the Wayback Machine., Faulkner University
^ abcdefg Conzen, Kathleen (1980), "Germans", in Stephan Thernstrom, Harvard Encyclopedia of American Ethnic Groups, Belknap Press, p. 407
^ ab Knittle, Walter Allen (1937), Early Eighteenth Century Palatine Emigration, Philadelphia: Dorrance
^ Philip Otterness, Becoming German: The 1709 Palatine Migration to New York (2004)
^ Axel Madsen, John Jacob Astor: America's First Multimillionaire (2001) excerpt
^ J. Hanno Deiler, retrieved 2007-11-30
^ Germanna History, retrieved 2009-08-02
^ ASIN 0806302925
^ ab Faust, Albert Bernhardt (1909), The German Element in the United States with Special Reference to Its Political, Moral, Social, and Educational Influence, Boston: Houghton-Mifflin
^ "Loyalists (Royalists, Tories) in South Carolina". Sciway3.net. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
^ Hostetler, John A. (1993). Amish Society. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 241.
^ De Grauwe, Luc, "Emerging mother-tongues awareness in Dutch and German". In Linn & McLelland (eds). Standardization: Studies from the Germanic Languages. p. 101, 104, passim.
^ Ralph Wood (ed.), The Pennsylvania Germans, Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press
^ Patrick Foster, Studebaker: The Complete History (2008)
^ American Council of Learned Societies Devoted to Humanistic Studies. Committee on Linguistic and National Stocks in the Population of the United States. (1969), Surnames in the United States Census of 1790: An Analysis of National Origins of the Population, Baltimore: Genealogical Publishing Co.
^ Edward J. Lowell, The Hessians and the Other German Auxiliaries (1965)
^ Don Heinrich Tolzmann, ed.; German Americans in the Revolution: Henry Melchoir Muhlenberg Richards' History (2013, based on 1908 history).
^ Theodore G. Tappert, "Henry Melchior Muhlenberg and the American Revolution." Church History 11.4 (1942): 284-301. online.
^ Henry Augustus Muhlenberg, The Life of Major-General Peter Muhlenberg: Of the Revolutionary Army (1849). online
^ Theodore G. Tappert, "Henry Melchior Muhlenberg and the American Revolution." Church History 11.4 (1942): 284-301. online
^ Birte Pfleger, "'Miserable Germans' and Fries's Rebellion: Language, Ethnicity, and Citizenship in the Early Republic," Early American Studies: an Interdisciplinary Journal 2004 2#2: 343-361
^ "Where and when was the first German Immigration?". prezi.com.
^ ab Wittke, Carl (1952), Refugees of Revolution, Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania press
^ Naomi Wiener Cohen, Encounter with Emancipation: The German Jews in the United States, 1830-1914 (Varda Books, 2001).
^ Zev Eleff, Who Rules the Synagogue?: Religious Authority and the Formation of American Judaism (Oxford Up, 2016).
^ Cornelia Wilhelm, The Independent Orders of B'nai B'rith and True Sisters: Pioneers of a New Jewish Identity, 1843-1914 (2011).
^ Census data from Bureau of the Census, Thirteenth census of the United States taken in the year 1910 (1913)
^ Stephenson, Orlando (1927). Ann Arbor the First Hundred Years (Hardcover). Ann Arbor: Ann Arbor Chamber of Commerce. p. 81. Retrieved 25 February 2016.
^ German Village Society, archived from the original on 9 May 2008, retrieved 19 November 2009
^ Trudy Knauss Paradis, et al. German Milwaukee (2006)
^ Richard Sisson, ed. The American Midwest (2007), p. 208; Gross (1996); Johnson (1951).
^ German Settlers in Louisiana and New Orleans, archived from the original on 2008-12-04, retrieved 2007-11-30
^
A 10K Walk Through German-Texas Heritage in Austin, Texas. The University of Texas at Austin. 3/6. Retrieved on November 15, 2009.
^ "GERMANS", Handbook of Texas Online
^ Elwyn B. Robinson, History of North Dakota (1966) pp. 285–87, 557; Gordon L. Iseminger, "Are We Germans, or Russians, or Americans? The McIntosh County German-Russians During World War I", North Dakota History 1992 59(2): 2–16.
^ "Inventory of the Hermann Raster Papers". The Newberry Library.
^ "Honor Herman Raster." Chicago Tribune 12 August 1891: 2. Print.
^ ab Christian B. Keller, "Flying Dutchmen and Drunken Irishmen: The Myths and Realities of Ethnic Civil War Soldiers", Journal of Military History, Vol/ 73, No. 1, January 2009, pp. 117–145; for primary sources see Walter D. Kamphoefner and Wolfgang Helbich, eds., Germans in the Civil War: The Letters They Wrote Home (2006).
^ The number of Confederate soldiers born in Germany is not known. Faust, page 523. Quoting from an 1869 ethnicity study by B. A. Gould; online.
^ Poole, John F., I'm Going to Fight Mit Sigel, New York: H. de Marsan
^ C. B. Schmidt, "Reminiscences of Foreign Immigration Work for Kansas," Kansas Historical Collections, 1905–1906 9 (1906): 485–97; J. Neale Carman, ed. and trans., "German Settlements Along the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway," Kansas Historical Quarterly 28 (Autumn 1962): 310–16; cited in Turk, "Germans in Kansas," (2005) p 57.
^ Sonya Salamon, Prairie Patrimony: Family, Farming, and Community in the Midwest (U. of North Carolina Press, 1992) pp. 53, 101
^ Salamon, Prairie Patrimony p 101
^ Matthew Lindaman, "Heimat in the heartland: The significance of an ethnic newspaper." Journal of American ethnic history (2004): 78-98. in JSTOR
^ Richard J. Jensen (1971). The Winning of the Midwest: Social and Political Conflict, 1888-1896. Richard Jensen. p. 292. ISBN 978-0-226-39825-9.
^ Kristen L. Anderson, "German Americans, African Americans, and the Republican Party in St. Louis, 1865-1872." Journal of American Ethnic History 28.1 (2008): 34-51. in JSTOR
^ Dorothee Schneider (1994). Trade Unions and Community: The German Working Class in New York City, 1870-1900. p. 36.
^ Hartmut Keil, and John B. Jentz, eds., German Workers in Industrial Chicago, 1850-1910: A Comparative Perspective (1983).
^ Goyens, Tom. "Beer and Revolution: Some Aspects of German Anarchist Culture in New York, 1880–1900". Social Anarchism journal. Retrieved 8 July 2012.
^ Jutta Spillmann, and Lothar Spillmann. "The rise and fall of Hugo Münsterberg." Journal of the History of the Behavioral Sciences 29#4 (1993): 322-338.
^ Rory T. Conley, "Arthur Preuss, German-Catholic Exile in America." US Catholic Historian (1994): 41-62. in JSTOR
^ Rory T. Conley, Arthur Preuss: Journalist and Voice of German and Conservative Catholics in America, 1871-1934 (1998).
^ Jutta Spillmann and Lothar Spillmann. "The rise and fall of Hugo Münsterberg." Journal of the History of the Behavioral Sciences 29.4 (1993) 322-338.
^ "Untitled Document". Earlham.edu. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
^ The War Department: Keeper of Our Nation's Enemy Aliens During World War I by Mitchel Yockelson. Presented to the Society for Military History Annual Meeting, April 1998.
^ "Get the Rope! Anti-German Violence in World War I-era Wisconsin", History Matters, George Mason University, retrieved 2008-08-01
^ Hickey, Donald R. (Summer 1969), "The Prager Affair: A Study in Wartime Hysteria", Journal of the Illinois State Historical Society: 126–127
^ Brinkley, Alan, "Civil Liberties in Times of Crisis" (PDF), Bulletin of the American Academy of Arts & Sciences (Winter 2006): 26–29, retrieved November 19, 2009
^ "Cincinnati's Century of Change - May". Enquirer.com. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
^ Meyer v. Nebraska, 262 U.S. 390 (1923).
^ ab Hawgood, John (1970), The Tragedy of German-America, New York: Arno Press
^ A German-American Chronology, adapted from: The German Americans: An Ethnic Experience by LaVern J. Rippley and Eberhard Reichmann.
^ German American Bund, United States Holocaust Memorial Museum, Washington, D.C.
^ Statement of Senator Russell D. Feingold Archived August 29, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
^ "Text of H.R. 3198 (109th): Wartime Treatment Study Act (Introduced version) - GovTrack.us". GovTrack.us. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
^ "German American Internee Coalition". Archived from the original on 5 March 2015. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
^ "German Internment Camps in World War II (thing)". Everything2.com. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
^ "BBC NEWS - Americas - The lost voices of Crystal City". News.bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
^ "German Internees Time Line". Traces.org. Archived from the original on 21 March 2015. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
^ "Wartime Policies". Traces.org. Archived from the original on 25 March 2015. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
^ Tischauser, (1990); Tolzmann, (1995)
^ Rank of States for Selected Ancestry Groups with 100,00 or more persons: 1980 (PDF), United States Census Bureau, retrieved 30 November 2012
^ 1990 Census of Population Detailed Ancestry Groups for States (PDF), United States Census Bureau, 18 September 1992, retrieved 30 November 2012
^ Ancestry: 2000, United States Census Bureau, retrieved 30 November 2012
^ Total ancestry categories tallied for people with one or more ancestry categories reported 2010 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates, United States Census Bureau, retrieved 30 November 2012
^ "German Missions in the United States - Home". Germany.info. Archived from the original on 4 September 2008. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
^ "Teacher Resources - Library of Congress". Rs6.loc.gov. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
^ "Chronology : The Germans in America (European Reading Room, Library of Congress)". Loc.gov. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
^ United States Census Bureau, US demographic census, archived from the original on 2011-11-24, retrieved 2007-04-15
^ "Wayback Machine" (PDF). 20 September 2004. Archived from the original on 20 September 2004.CS1 maint: BOT: original-url status unknown (link)
^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2004-12-04. Retrieved 2008-06-01.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ Bureau, U.S. Census. "American FactFinder - Results". factfinder.census.gov. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
^ abc Zeitlin, Richard (2000), Germans in Wisconsin, Madison: State Historical Society of Wisconsin
^ U.S. Census Bureau. American FactFinder
^ Ancestry Map of German Communities, Epodunk.com, retrieved 2008-08-12
^ "City & County Information, Town & Community Information". ePodunk. Retrieved 2014-08-10.
^ "Top 101 cities with the most residents born in Germany (population 500+)". city-data.com. Advameg, Inc. 2012. Retrieved May 11, 2012.
^ ""Deutsch-Athen Revisited…"". Uwm.edu. Archived from the original on 7 December 2008. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
^ Noel Iverson, Germania, U.S.A. (1966).
^ Andrew Yox, "The German-American Community as a Nationality, 1880-1940", Yearbook of German-American Studies 2001 36: 181-193; Kazal (2004)
^ Lucile E. Hackett, "Johann Conrad Beissel: Early German-American Mystic and Musician", Studies in Puritan American Spirituality 1995 5: 95–121
^ Philip V. Bohlman and Otto Holzapfel, eds. Land without Nightingales: Music in the Making of German-America. (U. of Wisconsin Press, 2002)
^ Edward C. Wolf, "Wheeling's German Singing Societies", West Virginia History 1980–1981 42(1–2): 1–56
^ Erna Ottl Gwinn, "The Liederkranz in Louisville, 1848–1877", Filson Club History Quarterly 1975 49(3): 276–290,
^ Jessica C. E. Gienow-Hecht, "Trumpeting down the Walls of Jericho: The Politics of Art, Music and Emotion in German-American Relations, 1870–1920", Journal of Social History 2003 36(3): 585–613,
^ Annette R. Hofmann, "Transformation and Americanization: The American Turners and Their New Identity", International Journal of the History of Sport 2002 19(1): 91-118
^ Carl Wittke, The German-Language Press in America (1957)
^ Peter Conolly-Smith, "Transforming an Ethnic Readership Through "Word and Image": William Randolph Hearst's Deutsches Journal and New York's German-Language Press, 1895–1918", Volume 19, Number 1, 2009 in Project MUSE; Peter Conolly-Smith, Translating America: An Ethnic Press Visualizes Popular American Culture, 1895–1918 (2004); Carl Wittke, The German-Language Press in America (1957).
^ Richard Jensen, The Winning of the Midwest: Social and Political Conflict, 1888–1896 (1971) ch. 5
^ Wittke, The German-Language Press in America. p. 6
^ Shore, "Introduction." in The German-American Radical Press.
^ Arndt, The German Language Press of the Americas
^ Wittke, The German-Language Press in America
^ La Verne Rippley, The German Americans, Lanham, Maryland: University Press of America, 1984, p. 164.
^ ab Dobbert, G.A. "German-Americans between New and Old Fatherland, 1870-1914." American Quarterly. 19.4 (1967): 663-680.
^ Shell, Marc. "Hyphens: Between Deitsch and American." Multilingual America. Ed.. Werner Sollors. New York City: New York University Press, 1998.
^ Thomas Adam (Ed.), Germany and the Americas: Culture, Politics, and History, Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO, 2005, p. 319.
^ Rippley, p. 166.
^ Annette R. Hofmann, "Between Ethnic Separation and Assimilation: German Immigrants and Their Athletic Endeavours in Their New American Home Country", International Journal of the History of Sport 2008 25(8): 993-1009,
^ The Amish, archived from the original on 2006-11-07, retrieved 2006-10-06
^ Allard, William Albert (2006), Hutterite Sojourn, Washington, D.C.: National Geographic Society
^ Donald B. Kraybill and Nelson Hostetter: Anabaptist World USA, 2001, Scottdale, PA, and Waterloo, ON, page 115.
^ Almen, Lowell (1997), One Great Cloud of Witnesses, Minneapolis: Augsburg Fortress
^ Edward S. Shapiro, "Jews", in Elliott Barkan, ed. A Nation of Peoples (1999) 330–36.
^ "Appendix Table 2. Languages Spoken at Home: 1980, 1990, 2000, and 2007". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved August 6, 2012.
^ "Detailed Language Spoken at Home and Ability to Speak English for Persons 5 Years and Over --50 Languages with Greatest Number of Speakers: United States 1990". United States Census Bureau. 1990. Retrieved July 22, 2012.
^ "Language Spoken at Home: 2000". United States Bureau of the Census. Retrieved August 8, 2012.
^ "Language Use in the United States:2007" (PDF). United States Bureau of the Census. Retrieved June 24, 2014.
^ "Mother Tongue of the Foreign-Born Population: 1910 to 1940, 1960, and 1970". United States Census Bureau. March 9, 1999. Retrieved August 6, 2012.
^ "Language loyalty in the German-American Church: the Case of an Over-confident Minority". Ccat.sas.upenn.edu. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
^ see U.S. State Department, "German Language in the U.S"
^ Robert J. Ulrich, The Bennett Law of Eighteen Eighty-Nine: Education and Politics in Wisconsin (1981).
^ https://www.economist.com/united-states/2015/02/05/the-silent-minority
^ abcdefghijkl Holli, Melvin G. (1995). "German American Ethnic and Cultural Identity from 1890 Onward". In Holli, Melvin G.; Jones, Peter d'A. Ethnic Chicago: A Multicultural Portrait. William B. Eerdmans Publishing Company.
^ Leslie, W. Bruce (1997). "German Americans". In Parish, Peter J. Reader's Guide to American History. Fitzroy Dearborn Publishers.
^ abcdefg Ludden, Jennifer (April 1, 2009). "German". National Public Radio. Retrieved December 23, 2012.
^ abcde Moothart O'Bannon, Cynthia. "WWI altered the German accent of Allen County". fortwayne.com.
^ Ebert, Roger (April 12, 2002). ""I could hear the pain in my German-American father's voice"". Chicago Sun-Times. Retrieved December 23, 2012.
^ Wiley, Terrence G. (1998). "What Happens After English is Declared the Official Language of the United States?". In Kibbee, Douglas A. Language Legislation and Linguistic Rights. John Benjamins Publishing Company.
^ Edward R. Kantowicz, Corporation Sole: Cardinal Mundelein and Chicago Catholicism (1983)
^ https://loyolanotredamelib.org/php/report05/articles/pdfs/report44Holian81-98.pdf
^ https://ttu-ir.tdl.org/ttu-ir/bitstream/handle/2346/12405/31295019381176.pdf?sequence
^ ab Hansler, Jennifer (28 November 2017). "Trump's family denied German heritage for years". CNN.
^ Carlström, Vilhelm (28 November 2017). "Donald Trump claimed he was of Swedish ancestry - but it's a lie". Business Insider.
^ Horowitz, Jason (21 August 2016). "For Donald Trump's Family, an Immigrant's Tale With 2 Beginnings". New York Times.
^ Russell A. Kazal, "Revisiting Assimilation: The Rise, Fall, and Reappraisal of a Concept." American Historical Review 100 (1995): 437-71. in JSTOR
^ abcdefghijkl Russell A. Kazal, Becoming Old Stock: The Paradox of German-American Identity (2004).
^ ab Waters, Mary C. (1990). Ethnic Options: Choosing Identities in America. University of California Press.
^ ab "From Bone Depth": German-American Communities in Rural Minnesota before the Great War on JSTOR
^ Going Deutsch: Heritage Tourism and Identity in German Texas, p. 45
^ Germans
^ abcde Islands of Deutschtum: German Americans in Manchester, New Hampshire and Lawrence, Massachusetts, 1870-1942
^ ab Baker, Jason Todd (2008). "Pulitzer, Preetorius, and the German American Identity Project of the Westliche Post in St. Louis". In Schulze, Mathias; Skidmore, James M.; John, David G.; Liebscher, Grit; Siebel-Achenbach, Sebastian. German Diasporic Experiences: Identity, Migration and Loss. Wilfrid Laurier University Press.
^ ab How German Is American? Building Communities
^ Cayton, Andrew R. L. (2002). Ohio: The History of a People. The Ohio State University Press.
^ abc Miller, Randall M. (1988). "Immigration through New Orleans: A Comment". In Stolarik, M. Mark. Forgotten Doors: The Other Ports of Entry to the United States. Associated University Presses.
^ https://library.ndsu.edu/grhc/articles/newspapers/news/gutentag.html
^ "Germans from Russia Heritage Collection". Library.ndsu.edu. September 18, 2004. Retrieved April 18, 2013.
^ Brooke, James (2 March 1996). "North Dakota, With German Roots, Adopts Spanish as Second Language". NYTimes.com. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
^ Skutsch, Carl (2005). Encyclopedia of the World's Minorities. Routledge. p. 101.
^ Languages in East Amana, Iowa (Unincorporated Place) - Statistical Atlas
^ SCHURZ, Carl, (1829 - 1906), United States Congress, retrieved 19 November 2009
^ "Outstanding German Scientists Being Brought to U.S.", War Department press release, V2Rocket.com, 1945-10-01
^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2013-07-30. Retrieved 2013-07-30.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ BeerHistory.com. "Yuengling of Pottsville: America's Oldest Brewery". Retrieved December 8, 2006.
^ ab Amy Mittelman, Brewing Battles: A History of American Beer (2007)
^ "Oktoberfest Zinzinnati". Oktoberfest-zinzinnati.com. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
^ "About Oktoberfest - Oktoberfest Zinzinnati". Oktoberfestzinzinnati.com. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2012-01-17. Retrieved 2012-01-14.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link) "'About the Teutonia Männerchor' -- THE EARLY 1800s – Around the early and the mid-1800s and through the end of the 20th century, there was a mass immigration from all across Europe to the United States. Many of the immigrants from Germany and other German-speaking countries came to Pennsylvania to what was then "Allegheny City" (now the Northside) – just across the river from the City of Pittsburgh. So many German speakers arrived, the area became known as "Deutschtown"."
^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2011-11-26. Retrieved 2011-11-03.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2012-03-06. Retrieved 2012-05-17.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link) "MÄNNERCHOR, DAMENCHOR, GEMISCHTER CHOR, ALPEN SCHUHPLATTLER UND TRACHTENVEREIN, PITTSBURGH DISTRICT KINDERCHOR, SCHÜTZENKAMERADEN, TEUTONIA HAUSKAPELLE, LUSTIGEN MUSIKANTEN, and 66 CARD LEAGUE"
^ Sass, Ed. "GermAmChron". www.eds-resources.com.
^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2013-10-15. Retrieved 2013-05-02.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ "Rating the Top Baseball Players of All Time". Baseballguru.com. Retrieved 2007-11-28.
^ Stephen E. Ambose Nixon chapter 1 (1987)
^ "Researchers: Obama has German roots", USA Today, June 4, 2009
^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2008-12-03. Retrieved 2008-10-09.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
Further reading
.mw-parser-output .refbegin{font-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul{list-style-type:none;margin-left:0}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>dd{margin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100{font-size:100%}
- Adams, Willi Paul. The German-Americans: An Ethnic Experience (1993).
- Bank, Michaela. Women of Two Countries: German-American Women, Women's Rights and Nativism, 1848–1890 (Berghahn, 2012).
- Baron, Frank, "Abraham Lincoln and the German Immigrants: Turners and Forty-Eighters," Yearbook of German-American Studies, 4 (Supplemental Issue 2012), 1–254.
- Barry, Colman J. The Catholic Church and German Americans. (1953).
- Bronner, Simon J. and Joshua R. Brown, eds. Pennsylvania Germans: An Interpretive Encyclopedia (: Johns Hopkins UP, 2017), xviii, 554 pp.
- Brancaforte, Charlotte L., ed. The German Forty-Eighters in the United States. (1989).
- Bungert, Heike, Cora Lee Kluge, & Robert C. Ostergren (eds.). Wisconsin German Land and Life. Madison, Wis.: Max Kade Institute, University of Wisconsin-Madison, 2006.
- Coburn, Carol K. Life at Four Corners: Religion, Gender, and Education in a German-Lutheran Community, 1868–1945. (1992).
- Conzen, Kathleen Neils. "Germans" in Stephan Thernstrom (ed.). Harvard Encyclopedia of American Ethnic Groups. (1980). pp. 405–425.
- Conzen, Kathleen Neils. Germans in Minnesota. (2003).
- Conzen, Kathleen Neils. Immigrant Milwaukee, 1836–1860: Accommodation and Community in a Frontier City. (1976).
- DeWitt, Petra. Degrees of Allegiance: Harassment and Loyalty in Missouri's German-American Community during World War I (Ohio University Press, 2012).
- Dobbert, Guido A. "German-Americans between New and Old Fatherland, 1870–1914". American Quarterly 19 (1967): 663–680.
- Efford, Alison Clark. German Immigrants: Race and Citizenship in the Civil War Era. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2013.
- Ellis, M. and P. Panayi. "German Minorities in World War I: A Comparative Study of Britain and the USA", Ethnic and Racial Studies 17 (April 1994): 238–259.
- Emmerich, Alexander. John Jacob Astor and the First Great American Fortune. (2013); Astor (1763-1848) came to the US in 1783
- Ernst, Robert. Immigrant Life in New York City, 1825-1863 (1949), detailed coverage of Germans and Irish.
- Faust, Albert Bernhardt. The German Element in the United States with Special Reference to Its Political, Moral, Social, and Educational Influence. 2 vol (1909). vol. 1, vol. 2
- Fogleman, Aaron. Hopeful Journeys: German Immigration, Settlement, and Political Culture in Colonial America, 1717–1775 (University of Pennsylvania Press, 1996) online
- "German-Americans: The silent minority". The Economist February 7, 2015, With a statistical map by counties
German Historical Institute. Immigrant Entrepreneurship: German-American Business Biographies, 1720 to the Present. (2010, updated continually)- Gross, Stephen John. "Handing down the farm: Values, strategies, and outcomes in inheritance practices among rural German Americans", Journal of Family History, (1996) 21: 2, 192–217.
- Grubb, Farley. German Immigration and Servitude in America, 1709–1920 (Routledge Explorations in Economic History) (2011).
- Guenther, Karen. "A Question of Loyalty: German Churches in Reading During the First World War," Pennsylvania History"" (2017) 84#3:325-53 online
- Hawgood, John. The Tragedy of German-America. (1940).
- Iverson, Noel. Germania, U.S.A.: Social Change in New Ulm, Minnesota. (1966). emphasizes Turners.
- Jensen, Richard. The Winning of the Midwest, Social and Political Conflict 1888–1896. (1971). Voting behavior of Germans, prohibition, language, and school issues.
- Johnson, Hildegard B. "The Location of German Immigrants in the Middle West". Annals of the Association of American Geographers 41 (1951): 1–41.
- Jordon, Terry G. German Seed in Texas Soil: Immigrant Farmers in Nineteenth-century Texas. (1966).
- Kamphoefner, Walter D. and Wolfgang Helbich, eds. German-American Immigration and Ethnicity in Comparative Perspective. Madison, Wisconsin: Max Kade Institute, University of Wisconsin–Madison (2004).
- Kamphoefner, Walter D., "Uprooted or Transplanted? Reflections on Patterns of German Immigration to Missouri," Missouri Historical Review, 103 (January 2009), 71-89.
- Kamphoefner, Walter D. "Immigrant Epistolary and Epistemology: On the Motivators and Mentality of Nineteenth-Century German Immigrants." Journal of American Ethnic History (2009): 34-54. in JSTOR, on deep-reading their letters
- Kazal, Russell A. Becoming Old Stock: The Paradox of German-American Identity. (2004).
- Keller, Christian B. "Flying Dutchmen and Drunken Irishmen: The Myths and Realities of Ethnic Civil War Soldiers," Journal of Military History, 73 (January 2009), 117–145.
- Keller, Phyllis. States of Belonging: German-American Intellectuals and the First World War. Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 1979.
- Knarr, Mary L. "Faith, frauen, and the formation of an ethnic identity: German Lutheran women in south and central Texas, 1831–1890". (Ph.D. dissertation, Texas Christian U. 2009). online
- Kulas, S. John. Der Wanderer of St. Paul: The First Decade, 1867-1877: a Mirror of the German-Catholic Immigrant Experience in Minnesota (Peter Lang, 1996).
- Levine, Bruce. The Spirit of 1848: German Immigrants, Labor Conflict, and the Coming of the Civil War. Urbana: University of Illinois Press, 1992.
- Lohne, Raymond. "Team of Friends: A New Lincoln Theory and Legacy", Journal of the Illinois State Historical Society Fall/Winter 2008, vol. 101 no. 3/4, pp. 285–314. German American politics and Abraham Lincoln
- Luebke, Frederick C. Bonds of Loyalty: German Americans During World War I. (1974).
- Luebke, Frederick C., ed. Ethnic Voters and the Election of Lincoln. (1971).
- Luebke, Frederick C. Germans in the New World. (1990).
- Luebke, Frederick. Immigrants and Politics: The Germans of Nebraska, 1880–1900. (1969).
- Nadel, Stanley. Little Germany: Ethnicity, Religion, and Class in New York City, 1845-80 (1990).
- O'Connor, Richard. German-Americans: an Informal History. (1968), popular history
- Otterness, Philip. Becoming German: The 1709 Palatine Migration to New York (2004) 235 pp.
- Pickle, Linda. Contented among Strangers: Rural German-Speaking Women and Their Families in the Nineteenth-Century Midwest (1996).
- Pochmann, Henry A. and Arthur R. Schultz; German Culture in America, 1600–1900: Philosophical and Literary Influences. (1957).
- Ritter, Luke, "Sunday Regulation and the Formation of German American Identity in St. Louis, 1840–1860," Missouri Historical Review, (2012), vol. 107, no. 1, pp. 23–40.
- Roeber, A. G. Palatines, Liberty, and Property: German Lutherans in Colonial British America. (1998).
- Salamon, Sonya. Prairie Patrimony: Family, Farming, and Community in the Midwest (U of North Carolina Press, 1992), focus on German Americans.
- Salmons, Joseph C. The German Language in America, 1683-1991. Madison, Wis.: Max Kade Institute, University of Wisconsin-Madison, 1993.
- Schiffman, Harold. "Language loyalty in the German-American Church: The Case of an Over-confident Minority" (1987).
- Schirp, Francis. "Germans in the United States". The Catholic Encyclopedia. Vol. 6. New York: Appleton, 1909.
- Schlossman, Steven L. "Is there an American tradition of bilingual education? German in the public elementary schools, 1840-1919." American Journal of Education (1983): 139-186. in JSTOR
- Tatlock, Lynne and Matt Erlin, eds. German Culture in Nineteenth-Century America: Reception, Adaptation, Transformation. (2005).
- Thernstrom, Stephan, ed. Harvard Encyclopedia of American Ethnic Groups (1980) online
- Tischauser, Leslie V. The Burden of Ethnicity: The German Question in Chicago, 1914–1941. (1990).
- Tolzmann, Don H., ed. German Americans in the World Wars, 2 vols. Munich, Germany: K.G. Saur, (1995).
- Tolzmann, Don H. German-American Literature (Scarecrow Press, 1977).
- Trommler, Frank & Joseph McVeigh, eds. America and the Germans: An Assessment of a Three-Hundred-Year History. (2 vol 1985); vol 1: Immigration, Language, Ethnicity; vol 2: The Relationship in the Twentieth Century. Essays by scholars covering broad themes.
- Turk, Eleanor L. "Germans in Kansas: Review Essay". Kansas History: A Journal of the Central Plains 28 (Spring 2005): 44–71.
- van Ravenswaay, Charles. The Arts and Architecture of German Settlements in Missouri: A Survey of a Vanishing Culture (1977; reprint University of Missouri Press, 2006).
- Walker, Mack. Germany and the Emigration, 1816–1885 (1964).
Where Have All the Germans Gone?. New York: Films Media Group, 1976.- Wittke, Carl Frederick. The German-Language Press in America. (1957).
- Wittke, Carl Frederick. Refugees of Revolution: The German Forty-Eighters in America. (1952).
- Wittke, Carl Frederick. We Who Built America: The Saga of the Immigrant. (1939), ch. 6, 9.
- Wood, Ralph, ed. The Pennsylvania Germans. (1942).
- Zeitlin, Richard. Germans in Wisconsin. Madison: Wisconsin Historical Society, (2000).
Historiography
- Hustad, Bradley Jake. "Problems in Historiography: The Americanization of German Ethnics." (MA thesis, Mankato State University, 2013). online
- Kazal, Russell A. "Revisiting Assimilation: The Rise, Fall, and Reappraisal of a Concept". American Historical Review 100 (1995): 437–71.
- Kluge, Cora Lee. Other Witnesses: An Anthology of Literature of the German Americans, 1850–1914. Madison, Wis.: Max Kade Institute for German-American Studies, 2007.
- Ortlepp, Anke. "Deutsch-Athen Revisited: Writing the History of Germans in Milwaukee" in Margo Anderson and Victor Greene (eds.), Perspectives on Milwaukee's Past. Champaign: University of Illinois Press, 2009.
- Miller, Zane L. "Cincinnati Germans and the Invention of an Ethnic Group", Queen City Heritage: The Journal of the Cincinnati Historical Society 42 (Fall 1984): 13–22.
Parish, Peter J., ed. (2013). Reader's Guide to American History. Taylor & Francis. pp. 294–95.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: Extra text: authors list (link)
Primary sources
- Kamphoefner, Walter D., and Wolfgang Helbich, eds. Germans in the Civil War; The Letters They Wrote Home. (U of North Carolina Press, 2006).
- Kamphoefner, Walter D., Wolfgang Johannes Helbich and Ulrike Sommer, eds. News from the Land of Freedom: German Immigrants Write Home. (Cornell University Press, 1991).
"German". Chicago Foreign Language Press Survey. Chicago Public Library Omnibus Project of the Works Progress Administration of Illinois. 1942 – via Newberry Library. (English translations of selected German-language newspaper articles, 1855-1938).
In German
- Emmerich, Alexander. Geschichte der Deutschen in Amerika von 1680 bis in die Gegenwart. (2013).
- Rehs, Michael. Wurzeln in fremder Erde: Zur Geschichte der südwestdeutschen Auswanderung nach Amerika DRW-Verlag, 1984.
ISBN 3-87181-231-5
"List of Newspapers and Periodicals Printed Wholly or in Part in Languages Other Than English: German", American Newspaper Directory, New York: Geo. P. Rowell & Co., 1880
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to German Americans. |
German-American history and culture
- Chronology: Germans in America
- German Immigrant Culture in America: Syllabus (1998)
- Emigrant Letters to Germany (in German)
German-American Business Biographies from the German Historical Institute
- German-American Hall of Fame
- How German Is American?
- The German-Hollywood Connection
- Chicago Foreign Language Press Survey: English translations of 120,000 pages of newspaper articles from Chicago's foreign language press from 1855 to 1938, many from German papers.
German-American organizations
- German-American Heritage Museum of the USA
- Steuben Society of America
- German American Heritage Center
- Germans from Russia Heritage Society
Max Kade Institute for German-American Studies at the University of Wisconsin-Madison
Max Kade German-American Center at Indiana University – Purdue University Indianapolis
- The Germantown Historical Society (Philadelphia)
- The German Society of Pennsylvania (oldest German Society in the U.S.)
- The Pennsylvania German Society
Pennsylvania German Cultural Heritage Center at Kutztown University
- Indiana German Heritage Society
Local German-American history and culture
- Germans in Chicago
- German Traces NYC from the Goethe-Institut
- Interactive German-History Map of Pittsburgh
- Zinzinnati History (Cincinnati, Ohio)
- Milwaukee German-American Radio Program
- Teutonia Männerchor in Pittsburgh
- Some German Contributions to Wisconsin Life

