Merseyrail
 Class 507 at Birkenhead North in 2014 | |
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Franchise(s) | Merseyrail 20 July 2003–2028[1] |
| Main Region(s) | Liverpool City Region |
| Other Region(s) | Cheshire West and Chester, West Lancashire |
| Fleet size | 59 |
| Stations called at | 68[2] |
| Stations operated | 67[3] |
| Route km operated | 120.7 |
| National Rail abbreviation | ME |
| Parent company | Serco-Abellio |
| Website | www.merseyrail.org |
| Technical | |
| Track length | 75 miles |
Merseyrail is both a train operating company (TOC) and a commuter rail network in and around Liverpool City Region, England. It is a part of Serco-Abellio,[4] and is formed of two electrified lines of the National Rail network known as the Northern Line and the Wirral Line which run underground in central Liverpool. A third line, separate from the electrified network, is named the City Line, which is a term used by the governing body Merseytravel referring to local services it sponsors on the Liverpool to Manchester Lines and Liverpool to Wigan Line operated by Northern.[5]
The Merseyrail network has 68 stations and 75 miles of route, of which 6.5 miles are underground. Carrying approximately 110,000 passengers each weekday,[6] or 34 million passengers per year,[7] it forms the most heavily used urban railway network in the UK outside London.[8][9] The network is operated by a joint venture between franchise holder Serco and Abellio, who superseded Arriva Trains Merseyside in 2003. The contract is for 25 years expiring in 2028.[1] Serco-Abellio operate a fleet of 59 trains and as of 2015, employ 1,200 people.[10]
The large comprehensive urban network was formed in 1977 by merging separate rail lines by the construction of new tunnels under Liverpool city centre and Birkenhead.[5] Although financial constraints have prevented some of the 1970s plans for the network being realised, the network has been extended, with additional extensions proposed.
The Merseyrail name became the official brand for the network in the days of British Rail, surviving several franchise holders, although the name was not used by Arriva when holding the franchise. Despite this, Merseytravel continued the Merseyrail branding at stations, allowing the name to be adopted colloquially. Merseyrail is referred to as "Merseyrail Electrics" by National Rail Enquiries, and as "Serco/Abellio Merseyrail" by Merseytravel.
Contents
1 Current system
1.1 Northern Line
1.2 Wirral Line
1.3 City Line
2 Services
3 Fleet
3.1 Current fleet
3.2 Past fleet
3.3 Future fleet
4 Depots
5 Franchise and concession history
6 Performance
7 Financial performance
8 Enforcement of by-laws
9 History
9.1 Collection of separate railways
9.2 Creation of Merseyrail
9.3 The Loop and Link Project
9.3.1 The Loop Line (Wirral Line)
9.3.2 The Link Line (Northern Line)
9.3.3 The Hamilton Square Burrowing Junction
9.3.4 Liverpool Central South Junction
9.4 Expanding the Network (1977 – present)
9.4.1 Walton to Kirkby
9.4.2 Liverpool Central to Garston
9.4.3 Garston to Hunts Cross
9.4.4 Rock Ferry to Hooton, Chester and Ellesmere Port
9.4.5 New stations
10 Future
10.1 Future stations
10.2 Fleet proposals
10.2.1 Dual-voltage trains
10.2.2 Tram-trains
10.3 Electrification
10.3.1 Kirkby to Wigan
10.3.2 Ormskirk to Preston
10.3.3 Bidston to Wrexham
10.3.4 Hunts Cross to Warrington
10.3.5 Southport to Wigan
10.3.6 Other electrification proposals
10.4 Battery train trials
10.5 Reopening
10.5.1 Burscough Curves
10.5.2 Edge Hill to Bootle
10.5.3 North Mersey Branch
10.5.4 Skelmersdale Branch
10.5.5 Halton Curve
10.5.6 The Outer Rail Loop
10.5.7 The Edge Hill Spur
10.5.8 St James Station
11 See also
12 References
12.1 Sources
13 Further reading
14 External links
Current system
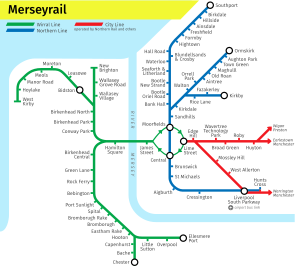
Merseyrail map
Kirby
Merseyrail lines shown in Merseyside
Northern line
Wirral line
City Line
Primary route
Secondary route
Rural route
Goods line
Disused line
The network is composed of two lines known as the Northern Line and the Wirral Line which are operated by the Merseyrail train operating company and are electrified throughout using the third-rail 750 V DC system. The Power Supply to the Third Rail is monitored and controlled by the Electric Control Room at Sandhills. The City Line (marked red on the map) is operated primarily by Northern with funding from Merseytravel. The line is mainly electrified with one branch, the Liverpool to Manchester line via Warrington, operated by diesel trains.[11][12]
Trains on the Northern Line and Wirral Line cover the Liverpool City Region. Their total track length is 75 miles (121 km), with 68 stations. The lines connect Liverpool city centre with cities and towns on the outer reaches of the city region, such as Southport and Chester. Frequent intermediate stops serve other sections of the urban area. Trains run at an off-peak interval of fifteen minutes on most branches, with lines converging to provide a frequency of up to every five minutes within central Liverpool, and under the Mersey to Birkenhead.
The three lines interchange as follows:
- Northern and City Line services interchange at Liverpool South Parkway and Hunts Cross in the south of the city.
- Wirral and City Lines interchange at Lime Street in the city centre.
- Northern and Wirral lines interchange at Liverpool Central and Moorfields in the city centre.
Northern Line
The Northern Line is shown in blue on the Merseyrail map. Services operate on three main routes: from Hunts Cross in the south of Liverpool to Southport via the Link tunnel from Brunswick Station through central Liverpool, from Liverpool Central to Ormskirk and from Liverpool Central to Kirkby. Each route operates a train every 15 minutes from Monday to Saturday, giving a frequent interval between trains on the central section. Some additional trains run at peak hours on the Southport line.
Connections are available at Southport to Wigan Wallgate and Manchester Airport; at Liverpool South Parkway for services operated by London Midland, East Midlands Trains, TransPennine Express and Northern serving Birmingham New Street, Manchester Oxford Road, Blackpool North and various destinations within Yorkshire and the West Midlands; at Hunts Cross to Warrington Central and Manchester Oxford Road; at Ormskirk to Preston and at Kirkby to Wigan Wallgate and Manchester Victoria.[13]
On matchdays at the stadiums of Liverpool F.C.'s Anfield and Everton F.C.'s Goodison Park, Northern Line services connect with the SoccerBus service at Sandhills to transport fans to the stadiums. The buses depart at frequent intervals from Sandhills station and a ticket combining both methods of travel is available. Kirkdale station is within walking distance of Goodison Park.
Wirral Line

A Wirral Line train at Liverpool Central
The Wirral Line is shown in green on the Merseyrail map. Services operate from the four terminus stations of: Chester, Ellesmere Port, New Brighton and West Kirby. Each line from the terminus stations runs to Hamilton Square underground station in Birkenhead and through the Mersey Railway Tunnel, continuing around the single track underground loop tunnel in Liverpool's city centre. Trains head back into the Mersey Railway Tunnel to return to one of the Wirral's terminus stations.
Monday-Saturday services are every 15 minutes from Liverpool to Chester, New Brighton and West Kirby, and every 30 minutes to Ellesmere Port (Monday - Sunday). These combine to give a service at least every five minutes from Birkenhead Hamilton Square and around the loop under Liverpool's city centre.[13]
Connections are provided at Bidston on the West Kirby branch for the Borderlands Line to Wrexham, operated by Transport for Wales, and at Chester to Crewe and London Euston, Wrexham and Shrewsbury, the North Wales Coast line to Llandudno and Holyhead, and to Manchester either via Warrington or via Northwich and Knutsford. At Ellesmere Port there is a minimal service to and from Warrington.[13]
City Line
The City Line, shown in red on the Merseyrail map, is a term used by local transport authority Merseytravel to describe the suburban services which depart from Liverpool Lime Street on the Liverpool to Wigan, Liverpool to Manchester Lines and Liverpool to Crewe line. The City Line is not operated by Merseyrail trains; however, the trains stop at two stations operated by Merseyrail. Services are less frequent than those on the Northern Line and Wirral Line, generally half-hourly on weekdays. The electric trains are branded Northern Electrics on the services using the Class 319s.
The line consists of a number of services departing Liverpool Lime Street station, namely the line to Wigan North Western, both routes to Manchester, via Warrington or Newton-le-Willows, and services to Crewe via Runcorn. Of these, only the service to Manchester via Warrington Central is not currently electrified. Services are provided by the Northern and London Midland train operating companies. Stopping services running through Merseyside are sponsored by Merseytravel and stations are given Merseyrail branding.
Work on the electrification of the two remaining branches of the City Line on the 25kV overhead system was completed in 2015. Earlier, in February 2010 Network Rail announced that four electrified tracks will be provided from Broad Green Station to Huyton Station. This is to enable segregation of the longer distance limited stop train services to Manchester and beyond from the stopping services of the City Line.[14]
Class 319 electrical multiple units have been transferred from the Thameslink route, refitted with new interiors, repainted in Northern livery and after the removal of the third rail collector shoe, are operating on the newly electrified lines between Liverpool, Wigan and Manchester, which incorporates the City Line.[12]
Services
Typical weekday off-peak service on the Merseyrail-run Northern and Wirral lines is as follows:[15][16]
| Northern Line | ||
|---|---|---|
| Route | tph | Calling at |
Hunts Cross to Southport | 4 | Liverpool South Parkway, Cressington, Aigburth, St Michaels, Brunswick, Liverpool Central, Moorfields, Sandhills, Bank Hall, Bootle Oriel Road, Bootle New Strand, Seaforth & Litherland, Waterloo, Blundellsands & Crosby, Hall Road, Hightown, Formby, Freshfield, Ainsdale, Hillside and Birkdale |
| Liverpool Central to Ormskirk | 4 | Moorfields, Sandhills, Kirkdale, Walton, Orrell Park, Aintree, Old Roan, Maghull, Maghull North, Town Green and Aughton Park |
| Liverpool Central to Kirkby | 4 | Moorfields, Sandhills, Kirkdale, Rice Lane and Fazakerley |
| Wirral Line | ||
| Route | tph | Calling at |
Liverpool Lime Street to New Brighton | 4 | Liverpool Central (from Lime Street only) / Moorfields (to Lime Street only), Liverpool James Street, Birkenhead Hamilton Square, Conway Park, Birkenhead Park, Birkenhead North, Wallasey Village and Wallasey Grove Road |
| Liverpool Lime Street to West Kirby | 4 | Liverpool Central (from Lime Street only) / Moorfields (to Lime Street only), James Street, Hamilton Square, Conway Park, Birkenhead Park, Birkenhead North, Bidston, Leasowe, Moreton, Meols, Manor Road and Hoylake |
| Liverpool Lime Street to Chester | 4 | Liverpool Central (from Lime Street only) / Moorfields (to Lime Street only), James Street, Hamilton Square, Birkenhead Central, Green Lane, Rock Ferry, Bebington, Port Sunlight, Spital, Bromborough Rake, Bromborough, Eastham Rake, Hooton, Capenhurst and Bache |
| Liverpool Lime Street to Ellesmere Port | 2 | Liverpool Central (from Lime Street only) / Moorfields (to Lime Street only), James Street, Hamilton Square, Birkenhead Central, Green Lane, Rock Ferry, Bebington, Port Sunlight, Spital, Bromborough Rake, Bromborough, Eastham Rake, Hooton, Little Sutton and Overpool |
City Line services are not operated by Merseyrail, but have timetables produced by Merseytravel and are included here for completeness. Typical off-peak weekday service is as follows:[17]
| City Line | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Route | tph | Calling at | Operator |
| Liverpool Lime Street to Wigan North Western | 2 | Edge Hill, Wavertree Technology Park, Broad Green, Roby, Huyton, Prescot, Eccleston Park, Thatto Heath, St Helens Central, Garswood and Bryn | Northern |
| Liverpool Lime Street to Blackpool North | 1 | Huyton, St Helens Central, Wigan North Western, Euxton Balshaw Lane, Leyland, Preston, Kirkham & Wesham and Poulton-le-Fylde | |
| Liverpool Lime Street to Warrington Bank Quay | 1 | Edge Hill, Wavertree Technology Park, Broad Green, Roby, Huyton, Whiston, Rainhill, Lea Green, St Helens Junction and Earlestown | |
| Liverpool Lime Street to Manchester Airport | 1 | Edge Hill, Wavertree Technology Park, Broad Green, Roby, Huyton, Whiston, Rainhill, Lea Green, St Helens Junction, Earlestown, Newton-le-Willows, Patricroft, Eccles, Manchester Oxford Road, Manchester Piccadilly, Mauldeth Road, Burnage, East Didsbury, Gatley and Heald Green trains continue to Crewe | |
| Liverpool Lime Street to Manchester Victoria | 1 | Lea Green trains continue to Scarborough | TransPennine Express |
| 1 | Newton-le-Willows trains continue to Newcastle | ||
| Liverpool Lime Street to Manchester Oxford Road | 1 | Edge Hill, Mossley Hill, West Allerton, Liverpool South Parkway, Hunts Cross, Halewood, Hough Green, Widnes, Sankey for Penketh, Warrington Central, Birchwood, Irlam, Urmston and Deansgate | Northern |
| 0.5 | Mossley Hill, West Allerton, Liverpool South Parkway, Hough Green, Widnes, Warrington Central, Padgate, Birchwood, Glazebrook, Irlam, Flixton, Chassen Road, Urmston and Deansgate | ||
| 0.5 | Mossley Hill, West Allerton, Liverpool South Parkway, Hough Green, Widnes, Warrington Central, Padgate, Birchwood, Irlam, Flixton, Urmston, Humphrey Park, Trafford Park and Deansgate | ||
| Liverpool Lime Street to Manchester Airport | 1 | Liverpool South Parkway, Warrington Central, Birchwood, Manchester Oxford Road, Manchester Piccadilly and Mauldeth Road | |
| Liverpool Lime Street to Manchester Piccadilly | 1 | Liverpool South Parkway, Widnes, Warrington Central and Manchester Oxford Road trains continue to Nottingham and Norwich | East Midlands Trains |
| Liverpool Lime Street to Crewe | 2 | Liverpool South Parkway, Runcorn, Acton Bridge (limited), Hartford and Winsford (1tph) trains continue to Birmingham | London Northwestern Railway |
| 1 | Runcorn trains continue to London | Virgin Trains | |
Fleet
Services on the electrified Merseyrail network are operated exclusively by Class 507 and Class 508 electric multiple unit trains (EMUs). These replaced pre-war Class 502 (originally constructed by the LMS) and almost identical Class 503 EMUs. There are 59 trains in service on the network. This is down from an initial 76: twelve 508s were transferred to Connex South Eastern in 1996, and a further three were transferred to Silverlink to supplement its fleet of Class 313 EMUs in North London. These train sets had been stored on Merseyside as surplus from during the 1990s.
Two sets have been written off and scrapped. These are unit 507022 in 1991, after a collision, and unit 508118, which had been gutted by fire in an arson attack in Birkenhead in 2001.

Merseyrail's specially painted 507019 unit, celebrating Liverpool's capital of culture year
The fleet was refurbished between 2002 and 2005 by Alstom at a cost of £32 million, involving trainsets being transported to and from Eastleigh works behind Class 67 locomotives. Improvements to the trains included new high-backed seating, interior panel replacement, new lighting, the installation of a Passenger Information System and a new external livery.[18]
To celebrate Liverpool's successful 2008 European Capital of Culture bid, Merseyrail named one of its train sets (508136) Capital of Culture. A press ceremony took place at Kirkdale TMD where Cherie Blair, the wife of then-Prime Minister Tony Blair, named 508143 Capital of Culture. The name, a vinyl stick-on, was removed in 2009. In February 2008 the first of four sets in a special Capital of Culture promotional livery was released. Set number 508134 was emblazoned with a purple livery showcasing the "creative" element of the city.[19] Three more followed in blue "maritime", green "heritage" and red "sport" colours, but these liveries were removed in November 2009. On 11 October 2011, set 508111 was unveiled in a blue advertising livery for The Beatles Story, a museum for The Beatles in Liverpool.[20] A second advertising train, 507002, appeared in September 2012; it promotes Liverpool Hope University.[21]
From July 2008, four trains were named after Merseyside icons following a poll in the Liverpool Echo. The first, Red Rum, was unveiled at Southport on 14 July 2008 by Ginger McCain. Three more have followed, named Bob Paisley, Dixie Dean, and John Peel.[22] Further trains were named Councillor Jack Spriggs, Operations Inspector Stuart Mason and Harold Wilson.[23][24][25]
In celebration of the tenth anniversary of the Serco-Abellio partnership operating Merseyrail, a unit was named Merseyrail - celebrating the first ten years 2003-2013 at Rock Ferry on 7 October 2013. It was also confirmed that the current fleet would undergo a refreshment package including interior improvements[26] and a new livery scheduled to begin in 2014 with interior refurbishments set to commence in 2015 and take just over a year to complete.[27][28][29]
Current fleet
| Class | Image | Type | Top speed | Cars | Number | Routes operated | Built | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mph | km/h | |||||||
507 |  | EMU | 75 | 120 | 3 | 32 |
| 1978–80 |
508/1 |  | EMU | 75 | 120 | 3 | 27 |
| 1979–80 |
Past fleet

A British Rail Class 503 train on the Liverpool Loop and Link underground system. This train was one of the original batch built by the LMS in 1938.
The original service on the Merseyrail lines was provided by British Rail Class 502 on the Northern Line, withdrawn by 1980, and British Rail Class 503 on the Wirral Line from June 1980 onwards,[30] the majority of the Class 503s were progressively withdrawn from June 1984, the final service train running on 29 March 1985.[31]

73 901 between two former Class 501 driving cars with a de-icing train at Chester on 26 March 1999
Merseyrail formerly had four Class 73 electro-diesel locomotives for shunting, sandite trains, engineering works and other departmental duties. These locomotives were sold to a preservation company in 2002.[citation needed]
Future fleet
In December 2016, Merseytravel announced that it had reached an agreement with Swiss rolling-stock manufacturer Stadler Rail for the provision of a new fleet trains with the capability of being driver only, to be built at Stadler's factory in Bussnang, Switzerland. The new units, which will be designated Class 777, are to be delivered from mid-2019 onwards, the final units being due to enter service 2021. The new trains will be bespoke for Merseyrail, allowing Merseytravel to have the new fleet designed specifically for its own railway network.[32]
The new trains will be of an articulated four-car design (as opposed to the three-car units currently in service) with a significantly increased overall capacity and faster acceleration and deceleration, which will allow for reduced journey times. A combination of reduced weight (99 tonnes, representing a 5.5 tonne weight reduction) and more efficient electrical systems will give a 20% reduction in energy use.
The first of the 52 units should be delivered in summer 2019, and the whole fleet is planned to be in service by 2021.[33] Merseytravel has an option for a further fifteen Class 777 units as part of the deal, which if exercised would see a total of 67 units built. The deal also involves the transfer of 155 of Merseyrail's maintenance workers and the operation of its maintenance depot at Kirkdale to Stadler Rail Service.
[34] The transfer of Kirkdale depot and Merseyrail engineering personnel took place in October 2017, as construction work to modernise the depot, which is the planned maintenance hub for the Class 777s, commenced.[35]
| Class | Image | Type | Top speed | Cars | Number | Planned routes | Built | In service | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mph | km/h | ||||||||
777 METRO | EMU | 75 | 120 | 4 | 52 |
| 2018–21 | 2019–21 | |
Depots
The electric fleet is maintained and stabled at Kirkdale TMD and Birkenhead North TMD, the two depots on the network. Minor repair work and stock cleaning takes place at Kirkdale, while overhauls are completed at Birkenhead.[36] Other depots at Hall Road and Birkenhead Central were closed in 1997, and the former was demolished in April 2009.[37]
There are also two depots near Southport station: Southport Wall Sidings and Southport Carriage Holding Sidings.
Franchise and concession history
As a result of the privatisation of British Rail, the Northern Line and Wirral Line were brought together as the Mersey Rail Electrics passenger franchise, being sold on 19 January 1997. Although franchises are awarded and administered on a national level (initially through various independent bodies, and later the Department of Transport directly), under the original privatisation legislation of 1993, PTEs were co-signatories of franchise agreements covering their areas - this role being later modified by the 2005 Transport Act.[38]
The first train operating company (TOC) awarded the Mersey Rail Electrics franchise contract was MTL, originally the operating arm of the PTE, but privatised itself in 1985. They used the brand name Merseyrail Electrics, but after MTL was sold to Arriva, the TOC was rebranded Arriva Trains Merseyside from 27 April 2001.
The City Line was also privatised under the 1993 Act, but as part of a different, much larger North West Regional Railways (NWRR) franchise. Upon sale on 2 March 1997, the first TOC awarded the NWRR franchise contract was North Western Trains (owned by Great Western Holdings). The TOC was later bought by FirstGroup and rebranded First North Western.
When the Mersey Rail Electrics franchise came up for renewal, reflecting the exclusive nature of the Northern and Wirral lines - being largely isolated from the rest of the National Rail network and with no through passenger services to/from outside the Merseyrail network, the decision was taken to remove it from the national franchising system and bring it into exclusive PTE control. As a result, using the Merseyrail Electrics Network Order 2002 the Secretary of State first exempted the two lines from being designated as a railway franchise under the 1993 Act. Coming into force on 20 July 2003, this then allowed the PTE to contract out the operation of the two lines themselves, which they did so as a concession to run for up to 25 years. The first successful bidder was Merseyrail Electrics (2002) Ltd, a joint venture between Serco and NedRailways (renamed Abellio in 2009).[38]
The City Line was not included in the 2003 exemption, and so it has continued as part of the nationally administered rail franchise system. From 11 December 2004, the NWRR franchise was merged into a new Northern franchise. The first TOC awarded this franchise contract was Northern Rail, also owned by a Serco-NedRail (Abellio) joint venture. Upon re-tendering, Northern Rail failed to retain the contract, and it passed to Arriva Rail North from 1 April 2016.
Due to the isolation of the Northern and Wirral lines, Merseyrail Electrics (2002) Ltd are keen to adopt vertical integration – taking responsibility for maintenance of the track from Network Rail. The current managing director of Merseyrail is Andy Heath.[39]
Performance
Operating as a self-contained network means there are relatively few problems because there is little conflict with other train operating companies. Merseyrail has publicly committed to aiming to be the best train operating company in the UK.[40][41] The latest figures released by NR (Network Rail) (as of period 12 of 2012/2013) report that Merseyrail's Public Performance Measure (PPM) was 96.2% and the moving annual average (MAA) stood at 95.5%.[42]
In February 2010, Merseyrail was named the most reliable operator of trains in the UK, with a reliability average of 96.33% during 2009-2010, the highest ever achieved by any UK train operator.[43]
Financial performance
(Figures shown are attributable to Merseyrail Electrics 2002 Ltd, (who operate the Northern and Wirral Line sections of the "Merseyrail" branded network).
| Year ending | Turnover (£m) | Gross profit (£m) | Trading profit (£m) | Pre-Tax profit (£m) | Retained profit (£m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| January 2010[44] | 124.5 | 12.1 | 12.5 | ||
| January 2009[45] | 127 | 11.4 | 6.5 | ||
| January 2008[46] | 116 | 9.2 |
Enforcement of by-laws
| Wikinews has related news: Student who put feet on chair walks free |
Merseyrail employs a team of officers who enforce railway by-laws relating to placing feet on seats, travelling without tickets, and other aspects of anti-social behaviour. The enforcement of the 'feet on seat' by-law by Merseyrail was judged to be "draconian"[47] in September 2007; however, Merseyrail stated that it did not want to take offenders to court, but was not allowed to fine offenders otherwise (unlike people who smoke on trains or station platforms).[48] Merseyrail is the only UK train operator to take such a vigorous approach, a stand which Merseyrail claims has proved very popular with commuters and has reduced anti-social behaviour on the system.[49]
History
Collection of separate railways

The Illustrated London News featuring the opening of the Mersey Railway Tunnel
The present Merseyrail system was merged from the lines of five former pre-Grouping rail systems:
- The Mersey Railway (Liverpool Central to Rock Ferry, Birkenhead Park)
- The Cheshire Lines Committee railway (Liverpool Central to Hunts Cross section).
- The Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (Liverpool Exchange to Kirkby, Ormskirk and Southport sections).
- The Wirral Railway (Birkenhead Park to New Brighton and West Kirby)[50]
Birkenhead Joint Railway (Rock Ferry to Hooton and Chester section and the Ellesmere Port branch).
The nucleus of the system was the Mersey Railway, which opened from Liverpool James Street to Green Lane, Birkenhead running through the Mersey Railway Tunnel, one of the world's first underwater railway tunnels in 1886.[13] The tunnelled route was extended to Liverpool Central in 1890. A tunnelled branch to Birkenhead Park was added in 1888 to connect with the Wirral Railway and the original line extended to Rock Ferry to connect with the Birkenhead Woodside to Chester line in 1891.[51]
The Mersey Railway was electrified in 1903 being the world's first full electrification of a steam railway.[13] This was followed by the separate Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway line from Liverpool Exchange to Southport, which was electrified in 1906. The electrification of the former Wirral Railway lines to (New Brighton and West Kirby) took place in 1937 and allowed through running into Liverpool via the Mersey Railway tunnel.
Creation of Merseyrail
The programme of route closures in the early 1960s, known as the Beeching Axe, included the closure of two of Liverpool's mainline terminal stations, Liverpool Exchange and Liverpool Central high-level in Liverpool, and also Woodside Station in Birkenhead.
Riverside terminal station at the Pier Head was the fourth terminal station to close. This was not a part of the Beeching cuts: the demise of the trans-Atlantic liner trade forced its closure in 1971.
The Beeching Report recommended that the suburban and outer-suburban commuter rail services into both Exchange and Central High-level stations be terminated and that long- and medium-distance routes be concentrated on Lime Street station. Liverpool City Council took a different view and proposed the retention of the suburban services and their integration into a regional rapid-transit network. This would divert all local urban routes from Lime Street mainline terminus station, releasing platform space at the station to focus on mid to long haul routes. This approach was backed up by the Merseyside Area Land Use and Transportation Study, the MALTS report.[52] Liverpool City Council's proposal was adopted and Merseyrail was born.[53]
The Merseyside Passenger Transport Authority, later named Merseytravel, was formed in 1969 with representatives from all Merseyside local authorities taking responsibility for the local rail network, henceforth known as 'Merseyrail'. At that time, the lines out of Liverpool Exchange, Liverpool Central Low Level and Liverpool Lime Street stations were completely separate and were given the names of 'Northern Line', 'Wirral Line' and 'City Line' respectively.
The Strategic Plan for the North West, the SPNW, in 1973 envisaged that the Outer Loop, the Edge Hill Spur connecting the east of the city to the central underground sections, and the lines to St. Helens, Wigan and Warrington would be electrified and all integrated into Merseyrail by 1991.[54]
The Loop and Link Project
The major engineering works required to integrate the Northern and Wirral lines became known as the 'Loop' and 'Link' Project. The 'Loop' was the Wirral Line tunnel and the 'Link' the Northern Line tunnel, both under Liverpool's city centre. The main works were undertaken between 1972 and 1977. A further project, known as the Edge Hill Spur, would have integrated the City Lines into the city centre underground network. This would have meshed the eastern section of the city into the core underground electric city centre section of the network, releasing platforms at mainline Lime Street station for mid to long haul routes.
The Loop Line (Wirral Line)
The Loop Line is a single-track loop tunnel under Liverpool's city centre serving the Wirral lines. It was built to allow both greater capacity and a wider choice of destinations for Wirral Line users, which included the business and shopping districts of Liverpool city centre and Lime Street station.
Trains from Wirral arriving via the original Mersey Railway tunnel enter the loop beneath Mann Island continuing in a clockwise direction through James Street, Moorfields, Lime Street and Central, returning to the Wirral via James Street station.[55]
The Link Line (Northern Line)

The original Mersey Railway tunnel from James Street to Central station, in red, still exists. The Link line, is shown in blue with the Loop line in green.
The Link Line is a double-track tunnel that links the Hunts Cross branch to the south with the Southport, Ormskirk and Kirkby branches to the north, thereby creating one line, the Northern Line. It provides direct access from the north and south of Liverpool to the shopping and business districts in the city centre via two underground stations, Liverpool Central and Moorfields, both of which also interchange with the Loop Line. The Northern Line effectively creates a north-south crossrail enabling passengers to travel from the south to the north of the city, and vice versa, via Liverpool city centre.
The present Northern Line underground station at Liverpool Central Low Level was originally the Mersey Railway terminus. A section of the original 1880s tunnel between James Street and Central stations was used to form the Link Tunnel. The remainder, between Paradise Street Junction and Derby Square Junction, was retained for use as a stock interchange line between the Northern and Wirral lines and also for a reversing siding for Wirral Line trains terminating at James Street when the Loop Tunnel is inoperative. The stock interchange section of the tunnel is not used for passenger traffic.[56]
The Link Tunnel was originally intended to link the urban lines north and south of the city creating a north-south crossrail and an additional function in completing the western section of a planned double-track electrified suburban orbital line, circling the city's outer suburbs, known as the 'Outer Rail Loop'. However, the eastern section of the Outer Loop was never built due to budget cuts.[57]
The Hamilton Square Burrowing Junction
A burrowing junction was constructed at Birkenhead Hamilton Square station, to increase traffic capacity on the Wirral Line by eliminating the flat junction to the west of the station. This included a new station tunnel at Hamilton Square to serve the lines to New Brighton and West Kirby.
Liverpool Central South Junction
To the south of Liverpool Central Low Level Station, a new track layout was constructed as part of the Link Line project. This layout permitted the former Mersey Railway route to be connected to the former Cheshire Lines Committee route from the closed Central High Level Station and so allow the Northern Line to be extended in a southerly direction to Garston and, later, Hunts Cross. It was accomplished by excavating the trackbed of the high-level tunnel to connect the two routes by means of a gradient. As it was still necessary to accommodate a reversing siding to serve Central Low Level, and as the width of the high-level tunnel did not permit a three-track alignment, a new section of single-track tunnel was built for the Central to Garston line. This tunnel starts to the south of the station and rises to join the high-level tunnel.
At the time of construction, the opportunity was taken to construct two short header tunnels for the proposed Edge Hill Spur project (see below). Should the project go ahead, the connecting tunnels could be constructed without the need to obstruct rail services on the existing route. The junction arrangement would be a burrowing junction, as at Hamilton Square (see above), with the grade separation of tracks increasing capacity.
[57]
Expanding the Network (1977 – present)

The loop line (Wirral Line) and link line (Northern Line) built under Liverpool in 1977

The Loop and Link project was followed by a programme of expansion, electrification and new stations, which built on the greater integration and capacity provided by the new infrastructure.
Walton to Kirkby
On 30 April 1977, Liverpool Exchange terminus station was closed as a part of the Link tunnel project to create the electrified Merseyrail north-south crossrail line named the Northern Line. Liverpool Exchange was the terminus of the northern Liverpool to Manchester route to Manchester Victoria via Wigan Wallgate station.
A tunnel under Liverpool's city centre, the Link tunnel, created the through Northern Line. The nearby Moorfields underground through station located on the new Link tunnel replaced Liverpool Exchange terminus station. Since diesel trains could not operate in the underground stations and tunnels for safety reasons, trains that had terminated at Liverpool Exchange terminus from Wigan Wallgate were as a temporary measure terminated at Sandhills station, the last surface station before the tunnel.
A year later in 1978, the short electrification from Walton to Kirkby extended the Merseyrail network, creating a Northern Line branch terminus and interchange station at Kirkby. The line was electrified using the standard 750 V DC third-rail Merseyrail system. The northern Liverpool to Manchester route was cut into two with differing modes of traction, electric and diesel. The diesel Wigan service terminating at Sandhills station was cut back to Kirkby. The Merseyrail electric and the Northern Rail diesel services use opposite ends of the same platform at Kirkby. Merseyrail and Northern Rail trains are generally timed to meet there for ease of interchange.
Liverpool Central to Garston
The reopening of the former Cheshire Lines Committee line from Liverpool Central to Garston was made possible by the excavation of the invert of the tunnel into Central High Level station to form a link into the southern end of Central Low Level station. This link had been envisaged when the Mersey Railway was extended to Central in the 1890s. The CLC line had been abandoned since the termination of the Liverpool Central to Gateacre service in 1972. On reopening, the line was electrified using the Merseyrail 750 V DC third-rail system and allowed through running via the Link Line tunnel to the Northern Line branches to Southport, Ormskirk and Kirkby. The line was opened in 1978.
Garston to Hunts Cross
This short extension at the southern end of the Northern Line opened in 1983. It allowed interchange between the Merseyrail Northern Line services with City Line and main line services from Lime Street. The reopened line passed under the West Coast Main Line Liverpool branch at Allerton but needed to cross the old Cheshire Lines Committee line to Manchester on the flat, which affected capacity.
Rock Ferry to Hooton, Chester and Ellesmere Port
Rock Ferry railway station had been a terminus for Wirral Line services since the Mersey Railway was extended there from Green Lane in 1891. Passengers for the lines to Chester and Helsby would change trains at this station from the electric service on to mainline services, operated by steam and diesel. Rock Ferry became one of the terminals for the Merseyrail Wirral Line. In 1985 the line from Rock Ferry to Hooton was electrified and incorporated in the Wirral Line of Merseyrail, Hooton thus becoming a new terminus.
Hooton is a junction station where the line to Helsby via Ellesmere Port branches off the main Chester line. The line from Hooton to Chester was electrified in 1993, Chester thus becoming a terminus station of the Wirral Line. The line from Hooton to Ellesmere Port was electrified in 1994 and incorporated into the Wirral Line, Ellesmere Port thus also becoming a terminus and interchange station.
New stations
A programme of new stations on the Merseyrail network expanded the coverage of the system. They are as follows:
Bache: On the Hooton to Chester line, opened in 1983 to replace the former Upton-by-Chester (Halt).
Bromborough Rake: On the Rock Ferry to Hooton line, opened in 1985 with the completion of electrification to Hooton.
Overpool: On the Hooton to Ellesmere Port line, opened in 1988.
- (Bache and Overpool are outside the PTE boundary and were funded by Cheshire County Council with some support from Merseytravel).
Eastham Rake: On the Rock Ferry to Hooton line, opened in 1995.
Brunswick: On the Liverpool Central to Hunts Cross line, opened in 1998. This station serves the South Docks regeneration area and also the Grafton Street area of Dingle high above the station via a staircase and footbridge.
Conway Park: On the Hamilton Square to Birkenhead Park underground line, opened in 1998. This station was originally intended to be built as 'cut and cover' with an office building on top. More onerous fire protection requirements arising from the Fennel report into the Kings Cross fire of 1987 made this prohibitively expensive and so the station was constructed in an open cut with lift access to the platforms. It serves the Europa Boulevard area of Birkenhead, a regeneration area.
Wavertree Technology Park: Opened in 2000 on the City Line route from Edge Hill to Huyton to serve the expanding Technology Park.

The former Holly Park Football ground, where Liverpool South Parkway Station now stands
Liverpool South Parkway: Opened in 2006 on the site of Holly Park football ground of South Liverpool F.C. in South Liverpool. It is an interchange station between the Merseyrail Northern Line from Liverpool Central to Hunts Cross and the City Line from Liverpool Lime Street to Runcorn and Warrington Central and also mainline services. The station also includes a bus terminal and large car park and has frequent bus services to Liverpool John Lennon Airport. The station was formed from an amalgamation of the four-track Allerton Station and the relocation of the Merseyrail Garston Station. Garston station was closed on the opening of the new facility, the first station closure on the Merseyrail network since Liverpool Exchange station in 1977.[57]
Maghull North: Construction of this station began in August 2017, with the station opening on 18 June 2018.[58]
Future
There have been various suggestions for ways to enlarge the Merseyrail network.[59] Some would extend beyond the current area, while others would use former existing lines or track beds. In November 2016 the details of the replacement to the current Merseyrail fleet is scheduled to be announced: if trains capable of use beyond the third-rail DC network are selected as replacements, various expansions can be achieved without electrification of the entire new route.[60] In August 2014 Merseytravel gave details of a 30-year plan for the network to be presented to the leaders of the city region.[61] the full plan is available at Liverpool City Region Long Term Rail Strategy
Future stations
In its 30-year plan of 2014 Merseytravel mentions the possibility of a new station between Moorfields and Sandhills in the Vauxhall area.[62]
Fleet proposals
In October 2012, Merseyrail announced a new project director to lead the procurement of a new fleet.[63] Merseyrail has an existing option to extend the current fleet lease by two years until March 2018 and is seeking to negotiate an extra year on top of that from the rolling stock leaser Angel Trains taking the lease to March 2019.
In January 2016 it was announced that Merseytravel had drawn up a shortlist of five bidders for the project. These were: Bombardier, Siemens, Stadler, CAF and Mitsui, who submitted their bids in April.[64] In December 2016, Merseytravel announced that Stadler had won the £460 million contract and that the new trains would be delivered from summer 2019 with all the old trains replaced by 2021.[65]
Dual-voltage trains
The Route Utilisation Strategy document makes note of the benefits of dual-voltage electric multiple-unit trains that could be used both on the third-rail Merseyrail network and on future electrified lines using overhead wires.[66] All new third-rail rolling stock must be capable of simple conversion to the overhead wire 25kV electrical supply system, so any future rolling stock on the Merseyrail DC third-rail lines will have provision for an overhead wire pantograph.
Tram-trains
Network Rail has suggested that tram-trains could offer an opportunity to connect more areas of Merseyside to the rail network. This would allow street running, providing an alternative route through Liverpool city centre. It could potentially relieve pressure on the busy underground section of the network. This is a long-term aspiration suggested for around 2024 and would be dependent on successful trials of the technology elsewhere in the UK.[66][67]
In August 2009, it was reported that a new tram-train link to Liverpool John Lennon Airport and a link to Kings Dock from the east of the city had been proposed.[68]
John Lennon Airport: the existing Northern Line and the City Line from Liverpool Lime Street to Liverpool South Parkway are being assessed. From South Parkway the tram-trains would transfer to a new tramway. Merseytravel commissioned a feasibility study into increasing rail links with the airport in 1995 but no further work has been undertaken.[69]
Kings Dock to Edge Hill: a link from Edge Hill in the east of the city to the Arena at Kings Dock in the city centre is also being considered. The disused 1829 1.26 mi Wapping Tunnel links the two locations. Tram-trains could then access existing and proposed electrified lines to the east and south of the city.
Electrification
Many proposals to electrify lines and add them to the existing Merseyrail service have been put forward.
Kirkby to Wigan
In 1977, the Liverpool to Kirkby section of the Liverpool-to-Bolton route was electrified and merged into Merseyrail. Kirkby became the terminus of the Northern Line Kirkby branch. The former through service to Bolton was split in two, with passengers wanting to make through journeys forced to change at Kirkby from the Merseyrail electric network to the Northern Rail diesel network onwards to Bolton.
In 2007 Merseytravel announced that funding had been secured to extend the electrification beyond Kirkby to a new station at Headbolt Lane to serve the extensive Tower Hill housing estate; however, no work commenced.[70] Further mention of this was made in Merseytravel's 30-year plan.[61]
The electrification extending Merseyrail through to Wigan Wallgate was a long-term aspiration of Merseytravel in 2014[61][71] and was identified by Network Rail as a route where electrification would enable new patterns of passenger service to operate.[72] There is acceleration of the aspiration as in March 2015 the Electrification Task force placed electrifying the line from Kirkby to Salford Crescent in a Tier 1 priority category.[73][74]
Ormskirk to Preston
Electrification from Ormskirk to Preston has been considered in conjunction with the Burscough Curves reopening detailed below. It would re-establish the most direct Liverpool-Preston route and is one of Merseytravel's long-term aspirations.[71] However, in 2008 Network Rail said the benefit-to-cost ratio of the scheme was insufficient to justify this scheme in the near future[75] though the scheme continued to be mentioned by Network Rail.[72] Third rail electric/battery train trials are to be undertaken in 2020 by Merseyrail on this section of track.[76]
Bidston to Wrexham

The Bidston interchange terminal of the Borderlands Line and through station for the Wirral Line to West Kirby.
The Borderlands Line from Bidston to Wrexham Central is operated by Transport for Wales using diesel trains on unelectrified track. Using zero emissions trains operating on electric traction motors, would allow trains to operate in the underground section of the Wirral Line, which continues on the same alignment as the Borderland Line. This would connect the Borderlands Line at Bidston onto the section of Wirral Line heading towards Liverpool, giving a direct service from Wrexham through to central Liverpool via Birkenhead's centre.
There has been various proposals to electrify some or all of the line over the years. The most recent study, conducted by Network Rail in 2008, investigated the costs of extending the Merseyrail network third-rail electrification to Wrexham. However, when the cost was estimated at £207 million,[77] Merseytravel announced that cheaper overhead line electrification would be considered instead. This would require dual-voltage trains with third-rail and overhead-wire capability.[78] The Welsh government is pushing for improved rail connections between North Wales and Liverpool which may accelerate the electrification of the line,[79] and the scheme continues to be mentioned by Network Rail[72] and Merseytravel.[61] Merseytravel believe that increasing the frequency of the trains will increase the levels of passengers and make the case for electricification stronger.[80]
A trial of a converted Electrostar train using energy from overhead wires and batteries when on non-electrified sections of track was undertaken in January and February 2015 on the Mayflower line.[81] A month later in March 2015, the introduction of battery powered trains was proposed for the Borderlands line by Network Rail.[82] The Network Rail document proposes that using battery powered rolling stock precluding full electrification of the line, provides a cheaper method of increasing connectivity into the electrified Birkenhead and Liverpool sections of the Wirral line. From the document:
- "In the longer term, potential deployment of rolling stock with the ability to operate on battery power for part of their journey may provide the ability in an affordable manner to improve the service offering between the Wrexham – Bidston route and Liverpool."[82]
In June 2018, KeolisAmey Wales were announced as the winners of the bid to operate the Wales and Borders rail service.[83] Part of their plans are to use refurbished Class 230 Metro trains with battery/diesel power to serve the line between Wrexham and Bidston.[84] Welsh Economy Secretary, Ken Skates, stated that the Welsh government were in an advanced stage of talks with Merseytravel about running a direct service from Wrexham to Liverpool.[85]
Hunts Cross to Warrington
The Strategic Plan for the North West, the SPNW, in 1973 envisaged that the Liverpool to Warrington line would be electrified and integrated into Merseyrail by 1991 as a part of the Northern Line.[54] In March 2015 the Electrification Task force placed electrifying the line from Liverpool to Manchester via Warrington Central in the Tier 1 priority category.[73]
Southport to Wigan
Southport to Wigan has been identified by Network Rail as a route where electrification in conjunction with extension of electrification from Ormskirk to Preston and reinstatement of the Burscough Curves would enable new patterns of passenger service to operate.[72] In March 2015 the Electrification Task force placed the electrifying the line from Southport to Salford Crescent via Wigan in the Tier 1 priority category.[73][74]
Other electrification proposals
The Ellesmere Port to Helsby route is included in Merseytravel's rail strategy as a "long-term aspiration".[61][71] No detailed analysis has been carried out into the feasibility. Third rail electric/battery train trials are to be undertaken in 2020 by Merseyrail on this section of track.[76]
Battery train trials
The Liverpool City Region Combined Authority, Long Term Rail Strategy document of October 2017, states that trials of new Merseyrail battery trains will be undertaken in 2020. A number of lines have been targeted for electric 3rd rail/battery train trials, which will allow electric Merseyrail trains to operate on unelectrified track, which otherwise would be precluded from track electrification on cost grounds.[76] The lines chosen for the trials are:
Ellesmere Port to Helsby: On page 37 of the Liverpool City Region Combined Authority, Long Term Rail Strategy document of October 2017, it states that a trial of new Merseyrail battery trains will be undertaken in view to put the 5.2 miles (8.4 km) stretch of track from Ellesmere Port to Helsby interchange station onto the Merseyrail network. If successful, Helsby will be one of the terminals of the Wirral Line, replacing Ellesmere Port with Stanlow and Thornton and Ince and Elton stations brought into the network.[76]
Ormskirk to Preston: Liverpool City Region Combined Authority, Long Term Rail Strategy document of October 2017, page 37, states a review to introduce new Merseyrail battery trains will be undertaken, in view to incorporate Preston onto the Merseyrail network by extending the Merseyrail Northern Line over 15 miles (24 km) from Ormskirk to Preston interchange station. The aim is to have Preston one of the terminals of the Northern Line, with Burscough Junction, Rufford and Croston stations brought onto the Merseyrail network. The document states, "The potential use of battery powered Merseyrail units may improve the business case".[76]
Reopening
Burscough Curves
The Burscough Curves were short chords linking the Ormskirk to Preston Line with the Manchester to Southport Line. The curves allowed northbound trains from Ormskirk to run directly to Southport to the west, and southbound trains from Preston run west to Southport. The last regular passenger trains ran over the curves in 1962; the tracks were subsequently lifted. The reinstatement of the Burscough Curves would allow direct Preston-Southport & Ormskirk-Southport services and provide an alternative Liverpool-Southport route via Ormskirk. Network Rail has recommended that a strategy for the Burscough Curves be developed further.[72][75]
In a parliamentary debate on 27 April 2011, the Burscough Curves were a prime point of the debate. The transport minister wished to meet Southport MP John Pugh regarding the reinstatement of the curves.[86] The latest refresh of Merseytravel's Long Term Strategy puts the opening of the curves in Network Rail's CP7 period.[87]
A review in 2020 to introduce new Merseyrail battery trains will be undertaken, as stated in the Liverpool City Region Combined Authority, Long Term Rail Strategy document of October 2017, page 37. The document highlights that Battery train introduction may improve the business case to reopen the Burscough Curves, allowing Northern Line trains to travel from Ormskirk to Southport, giving two routes from Liverpool to Southport. If realised Burscough Junction, Burscough Bridge, New Lane, Bescar Lane and Meols Cop stations may be incorporated into Merseyrail.[76]
Edge Hill to Bootle

Liverpool2 Container terminal extension under construction, which is served by the Bootle Branch line.
Known as either the Canada Dock Branch line or the Bootle Branch line[88] is an unelectrified line running from Edge Hill Junction in the east of the city in a long curve to the container terminal to the north of the city. Originally only serving Canada Dock, the line was extended north to the container terminal in the 1970s. The line meets and runs parallel to Merseyrail's Northern Line at a junction between Bank Hall and Bootle Oriel Road stations. The line's last passenger trains were withdrawn in 1977. This was a temporary service from Southport to Liverpool Lime Street during the construction of the Merseyrail network of tunnels under Liverpool's city centre. On the completion of Merseyrail, trains from Southport used the Merseyrail network. Being the only line currently into Liverpool docks, freight to Seaforth Container Terminal ensures constant use.[89]
The line has been mooted on many occasions for electrifying and reopening to passengers, giving scope to reopen stations along its length: Spellow, Walton & Anfield, Breck Road, Tuebrook, Stanley and Edge Lane. The line from Edge Lane would continue through Edge Hill junction via Edge Hill station and terminate at Lime Street. A disadvantage is that the northern end of the line does not loop back to Liverpool city centre at Kirkdale. The line would be a point to point line from Lime Street station to Bootle reducing the appeal to attract passengers. To loop the line back to Liverpool's city centre giving greater passenger appeal, branching into the Northern Line, would entail constructing sweeping curves after Kirkdale station or short tunnels from the deep cutting before Kirkdale station into the unused twin Breeze Hill tunnels near parallel to the tunnels. One tunnel is complete, the other was never fully completed and abandoned by the Victorians, however, the western section emerging at Kirkdale station is nearly complete. The tunnels which run north east from Kirkdale station to the Rice Lane road flyover at Queens Drive, have two portals at an ideal location for trains to run onto the platforms at Kirkdale station.[61]
Network Rail investigated options for the Canada Dock Branch in its March 2009 Route Utilisation Strategy for Merseyside[67] and concluded that the expected benefits did not justify the investment in new infrastructure.
The Department for Transport's Rail electrification document of July 2009 stated that the route to Liverpool Docks would be electrified via overhead wires. The Canada Dock Branch Line is the only line into the docks.[89] From the document:
- 70. Electrification of this route will offer electric haulage options for freight.
- There will be an alternative route to Liverpool docks for electrically-operated freight trains, and better opportunities of electrified access to the proposed freight terminal at Parkside near Newton-le-Willows.
The document states "route to Liverpool docks for electrically-operated freight trains", which is the Bootle Branch line being the only line into Liverpool docks. However, the initial phases of electrification scheduled until 2016 do not list this line.[90] This delay may impede the efficiency of Liverpool docks container terminal which is being extended to accommodate the largest post-Panamax container ships increasing container throughput of the terminal by 25%, entailing increased usage of the line. Local residents are campaigning to have the majority of containers to be transported by rail easing road congestion and pollution, which may increase rail traffic even further.[91] This delay in electrification may delay any proposed passenger use for the line.
The March 2009 Merseyside RUS document was published before the Department for Transport's Rail electrification document of July 2009. Major infrastructure costs will be met with the electrification project which now casts a positive light on future passenger usage for this line. To elevate the case further Merseyrail is acquiring dual-voltage, third-rail and overhead-wire passenger trains which can operate on the line. These points plus serving Liverpool and Everton FC's stadia, would lever recommissioning of passenger train introduction.[92]
The Liverpool City Region Combined Authority, Long Term Rail Strategy document of October 2017, page 37, states:
A long term proposal which will need to be considered alongside the developing freight strategy for the region and the expansion of the Port of Liverpool. The proposal envisages the introduction of passenger services which will operate from the Bootle Branch into Lime Street. An initial study is required to understand fully the freight requirements for the line and what the realistic potential for operating passenger services over the line is.[76]
The Institution of Mechanical Engineers in January 2018 recommended:
DfT instruct Network Rail to develop an appropriate specification for railway electrification that will achieve an affordable business case for a rolling programme to complete the electrification of the main lines between Britain’s principal cities and ports, and of the urban rail networks through our major city centres.[93]
North Mersey Branch
The North Mersey Branch from Bootle to Aintree is currently used only by engineering trains to gain access to Merseyrail tracks; however, Merseytravel has long-term goals to reopen and electrify the line.[61][71] The line was considered in the Merseyside Route Utilisation Strategy document, concluding that reopening could not yet be recommended. However, the Route Utilisation Strategy document went on to state:
The possibility of running passenger trains along the North Mersey and Bootle branches was examined by the RUS and cannot yet be recommended. However, future development and regeneration could lead to increased demand for such services. Any such passenger services would need to be implemented in a way that ensures current and future freight demand can be accommodated. There is also a possibility in the longer term of using other infrastructure, including the disused Wapping and Waterloo tunnels, to provide new journey opportunities.[67]

A 1909 map showing some of the rail lines around Liverpool
Skelmersdale Branch
The reopening of a section of the Skelmersdale Branch from Upholland to Skelmersdale town centre has been proposed.[61] The line was completely closed in 1963. This would give Skelmersdale, the second largest town in North West England without a railway service, direct access to Liverpool city centre. Network Rail has recommended that a further feasibility study be carried out.[67][94]
In the 1969 MALTS report, this section is referred to as the Tawd Vale branch.
In June 2009, the Association of Train Operating Companies, in its Connecting Communities: Expanding Access to the Rail Network report, called for funding for the reopening of the line from Ormskirk to Skelmersdale as part of a £500m scheme to open 33 stations on 14 lines closed in the Beeching Axe, including seven new parkway stations.[95][96] The report proposes extending the line from Ormskirk railway station by laying 3 miles of new single track along the previous route towards Rainford Junction, at a cost estimated to be in the region of £31m. The route is largely intact, however, a slight deviation north of Westhead where houses have been built on the old trackbed would be required. The proposed station would be on the north-west corner of the town near the Skelmersdale Ring Road, next to where the old station once stood.[96][97]
In December 2012 Merseytravel commissioned Network Rail to study route options and costs of connecting to Skelmersdale with Merseytravel contributing £50,000 and West Lancashire Council contributing £100,000.[98] The range of options considered including a simple park and ride on the existing Northern Line Kirkby branch, an extension of the Northern Line Kirkby branch to a new terminus in Skelmersdale and finally a connection from the Northern Line Ormskirk branch, possibly extended to create a loop via Skelmersdale between Kirkby and Ormskirk. Merseytravel are represented on a board led by Lancashire County Council which has developed a flowchart detailing how the scheme may be delivered.[99]
Lancashire County Council announced in January 2017 that the preferred site for the railway terminal station was the former Glenburn Sports College and Skelmersdale College's West Bank Campus. Whilst the council owns the land that Glenburn Sports College occupies, the currently unused West Bank Campus site is owned by Newcastle College and the council have started the process of acquiring this land. A partnership formed between the council, Merseytravel and West Lancashire Borough Council hope to deliver a service of two trains an hour to Liverpool from Skemersdale.[100] Network Rail expect the construction of the project to start in 2021 with the station being ready in 2023.[101] An October 2014 plan envisaged the station also providing services to Wigan.[102]
On page 36 of the Liverpool City Region Combined Authority, Long Term Rail Strategy document of October 2017, it states that Merseytravel is currently working with Lancashire County Council and Network Rail to
develop a plan to extend the Merseyrail network from Kirkby through to Skelmersdale, with work completed in 2019. They are considering 3rd rail electrification and other alternatives with a new station at Headbolt Lane to serve the Northwood area of Kirkby.[76]
Halton Curve

Alstom Coradia iLint hydrogen fuel cell train to be trialled on the Halton Curve.
The Halton Curve is a short section of track from Frodsham to Runcorn which currently operates one passenger train per week. The line escaped closure during the Beeching Cuts during the 1960s but all passenger services were withdrawn by the 1970s. The curve was threatened with closure in 2004 being later reprieved.
In 2016 the Liverpool City Region Combined Authority approved works to make the track bi-directional with improved signalling which would allow a greater volume of traffic to be handled by the line. The Curve will allow an hourly service from Liverpool Lime Street via Liverpool South Parkway (John Lennon Airport) to Chester.[103] Work started on the project in June 2017 with the track being ready to accept new routes by December 2018.[104][105]
The Chester to Liverpool line via the Halton Curve, which is scheduled to open in December 2018, is proposed for a trial by Alstom of their zero emissions hydrogen fuel cell trains. The line was chosen as Alstom's new technology facility is at Halebank on the Liverpool border adjacent to the line, with hydrogen supplied via the nearby Stanlow refinery.[106]
The Outer Rail Loop

West Derby station on the North Liverpool Extension Line which was to be a part of Merseyrail's Outer Loop.
The Orbital Outer Rail Loop was a part of the initial Merseyrail plans of the 1970s. The route circled the outer fringes of the city of Liverpool using primarily existing rail lines merged to create the loop. With Liverpool city having a semi-circular footprint with the city centre at the western fringe against the River Mersey, the western section of the loop would run through the city centre. The scheme was started along with the creation of Merseyrail however postponed due to cost cutting.
The concept of using the former Cheshire Lines Committee's North Liverpool Extension Line[107] route through the eastern suburbs of Liverpool as the eastern section of a rapid-transit orbital route circling the outskirts of the city first emerged before the Second World War. The proposal was for a 'belt' line using the now demolished Liverpool Overhead Railway, which ran along the river front, as its western section. In the 1960s during the planning for Merseyrail, this was developed into the Outer Rail Loop scheme - an electric rapid-transit passenger line circling the outer districts of the city by using a combination of newly electrified existing lines and a new link tunnel under the city centre merging lines to the north and south of the city centre completing the loop. A feature was that passengers on the mainline radial routes into Lime Street from the east and south could transfer onto the Outer Loop at two parkway interchange stations and complete their journey to Liverpool suburbs avoiding the need to travel into the city centre - Liverpool South Parkway was one of these stations opening thirty years after the initial proposal. The Outer Loop would have connected the eastern suburbs of the city: Gateacre, Childwall, Broad Green, Knotty Ash, West Derby, Norris Green and Walton with the city centre.[57]
As finally developed, the Outer Loop consisted of two sub-loops - serving the northern and southern suburbs with both running through the city centre from the east. These sub-loops allowed more direct journeys to the city centre from the eastern suburbs giving the overall scheme greater viability.
The eastern section of the Outer Rail Loop project was cancelled in the late 1970s because of delays and cost overruns on the Loop (Wirral Line) and Link (Northern Line) projects and local political opposition. Only the western section was built of the loop. The project was abandoned as a working proposal by Merseytravel in the 1980s. Much expense was incurred in constructing a large bridge taking the M62 over the eastern section and header tunnels at Liverpool Central station. The route is still largely intact, complete with bridges, although now the eastern section mainly forms the Liverpool Loop Country Park - a walking and cycling trail through the suburbs.
The key components of the Loop were as follows:
The West Section - The existing Merseyrail Electrics Northern Line from Sandhills in the north (later Aintree on the Ormskirk branch) to Hunts Cross. This section includes the most expensive part of the Outer Rail Loop - the Link Line tunnel under Liverpool city centre - and the reopened and electrified line from Liverpool Central to Hunts Cross.
The East Section - The former Cheshire Lines Committee North Liverpool Extension Line initially from Hunts Cross to Walton however amended to Aintree. This is now the Country Park.
The North Section - Originally the CLC line from Walton to Kirkdale via the Breeze Hill tunnel. In later versions of the scheme the North Mersey Branch from Aintree to Bootle was substituted. The latter is still intact although only used by maintenance trains whilst the former is now partially built over.
The Central Section - The central section was a later addition to the plan and effectively divided the loop into two sub-loops and also gave city centre access for the towns east of Merseyside. This included the unrealised Edge Hill Spur scheme from Liverpool Central Low Level to Edge Hill using the Waterloo Tunnel and a section of the City Line from Edge Hill to Broad Green. A major junction was to have been formed at Broad Green with the eastern section of the Outer Loop with a six platform underground station to be named Rocket under the car park of the Rocket pub near the M62/Queens Drive road junction.
The Outer Rail Loop would have been double track throughout and electrified using the 750 V DC third-rail system used by the Merseyrail Electrics network.
Although no official proposals have been made to revive the scheme in recent years, the route is effectively safeguarded with periodic calls being made by local politicians for the revival of the complete project or just the short stretch of route from Hunts Cross to Gateacre. The Gateacre service was the last to operate out of the former Liverpool Central High Level Station prior to its closure in 1972.
Since the postponement of the project, a number of Route Utilisation Strategy documents have mentioned re-opening the North Mersey Branch line, the northern section of the loop, to form a passenger link between Bootle and Aintree with stations to serve Ford and Girobank.[57][108]
The Edge Hill Spur

Victoria/Waterloo Tunnel portal at Edge Hill Station. The tunnel is an option for the Edge Hill Spur scheme.
In the 1960s/early 1970s the Edge Hill Spur scheme was proposed, to link the east of the city with the central underground section. It would have extended the Merseyrail underground network from Liverpool Central Station to Edge Hill Station using existing freight tunnels. Although part of the original Merseyrail plan with construction started, the scheme was dropped. A junction and two headers tunnels to facilitate future construction of the Spur, were built south of Central station during the construction of the Northern Line tunnel, which is a Liverpool north-south crossrail line.[109]
The construction of the Spur would have connected the City Line branches to the east of Liverpool into the electrified Merseyrail network and importantly the underground section in Liverpool's city centre. An increase in integration and connectivity of the network would have been achieved. The Spur would have also formed the central section of the proposed Outer Rail Loop splitting the loop into two smaller loops (see Outer Loop section). An additional and substantial benefit was diverting local urban trains entering the city from the east underground in the city centre. This would release platform space at Lime Street mainline terminus station for the use of only mid and long-haul mainline routes.
The initial and cheaper proposal was to re-use the 1829 Wapping freight tunnel, by means of two new single-track tunnels branched off the Northern Line tunnel at a new junction named Liverpool Central South Junction, south of Central Station. The Wapping Tunnel would have given access to Edge Hill via the historic Cavendish cutting, built for the 1830 Liverpool and Manchester Railway. Access to the City Line would have been obtained via a flyover to the east of Edge Hill Station over the main lines from Lime Street. This flyover has since been demolished.
In the early 1970s, Liverpool City Council planners proposed an alternative scheme, which was subsequently adopted. This revised route would permit a new underground station to be constructed to serve Liverpool University, behind the Student's Union building in Mount Pleasant. It would extend the two connecting tunnels from Central Station in a large radius curve to the north, passing beneath the mainline Lime Street station approach cutting accessing Edge Hill via a section of the Waterloo/Victoria Tunnel. On emerging from this tunnel at the existing Edge Hill Station, the route would be on the north side of the main lines thereby removing the need for a flyover.[57]
Although powers were obtained to build this line under the 1975 Merseyside Metropolitan Railway Act, construction was postponed due to the financial cutbacks and political opposition that also halted the Outer Rail Loop project. The east of Liverpool has suffered in many aspects ever since. An attempt was made to revive the project in the mid-1980s but it was found to be not financially viable.
Following the collapse of the Merseytram scheme in 2006, proposals were considered to revive the project.[110] and the route of the tunnels is safeguarded. Further references are made to the scheme, as a future option, in MerseyTravel's 30-year plan.[61]
A further proposal to resurrect the Edge Hill spur scheme with a new station at Paddington Village was revealed in 2016 by Liverpool's mayor Joe Anderson, as part of a scheme to extend Liverpool's Knowledge Quarter onto the site of the former Archbishop Blanche School.[111] A feasibility study to reopen the Wapping Tunnel was commissioned and delivered in May 2016. The report found that the Wapping Tunnel was in good condition though suffered from flooding in places and would require some remedial work, but that the concept of re-opening the tunnel was viable[112]
St James Station
Liverpool’s Strategic Investment Framework, the blueprint for the city’s regeneration published in November 2012, states the importance of reopening St James’ station.[113] further mention was made in Merseytravel's 30-year plan of 2014.[61] The station, which is located on the corner of St.James' Place and Parliament Street - immediately south of Liverpool's city centre - was closed in 1917. The station saw little use being the next station to Liverpool Central high-level terminus station. The station is in a deep cutting on the operational crossrail Northern Line tunnel section between Liverpool Central Station and Brunswick Station. Being on a well connected crossrail line the station now gives greater appeal for passenger usage than in 1917.
The original platforms and surface level buildings have mainly been removed leaving some platform level rooms carved out of the rock in the sides of the cutting. The cutting the original station was built in is not long enough to accommodate platforms for a six car train, and would entail the station being partially built inside the tunnel. As the cutting formerly contained three tracks with now only two tracks using the tunnel, ample room should be available for the construction of full width platforms to modern requirements. The original stair access would likely need to be replaced with lifts or escalators. Although located in a deep cutting, with tunnelled sections either side, the station should be sufficiently open to the air not to be classed as a sub-surface station and therefore not subject to the requirement for costly fire prevention measures as was the case with Conway Park railway station on the Merseyrail network in Birkenhead.
One aim of the Strategic Investment Framework is to boost the Baltic Triangle, which is becoming an important location for the city's creative sector. Local people and businesses have pledged to work with Liverpool Vision and Merseytravel to assess if the station may be re-opened. If so, the next step will be the development of a business plan for presentation to Network Rail.[114]
See also
- List of underground stations of the Merseyrail network
References
^ ab "Merseyrail". Merseytravel. Retrieved 26 March 2018..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ https://www.merseyrail.org/media/661807/dppp-merseyrail-passenger.pdf
^ "Merseyrail Key Statistics 2016-2017" (PDF). Office of Rail and Road. 6 July 2017. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
^ "Abellio Group Head Office" Group corporate website, Abellio, Utrecht, Netherlands, Undate. Retrieved 19 June 2015.
^ ab "Merseyrail A brief history" (PDF). Merseytravel. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
^ "Merseyrail performance" (PDF). Merseyrail. Retrieved 12 October 2015.
^ "Merseytravel Facts and Figures". Merseytravel. Retrieved 5 July 2016.
^ "Merseyrail at Serco". Serco. Retrieved 21 July 2009.
^ http://orr.gov.uk/__data/assets/pdf_file/0015/22056/passenger-rail-usage-2015-16-q4.pdf
^ "Merseyrail corporate information | Merseyrail Electrics | Serco | Abellio". Merseyrail. 20 July 2003. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
^ "Northern Rail Electric". Northern Rail. Archived from the original on 10 June 2015. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
^ ab "Electrifying Liverpool-Manchester". The Rail Engineer. Ashby-de-la-Zouch. 28 November 2012.
^ abcde "Merseyrail Trains History". Merseyrail. Archived from the original on 8 September 2008. Retrieved 20 July 2009.
^ "Electric rail link plans for town". The St Helens Reporter. 17 December 2009.
^ "Merseyrail Northern Line". Merseyrail. Retrieved 28 August 2018.
^ "Merseyrail Wirral Line". Merseyrail. Retrieved 28 August 2018.
^ "Merseyrail City Line". Merseyrail. Retrieved 28 August 2018.
^ DVV Media Group GmbH. "Merseyrail train refurbishment". Railway Gazette. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
^ "Step on the Culture train!". Merseytravel. 21 February 2008. Archived from the original on 26 December 2008.
^ Cox, Laura (11 October 2011). "Merseyrail train given a Beatles make-over to drive tourism". Liverpool Daily Post. Archived from the original on 11 November 2011. Retrieved 13 November 2011.
^ "Page Not Found - Liverpool Hope University". hope.ac.uk.
^ "Red Rum canters once again!". Merseytravel. 15 July 2008. Archived from the original on 17 July 2008.
^ Bartlett, David (26 October 2011). "Train Named in memory of Jack Spriggs". Liverpool Daily Post (blog). Archived from the original on 21 November 2011. Retrieved 30 October 2011.
^ "Train Naming Ceremony For Stuart Mason". Qlocal.co.uk. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
^ "Train named in honour of Harold Wilson". Merseytravel.gov.uk. 13 March 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
^ "Merseyrail reveals new-look seating for its trains". Liverpool Echo. Retrieved 6 March 2015.
^ "Merseyrail in talks over brand new train fleet | News Comment". Liverpool Confidential. Archived from the original on 29 November 2014. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
^ Hodgson, Neil (10 October 2013). "Bright future for Merseyrail, vow franchise partners". Liverpool Daily Post. Archived from the original on 18 October 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
^ "Refurbishment Work Research". Merseyrail. Archived from the original on 15 December 2013.
^ "Class 503, a brief history". Andrew Phillips. Archived from the original on 5 February 2016. Retrieved 8 June 2015.
^ Maund 2009, p. 214
^ https://www.smartrailworld.com/stadler-signs-700-million-deal-to-replace-the-uks-oldest-fleet-on-liverpools-merseytravel-line
^ "Merseyrail to get new train fleet". Global RailNews. 19 December 2016. Retrieved 19 December 2016.
^ "Merseytravel and Stadler sign new fleet deal, but legal challenge remains". Rail Technology Magazine. 16 February 2017.
^ "Construction begins on Kirkdale depot to maintain new Merseyrail fleet". Rail Technology Magazine. 28 September 2017.
^ "Route O - Merseyside" (PDF). Network Rail. 30 March 2010. p. 10. Retrieved 30 May 2011.
^ "Network Rail 2009 Strategic Business Plan - Merseyrail Route 21" (PDF). Network Rail. 2009. Retrieved 25 July 2009.
^ ab House of Common Briefing Paper SN6521 Railways: franchising policy, 30 September 2015, Louise Butcher
^ "Andy Heath appointed new managing director of Merseyrail". Merseyrail. Merseyrail. Retrieved 11 August 2018.
^ Hodgson, Neil (4 December 2007). "We have taken the 'misery' out of Merseyrail". Liverpool Echo.
^ Hodgson, Neil (14 December 2007). "Merseyrail trains in first place". Liverpool Echo.
^ "Performance by train operator". Network Rail.
^ Weston, Alan (11 February 2010). "Merseyrail trains are most reliable in the UK". Liverpool Echo. Retrieved 22 March 2010.
^ Turner, Alex (27 October 2010). "Merseyrail profits gather speed to reach record levels". Liverpool Daily Post. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
^ Turnbull, Barry (27 April 2009). "Merseyrail in record profits surge". Liverpool Daily Post. Retrieved 21 July 2009.
^ "Culture year is a boon for Merseyrail". Liverpool Daily Post. 10 September 2008. Retrieved 21 July 2009.
^ Neild, Larry (5 September 2007). "Merseyrail takes 840 to court over feet on seats". Liverpool Daily Post.
^ Neild, Larry (11 September 2007). "Is Merseyrail's feet on seats policy too harsh?". Liverpool Daily Post.
^ "Merseyrail - train times & timetables, journey planner & service updates". merseyrail.org.
^ "Liverpool Merseyrail". UrbanRail. Retrieved 21 July 2009.
^ "Birkenhead Monks Ferry". Disused Station. Retrieved 21 July 2009.
^ "Merseyside Area land use Transportation study (MALTS) project report. | The National Archives". Discovery.nationalarchives.gov.uk. Retrieved 23 July 2016.
^ "Liverpool City Centre Plan - City Centre Planning Group, 1965"
^ ab Couch, Chris (2003). City of change and challenge: urban planning and regeneration in Liverpool. Aldershot: Ashgate.
ISBN 978-1-84014-857-2
^ "OPSI Statutory Instrument 2003 No. 1696". OPSI. Retrieved 21 July 2009.
^ "Liverpool Central High Level". Disused Station. Retrieved 21 July 2009.
^ abcdef Maund, T.B. (2001). Merseyrail electrics: the inside story. Sheffield: NBC Books. OCLC 655126526.
^ "Planning approval granted for new Maghull North station scheme". Merseytravel. Retrieved 19 February 2017.
^ "Liverpool City Region Long Term Rail Strategy" (PDF). Merseytravel. Retrieved 7 September 2014.
^ Network Rail Strategic Development Plan for Merseyrail 2009-2014.
^ abcdefghij Shennan, Paddy (28 August 2014). "Merseytravel plan to open or reopen host of new stations". Liverpool Echo. Retrieved 30 August 2014.
^ http://www.merseytravel.gov.uk/Site%20Documents/LCR%20LTRS_Strategy%20Summary_01_08_14_Final%20Issue%20(6)_MTravel.pdf
^ Bartlett, David (11 October 2012). "Director announced for Merseyrail new trains project". Liverpool Daily Post.
^ "Merseytravel names five international bidders in new fleet and depot shortlist". Rail Technology Magazine. 12 January 2016. Retrieved 27 March 2016.
^ "Merseytravel reveals new £460m train fleet plans - with no train guards".
^ ab Broadbent, Steve (December 2008). "Merseyside RUS addresses serious growth issues". Rail (607). Peterborough. pp. 10–11.
^ abcd Merseyside Route Utilisation Strategy. Network Rail.
^ Schofield, Ben (3 August 2009). "Tram link bid for Liverpool airport". Liverpool Daily Post. Retrieved 20 August 2009.
^ "Liverpool Airport Rail Links Feasibility Study" (PDF). Merseytravel. Retrieved 4 March 2018.
^ "Millions to be spent on Mersey rail network". Liverpool Daily Post. 3 April 2007.
^ abcd "Welcome to the TravelWise Merseyside website" (PDF). transportmerseyside.org.
[permanent dead link]
^ abcde "Network RUS Electrification" (PDF). October 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 October 2014. Retrieved 20 October 2013.
^ abc Rudgard, Olivia (5 March 2015). "Two Merseyside lines prioritised for electrification". Liverpool Echo. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
^ ab "Place North West - Priority electrification routes sent to Government". 6 March 2015.
^ ab Lancashire and Cumbria Route Utilisation Strategy, Network Rail.
^ abcdefgh "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 November 2017. Retrieved 17 May 2018.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ "Merseytravel fury over £207m price tag for Bidston-Wrexham rail link". Wirral News. Liverpool. 5 November 2008. Archived from the original on 8 January 2009.
^ "The Wrexham to Bidston railway (The Borderlands line): Electrification plans". Penfmorfa. Retrieved 17 February 2007.
^ Hughes, Ian (25 October 2012). "Progress on Liverpool-North Wales rail link". North Wales Weekly News. Conwy.
^ "Loop line renewal is 'short-term pain worth long-term gain of rail boost' writes MerseyTravel chief". Wirral Globe. Retrieved 1 December 2016.
^ Clinnick, Richard (13 January 2015). "Battery-powered Electrostar enters traffic". RAIL. Retrieved 17 April 2015.
^ ab Long-term planning – Network Rail
^ "Transport for Wales announces Wales and Borders preferred bidder". www.keolisamey.cymru. Retrieved 11 June 2018.
^ "Vivarail to supply hybrid D-Train fleet in first train deal for new Wales franchise". www.railtechnologymagazine.com. Retrieved 11 June 2018.
^ Hughes, Owen (10 June 2018). "This is what the new rail franchise will mean for North Wales train passengers". northwales. Retrieved 11 June 2018.
^ Transport debate in Parliament 27 April 2011[permanent dead link], House of Commons.
^ "Merseytravel Committee Rail Development And Delivery" (PDF). Merseytravel. Retrieved 6 December 2016.
^ "Disused Stations: Canada Dock Station". subbrit.org.uk.
^ ab Rail Electrification Document, Department for Transport.
^ "Balfour Beatty wins second phase electrification contract in UK". Railway Technology. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
^ Johnson, Mark (15 November 2011). "Liverpool £210m River Mersey terminal to go ahead after dredging permission given". Liverpool Daily Post.
^ "Rail electrification" (PDF). Department for Transport. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 August 2009.
^ A Breath of Fresh Air: new solutions to reduce transport emissions
^ "The Railway". Skemheritage.org.uk. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
^ "Operators call for new rail lines". BBC News. 15 June 2009. Retrieved 15 June 2009.
^ ab "Connecting Communities – Expanding Access to the Rail Network" (PDF). London: Association of Train Operating Companies. June 2009. Retrieved 7 September 2018.
^ "Skelmersdale Station". Disused Stations. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
^ "Skelmersdale Rail Link" (PDF). Merseytravel. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
^ "Agenda item - Rail Schemes Development and Delivery". Merseytravel. 3 November 2016. Retrieved 1 December 2016.
^ "Preferred site for Skelmersdale's first railway station revealed". BBC News. 2 February 2017. Retrieved 2 February 2017.
^ "Skelmersdale link moves towards GRIP3". www.railmagazine.com. Retrieved 3 February 2017.
^ http://www.lancashire.gov.uk/media/313320/DRAFT-West-Lancashire-Masterplan-FINAL.pdf
^ "Cheshire Halton Curve rail could fully re-open in 2018". Railtechnologymagazine.com. Retrieved 23 July 2016.
^ "Maynard confirms Halton Curve will reopen at end of 2018". www.railtechnologymagazine.com. Retrieved 3 February 2017.
^ Halton Curve work will mean disruption to rail travellers - Chester Chronicle
^ Alstom eyes Liverpool trials for hydrogen fuel-cell powered train The Engineer
^ Cheshire Lines Committee Lines: North Liverpool Extension Line, Southport and Cheshire Lines Extension Railway, Garston and Liverpool Railway
(
ISBN 1158356277)
^ [1][dead link]
^ Eighth wonder – Rail Engineer
^ Coligan, Nick (17 July 2006). "The trams are dead, long live the train". Liverpool Echo. Retrieved 10 September 2008.
^ Neild, Larry (13 June 2016). "REVEALED: Liverpool set to get its own Paddington station". Liverpool Confidential. Retrieved 23 July 2016.
^ https://www.merseytravel.gov.uk/about-us/disclosure-logs/Documents/RSN16726%20-%20EIR%20Request%20-%20Wapping%20Tunnel%20Feasbility%20Study.pdf
^ "Liverpool St. James Station". Disused Stations. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
^ Houghton, Alistair (29 November 2012). "Bid to reopen St James's Station in Liverpool". Liverpool Echo. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
Sources
Maund, T.B. (2009). The Wirral Railway and its Predecessors. Gloucestershire: Lightmoor Press. ISBN 978-1-899-88938-9. OCLC 604772937.
Further reading
Hilbert, Martyn (2016). Merseyrail Electric. Fonthill Media. ISBN 9781781555132.
Maund, T.B. (2001). Merseyrail Electrics: The Inside Story. NBC Books. ASIN B0047EA3HU. OCLC 655126526.
Merseyside Passenger Transport Executive (1978). The Story of Merseyrail. Merseyside Passenger Transport Executive. ASIN B000MAYEK0. OCLC 8740619.
Rapson, David (August 1983). "The Mersey beat". Rail Enthusiast. EMAP National Publications. pp. 26–31. ISSN 0262-561X. OCLC 49957965.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Merseyrail. |
- Official Website
- Travel Wise: Merseyrail
| Preceded by Arriva Trains Merseyside | Operator of Merseyrail franchise 2003 - present | Incumbent |