German-occupied Europe
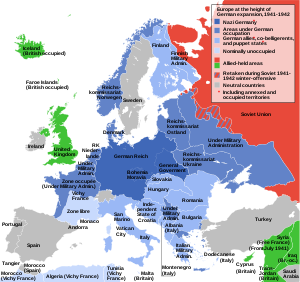
Europe at the height of German control in 1942
German-occupied Europe refers to the sovereign countries of Europe which were occupied and civil occupied including puppet government by the military forces and the government of Nazi Germany at various times between 1939 and 1945 and administered by the Nazi regime.[1]
The furthest east in Europe the German Wehrmacht managed to occupy was the town of Mozdok in the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics.
The furthest north in Europe the German Wehrmacht managed to occupy was the settlement of Barentsburg in the Kingdom of Norway.
The furthest south in Europe the German Wehrmacht managed to occupy was the island of Gavdos in the Kingdom of Greece.
The furthest west in Europe the German Wehrmacht managed to occupy was the island of Ushant in the French Republic.
Contents
1 Background
2 Occupied countries
2.1 Governments in exile
2.1.1 Allied governments in exile
2.1.2 Axis governments in exile
2.1.3 Neutral governments in exile
3 See also
4 References
5 Bibliography
6 External links
Background
Several German occupied countries entered World War II as Allies of the United Kingdom[2] or the Soviet Union.[3] Some were forced to surrender before outbreak of the war such as Czechoslovakia;[4] others like Poland (invaded on 1 September 1939)[1] were conquered in battle and then occupied. In some cases, the legitimate governments went into exile, in other cases the governments-in-exile were formed by their citizens in other Allied countries.[5] Some countries occupied by Nazi Germany were officially neutral. Others were former members of the Axis powers that were occupied by German forces at a later stage of the war.[6][7]
Occupied countries
The countries occupied included all, or most of the following:
Country or territory of occupation | Puppet state(s) or military administration(s) | Timeline of occupation(s) | German annexed territory | Resistance movement(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 September 1943 – 29 November 1944 | None | Albanian resistance | ||
| 30 June 1940 – 9 May 1945 | None | Guernseyian resistance | ||
| 1 July 1940 – 9 May 1945 | None | Jerseyian resistance | ||
|
| 1 October 1938 – 11 May 1945 | Czechoslovakian resistance | |
| None, see Anschluss | 12 March 1938 – 9 May 1945 | Austrian resistance | ||
| None | 1 September 1939 – 9 May 1945 | Danzigian resistance | ||
|
| 10 May 1940 – 9 May 1945 | French resistance | |
| 10 May 1940 – February 1945 | Luxembourg resistance | ||
| 8 September 1943 – 8 May 1945 | None | |||
| 10 May 1940 – February 1945 |
| Belgian resistance | |
| protectorate state | 9 April 1940 – 5 May 1945 | None | Danish resistance | |
| 6 April 1941 – 8 May 1945 | None | Greek resistance | |
| 19 March 1944 – May 1945 | None | Hungarian resistance | |
| 8 September 1943 – 2 May 1945 | None | Italian resistance | |
| 9 April 1940 – 8 May 1945 | None | Norwegian resistance | |
| 10 May 1940 – 20 May 1945 | None | Dutch resistance | ||
| 6 April 1941 – 15 May 1945 | Yugoslav resistance | ||
| None | 8 September 1943 – 3 September 1944 | None | ||
| None | 15 September 1944 – 25 April 1945 | None | Finnish resistance | |
Provisional Government of Lithuania | 22 March 1939 – 21 July 1940 23 June 1941 – 5 August 1941 | Lithuanian resistance | ||
| 1 September 1939 – 9 May 1945 | Polish resistance | ||
| None | 17 September 1944 – 20 September 1944 | None | ||
| April 30, 1941 – January 1945 | None | Serbian resistance | |
| 23 March 1939 – May 1945 | None | Slovakian resistance | ||
| None | 1 March 1935 – April 1945 |
| Saar Basinian resistance | |
| 30 June 1941 – September 1941 | Ukrainian resistance | |||
| 22 June 1941 – 10 May 1945 | Soviet resistance |
Governments in exile
Allied governments in exile
Government in exile | Capital in exile | Timeline of exile | Occupier(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1941 – 1945 | |||
(1940 – 1941)
| 1940 – August 31, 1944 |
| |
(September 29/30, 1939 – 1940) (1940 – June 12, 1940)
| September 29/30, 1939 – December 22, 1990 |
| |
(October 22, 1940 – September 8, 1944) | October 22, 1940 – September 8, 1944 |
| |
| 1943 – 1945 | |||
| 1940 – 1944 | |||
| April 29, 1941 – October 12, 1944 |
| ||
| June 7, 1940 – May 31, 1945 | |||
| June 7, 1941 – March 7, 1945 | Commissioner Government | ||
| 1940 – 1945 | |||
(October 2, 1939 – 1940)
| October 2, 1939 – April 2, 1945 |
|
Axis governments in exile
Government in exile | Capital in exile | Timeline of exile | Occupier(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| September 16, 1944 – May 10, 1945 |
| ||
| 1944 – April 22, 1945 | |||
| March 28, 1945 – May 7, 1945 |
| |
| 1944 – 1945 | |||
Montenegrin State Council | 1944 – May 8, 1945 | ||
| April 4, 1945 – 8 May 1945 |
Neutral governments in exile
Government in exile | Capital in exile | Timeline of exile | Occupier(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
(1923 – 1938)
| 1919 – present |
| |
(1944 – August 20, 1991)
| June 17, 1940 – August 20, 1991 |
| |
(1920 – 1939)
| 1920 – August 22, 1992 |
|
See also
Drang nach Osten ("The Drive Eastward")
Lebensraum ("Living Space")
Neuordnung ("New Order")- Areas annexed by Nazi Germany
- Pan-Germanism
References
^ ab Encyclopædia Britannica, German occupied Europe. World War II. Retrieved 1 September 2015 from the Internet Archive.
^ Prazmowska, Anita (1995-03-23). Britain and Poland 1939-1943: The Betrayed Ally. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521483858..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Moorhouse, Roger (2014-10-14). The Devils' Alliance: Hitler's Pact with Stalin, 1939-1941. Basic Books. ISBN 9780465054923.
^ Goldstein, Erik; Lukes, Igor (2012-10-12). The Munich Crisis, 1938: Prelude to World War II. Routledge. ISBN 9781136328329.
^ Conway, Martin; Gotovitch, José (2001-08-30). Europe in Exile: European Exile Communities in Britain 1940-45. Berghahn Books. ISBN 9781782389910.
^ Hanson, Victor Davis (2017-10-17). The Second World Wars: How the First Global Conflict Was Fought and Won. Basic Books. ISBN 9780465093199.
^ Cornelius, Deborah S. (2011). Hungary in World War II: Caught in the Cauldron. Fordham Univ Press. ISBN 9780823233434.
Bibliography
- Bank, Jan. Churches and Religion in the Second World War (Occupation in Europe) (2016)
- Gildea, Robert and Olivier Wieviorka. Surviving Hitler and Mussolini: Daily Life in Occupied Europe (2007).
- Klemann, Hein A.M. and Sergei Kudryashov, eds. Occupied Economies: An Economic History of Nazi-Occupied Europe, 1939-1945 (2011).
- Lagrou, Pieter. The Legacy of Nazi Occupation: Patriotic Memory and National Recovery in Western Europe, 1945-1965 (1999)
Mazower, Mark (2008). Hitler's Empire: Nazi Rule in Occupied Europe. London: Allen Lane. ISBN 9780713996814.
- Snyder, Timothy. Bloodlands: Europe Between Hitler and Stalin (2010), on Eastern Europe
- Toynbee, Arnold, ed. Survey of International Affairs, 1939–1946: Hitler's Europe (Oxford University Press. 1954) 730pp. online review; full text online free
- Carlyle Margaret, ed. Documents on International Affairs, 1939–1946. Volume II, Hitler's Europe (Oxford University Press. 1954) 362pp.)
External links
- Map of Europe in 1942
- http://www.worldwar2history.info/war/Allies.html
- http://www.bbc.co.uk/history/events/germany_advances_through_europe
http://www.holocaustresearchproject.org/nazioccupationʘ[permanent dead link]