Russo-Georgian War
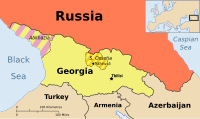
The Russo-Georgian War was a war between Georgia, Russia and the Russian-backed self-proclaimed republics of South Ossetia and Abkhazia.[note 3] The war took place in August 2008 following a period of worsening relations between Russia and Georgia, both formerly constituent republics of the Soviet Union. The fighting took place in the strategically important Transcaucasia region. It was regarded as the first European war of the 21st century.[30]
The Republic of Georgia declared its independence in early 1991 as the Soviet Union began to fall apart. Amidst this backdrop, a war between Georgia and separatists left parts of the former South Ossetian Autonomous Oblast under the de facto control of Russian-backed but internationally unrecognised separatists. Following the war, a joint peacekeeping force of Georgian, Russian, and Ossetian troops was stationed in the territory. Meanwhile, a similar stalemate developed in the region of Abkhazia, where Abkhaz separatists had waged their own war in 1992–1993. Following Vladimir Putin's rise to power in Russia in 2000 and a pro-Western change of power in Georgia in 2003, relations between Russia and Georgia began to deteriorate, reaching a full diplomatic crisis by April 2008. By 1 August 2008, South Ossetian separatists began shelling Georgian villages, with a sporadic response from Georgian peacekeepers in the area.[31][32][33][34][35] Artillery attacks by pro-Russian separatists broke a 1992 ceasefire agreement.[36][37] To put an end to these attacks and restore order, the Georgian Army was sent to the South Ossetian conflict zone on 7 August.[38] Georgians took control of most of Tskhinvali, a separatist stronghold, in hours.
Russian troops had illicitly crossed the Russo-Georgian state border and advanced into the South Ossetian conflict zone by 7 August before the Georgian military response.[37][39][40][41][42] Russia accused Georgia of "aggression against South Ossetia",[38] and launched a large-scale land, air and sea invasion of Georgia on 8 August with the pretext of "peace enforcement" operation.[43] Russian and South Ossetian forces battled Georgian forces in and around South Ossetia for several days, until Georgian forces retreated. Russian and Abkhaz forces opened a second front by attacking the Kodori Gorge held by Georgia. Russian naval forces blockaded part of the Georgian coast. The Russian air force attacked targets beyond the conflict zone, in undisputed parts of Georgia. This was the first war in history in which cyber warfare coincided with military action. An active information war was also waged during and after the conflict. The French presidency of the European Union, in the person of Nicolas Sarkozy, negotiated a ceasefire agreement on 12 August.
Russian forces temporarily occupied the Georgian cities of Zugdidi, Senaki, Poti, and Gori, holding on to these areas beyond the ceasefire. The South Ossetians destroyed most ethnic Georgian villages in South Ossetia and were responsible for an ethnic cleansing of Georgians. Russia recognised the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia from Georgia on 26 August; in response, the Georgian government severed diplomatic relations with Russia. Russia mostly completed its withdrawal of troops from undisputed parts of Georgia on 8 October. In the aftermath, Russia's international relations were largely unharmed. The war displaced 192,000 people and while many returned to their homes after the war, 20,272 people, mostly ethnic Georgians, remained displaced as of 2014. Russia has, since the war, occupied Abkhazia and South Ossetia in violation of the ceasefire agreement of August 2008.[44]
Contents
1 Background
1.1 History
1.2 Russian interests and involvement
1.3 Unresolved conflicts
1.4 Relations between Georgia and the West
2 Prelude
2.1 April–July 2008
2.2 Early August
3 Large-scale conflict
3.1 Battle of Tskhinvali
3.2 Bombing and occupation of Gori
3.3 Abkhaz front
3.4 Occupation of Poti
3.5 Bombing of Tbilisi and surroundings
3.6 Media and cyber war
4 Ceasefire agreement
5 Aftermath
5.1 Russian withdrawal
5.2 Recognition of Abkhazia and South Ossetia by Russia
5.3 International monitors
5.4 Geopolitical impact
6 Humanitarian impact and war crimes
7 Reactions
7.1 International reactions
7.2 NATO reaction in the Black Sea
8 Combatants
8.1 Georgian order of battle
8.2 Russo-South Ossetian-Abkhaz order of battle
8.3 Military analysis
8.3.1 Georgia
8.3.2 Russia
8.4 Equipment losses and cost
8.4.1 Georgia
8.4.2 Russia and South Ossetia
9 See also
10 Notes
11 References
12 Further reading
13 External links
Background
History

Fragment of the 1856 map by J. H. Colton, showing the territory of modern South Ossetia within Georgia and Imeria. Modern North Ossetia corresponds to "Ossia" (Ossetia) in the North Caucasus.

Creation of the South Ossetian AO in the place of Georgian regions in 1922.
In the 10th century AD, Georgia for the first time emerged as an ethnic concept in the territories where the Georgian language was used to perform Christian rituals. After the Mongol invasions of the region, the Kingdom of Georgia eventually was split into several states. In the 19th century, the Russian Empire gradually took over the Georgian lands. In the aftermath of the Russian revolution, Georgia declared independence on 26 May 1918.[45]
The Ossetian people are autochthonous to North Ossetia (located in the North Caucasus).[46] Controversy surrounds the date of Ossetian arrival in Transcaucasia. According to one theory, they first migrated there during the 13th and 14th centuries AD,[47] and resided alongside the Georgians peacefully for hundreds of years.[48] In 1918, conflict began between the landless Ossetian peasants living in Shida Kartli, who were affected by Bolshevism and demanded ownership of the lands they worked, and the Menshevik government backed ethnic Georgian nobility, who were legal owners. Although the Ossetians were initially discontented with the economic stance of Tbilisi authorities, the tension shortly transformed into ethnic conflict. During uprisings in 1919 and 1920, the Ossetians were covertly supported by Soviet Russia, but even so, were defeated.[49]
The independent Democratic Republic of Georgia was invaded by the Red Army in 1921 and a Soviet government was installed.[50] The government of Soviet Georgia created an autonomous administrative unit for Transcaucasian Ossetians in April 1922, called the South Ossetian Autonomous Oblast.[51] Historians such as Stephen F. Jones, Emil Souleimanov and Arsène Saparov believe that the Bolsheviks awarded this autonomy to the Ossetians in exchange for their help against the Democratic Republic of Georgia,[49][52][53] since this area had never been a separate entity prior to the Russian invasion.[38][54][55]
Nationalism in Soviet Georgia gained momentum in 1989 with the weakening of the Soviet Union. The Kremlin endorsed South Ossetian nationalism as a counter against the Georgian independence movement.[56] On 11 December 1990, the Supreme Soviet of Georgia, responding to South Ossetia's attempt at secession, annulled the region's autonomy.[57] A military conflict broke out between Georgia and South Ossetian separatists in January 1991.[58] Georgia declared its restoration of independence on 9 April 1991, thus becoming the first non-Baltic state of the Soviet Union to do so.[59] The South Ossetian separatists were aided by the former Soviet military units now controlled by Russia.[60] By June 1992, the possibility of a full-scale war between Russia and Georgia increased as bombing of Georgian capital Tbilisi in support of South Ossetian separatists was promised by Russian authorities.[61][62] Georgia endorsed a ceasefire agreement on 24 June 1992 to prevent the escalation of the conflict with Russia.[63] Georgian, South Ossetian, Russian and North Ossetian peacekeepers were posted in South Ossetian conflict zone under the Joint Control Commission's (JCC) mandate.[64] Some, mostly ethnically Georgian parts of the former South Ossetian Autonomous Oblast remained under the Georgian control.[58] The Tskhinvali-based separatist authorities of the self-proclaimed Republic of South Ossetia were in control of one third of the territory of the former South Ossetian Autonomous Oblast before the 2008 war.[65]
This situation was mirrored in Abkhazia, an autonomous republic in the Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic, where the Abkhaz separated from Georgia during the war in the early 1990s.[60] The population of Abkhazia was reduced to 216,000 after an ethnic cleansing of Georgians, the single largest ethnic group in the region, a decrease from 525,000 before the war.[66] The upper Kodori Gorge (in northeast Abkhazia) remained beyond the unrecognised Abkhaz separatist government's sway.[67]
Russian interests and involvement
Transcaucasia lies between the Russian region of the North Caucasus and the Middle East, constituting a "buffer zone" between Russia and the Middle East. It borders Turkey and Iran. The strategic importance of the region has made it a security concern for Russia. Significant economic reasons, such as presence or transportation of oil, also affect interest in Transcaucasia. Rule over Transcaucasia, according to Swedish academic Svante Cornell, would allow Russia to manage Western involvement in Central Asia, the area of geopolitical importance.[68]
Russia saw the Black Sea coast and being adjacent to Turkey as invaluable strategic attributes of Georgia.[69] Russia had more vested interests in Abkhazia than in South Ossetia, since the Russian military deployment on the Black Sea coast was seen as vital to Russian influence in the Black Sea.[43] Before the early 2000s, South Ossetia was originally intended as a tool to retain a grip on Georgia.[56]
Vladimir Putin became president of the Russian Federation in 2000, which had a profound impact on Russo-Georgian relations. The conflict between Russia and Georgia began to escalate in December 2000, when Georgia became the first and sole member of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) on which the Russian visa regime was enforced. Eduard Kokoity, an alleged member of mob, became de facto president of South Ossetia in December 2001; he was endorsed by Russia since he would subvert the peaceful reunification of South Ossetia with Georgia. The Russian government began massive allocation of Russian passports to the residents of Abkhazia and South Ossetia in 2002 without Georgia's permission; this "passportization" policy laid the foundation for Russia's future claim to these territories.[70] In 2003, President Putin began to consider the possibility of a military solution to the conflict with Georgia.[71]
After Georgia deported four suspected Russian spies in 2006, Russia began a full-scale diplomatic and economic war against Georgia, followed by the persecution of ethnic Georgians living in Russia.[70]
By 2008, most residents of South Ossetia had obtained Russian passports. According to Reuters, Russia supplied two-thirds of South Ossetia's yearly budget before the war.[72] South Ossetia's de facto government predominantly employed Russian citizens, who had occupied similar government posts in Russia, and Russian officers dominated in South Ossetia's security organisations.[73]
Unresolved conflicts

U.S. President George W. Bush and Georgian President Mikheil Saakashvili in Tbilisi, May 2005
The conflicts in Georgia remained at a stalemate until 2004,[74] when Mikheil Saakashvili came to power after Georgia's Rose Revolution, which ousted president Eduard Shevardnadze.[75] Restoring South Ossetia and Abkhazia to Georgian control was a first concern of Saakashvili.[76]
The Georgian government launched an initiative to curb smuggling from South Ossetia in 2004 after its success in restoring control in Adjara. Tensions were further escalated by South Ossetian authorities.[76] Intense fighting took place between Georgian forces and the South Ossetians between 8 and 19 August.[77]
At the Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe in Strasbourg in January 2005, Georgian president Saakashvili proposed a peace settlement for South Ossetia within a unified Georgian state. The proposal was rejected by South Ossetian leader Eduard Kokoity.[78] In 2006, Georgia sent security forces to the Kodori Valley region of Abkhazia, when a local militia leader rebelled against Georgian authorities.[67] In 2007, Georgia established what Russia called a "puppet government" in South Ossetia, led by Dmitry Sanakoyev (former South Ossetian prime minister), calling it a provisional administration.[79]
In early March 2008, Abkhazia and South Ossetia submitted formal requests for their recognition to Russia's parliament shortly after the West's recognition of Kosovo to which Russia had been resisting. Dmitry Rogozin, Russian ambassador to NATO, hinted that Georgia's aspiration to become a NATO member would cause Russia to support the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia.[80] The Russian State Duma adopted a resolution on 21 March, in which it called on the President of Russia and the government to consider the recognition.[81]
Georgia began proposing the placement of international peacekeepers in the separatist regions when Russia began to apply more force on Georgia after April 2008. The West launched new initiatives for peace settlement, with peace proposals being offered and discussions being organised by the European Union, the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) and Germany. The separatists dismissed the German project for Abkhazia approved by Georgia. Russia and the separatists did not attend an EU-backed meeting regarding Abkhazia. They also dismissed an OSCE offer to renew talks regarding South Ossetia.[82]
Relations between Georgia and the West
One of President Saakashvili's primary aims for Georgia was to become NATO's member,[74] which has been one of the major stumbling blocks in Georgia-Russia relations.[83]
Although Georgia has no notable gas or oil reserves, its territory hosts part of the Baku–Tbilisi–Ceyhan pipeline supplying Europe.[84] Russia, Iran and the Persian Gulf countries opposed the construction of the pipeline.[85] The pipeline circumvents both Russia and Iran. Because it has decreased Western dependence on Middle East's oil, the pipeline has been a major factor in the United States' backing for Georgia.[86]

Russian President Vladimir Putin at the 2008 Bucharest Summit
During the NATO summit in Bucharest in April 2008, American president George W. Bush campaigned for offering a Membership Action Plan (MAP) to Georgia and Ukraine. However, Germany and France said that offering MAP to Ukraine and Georgia would be "an unnecessary offence" for Russia.[87] NATO stated that Ukraine and Georgia would be admitted in the alliance and pledged to review the requests for MAP in December 2008.[88] Russian President Vladimir Putin was in Bucharest during the summit. At the conclusion of the summit on 4 April, Putin said that NATO's enlargement towards Russia "would be taken in Russia as a direct threat to the security of our country".[89] Following the Bucharest summit, Russian hostility increased and Russia started to actively prepare for the invasion of Georgia.[90]Chief of the General Staff of the Russian Armed Forces Yuri Baluyevsky said on 11 April that Russia would carry out "steps of a different nature" in addition to military action to block NATO membership of former Soviet republics.[91] General Baluyevsky admitted in 2012 that after President Putin had decided to attack Georgia prior to the May 2008 inauguration of Dmitry Medvedev as president of Russia, a military action was planned and explicit orders were issued in advance before August 2008. Russia aimed to stop Georgia's accession to NATO and also to bring about a "regime change".[71]
Secret cables released in 2010 revealed that while US President George Bush publicly pledged full support to Georgia, they did not actually want a war. Shortly before the war, the US diplomats were quoted in the cables to have warned that "war is a bad option for Georgia" and "military action by Georgia" would cost the country the support of NATO and Europe.[92][93][94]
Prelude
April–July 2008

Situation in Georgia before the war
On 16 April 2008, official ties between the Russian authorities and the separatists in Abkhazia and South Ossetia were sanctioned by an order of Russian president Vladimir Putin. The separatist-authored legislative documents and the separatist-accredited bodies were also recognised.[95] After a United Nations Security Council session on 23 April convened at Georgia's demand, the United States, the United Kingdom, France and Germany stated in a declaration: "We call on the Russian Federation to revoke or not to implement its decision." However, this was labelled a "tall order" by Vitaly Churkin, Russian Ambassador to the UN.[96]
A Georgian reconnaissance drone flying over Abkhazia was shot down by a Russian warplane on 20 April. However, Russia denied responsibility for the incident and Abkhazia claimed that an "L-39 aircraft of the Abkhaz Air Force" shot down the UAV.[97] An allegation of an attack by a NATO MiG-29 was made by the Russia' Ambassador to NATO, Dmitry Rogozin. NATO Secretary General Jaap de Hoop Scheffer commented that "he'd eat his tie if it turned out that a NATO MiG-29 had magically appeared in Abkhazia and shot down a Georgian drone."[98] On 26 May, a United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) inquiry concluded that the Russian warplane, either a MiG-29 "Fulcrum" or a Su-27 "Flanker", was responsible for the downing.[99]
In late April, the Russian government said that Georgia was assembling 1,500 troops and policemen in the upper Kodori Gorge area and was planning to "invade" Abkhazia,[100] and that Russia would "retaliate" against Georgian offensive and had deployed more military in the separatist regions.[101] Any boost in the Kodori Gorge or near the Abkhaz border by either party was not confirmed by the UNOMIG.[102][103]
The number of Russian peacekeepers deployed in Abkhazia was boosted to 2,542 in early May. But Russian troop levels remained under the cap of 3,000 troops imposed by a 1994 decision of CIS heads of state.[104] Georgia demonstrated video footage captured by a drone to the BBC allegedly proving that Russian forces used heavy weaponry in Abkhazia and were combat troops, rather than peacekeepers; Russia rejected the accusations.[105] On 15 May, the United Nations General Assembly passed a motion calling for the return of all exiled and uprooted people to Abkhazia.[106] Russia opposed the Georgian-advocated motion. The Russian Foreign Ministry said that the resolution was "a counterproductive move".[107]
Russia deployed railroad troops on 31 May to repair a rail line in Abkhazia. According to the Russian defence ministry, railroad troops were not armed. Georgia stated that the development was an "aggressive" act.[108] The European Parliament adopted a resolution on 5 June which condemned the deployment of Russian forces to Abkhazia. The resolution stated that the peacekeeping structure should be changed because Russia was no longer an unbiased player.[109] Russian railroad troops started withdrawal from Abkhazia on 30 July after attending the inauguration of the railroad.[110] The fixed railroad was used to transport military equipment by at least a part of the 9,000 Russian soldiers who entered Georgia from Abkhazia during the war.[111]
In late June, Russian military expert Pavel Felgenhauer predicted that Vladimir Putin would start a war against Georgia in Abkhazia and South Ossetia supposedly in August.[102][112] The Kavkaz Center reported in early July that Chechen separatists had intelligence data that Russia was preparing a military operation against Georgia in August–September 2008 which mainly aimed to expel Georgian forces from the Kodori Gorge; this would be followed by the expulsion of Georgian units and population from South Ossetia.[113]
In early July, the conditions in South Ossetia aggravated, when a South Ossetian separatist militia official was killed by blasts on 3 July and several hours later an unsuccessful assassination attempt on Dmitry Sanakoyev, the leader of the Georgian-backed Ossetian government, wounded three police officers.[114] On 7 July, four Georgian servicemen were captured by South Ossetian separatists. The next day, the Georgian law enforcement was ordered by the president to arrange the liberation of the soldiers.[115] Four Russian Air Force jets flew over South Ossetia on 8 July.[116] A scheduled visit of Condoleezza Rice, the US Secretary of State, to Georgia on the next day nearly coincided with the timing of the flight.[117] Georgia summoned back its ambassador to Russia after Russia admitted its jets had flown in Georgia's airspace to "let hot heads in Tbilisi cool down".[116] This was the first time in ten years that Russia had confessed to an overflight of Georgia.[118]
On 15 July, the United States and Russia began two parallel military trainings in the Caucasus, though Russia denied that the identical timing was intentional.[119] The joint US-Georgian exercise was called Immediate Response 2008 and also included servicemen from Ukraine, Azerbaijan and Armenia. A total of 1,630 servicemen, including 1,000 American troops, took part in the exercise, which concluded on 31 July.[120]Counter-insurgency action was the focal point of the joint exercise. The Georgian brigade was trained to serve in Iraq.[121] The Russian exercise was named Caucasus 2008 and units of the North Caucasus Military District, including the 58th Army, took part. The exercise included training to aid peacekeeping forces stationed in Abkhazia and South Ossetia.[122] During exercises, a pamphlet named "Soldier! Know your probable enemy!" was circulated among the Russian soldiers. The pamphlet described the Georgian Armed Forces.[123] Russian troops stayed near the border with Georgia after the end of their exercise on 2 August, instead of going back to their barracks.[102] Later, Dale Herspring, an expert on Russian military affairs at Kansas State University, described the Russian exercise as "exactly what they executed in Georgia just a few weeks later [...] a complete dress rehearsal."[121]
Early August
At 8:00 am on 1 August, an improvised explosive device detonated on the road near Tskhinvali and hit a Georgian police lorry, wounding five Georgian police officers. In response, Georgian snipers assaulted some of the South Ossetian positions, killing four Ossetians and wounding seven.[124] According to majority of reports, the South Ossetians were responsible for instigating the bomb explosion which marked the opening of hostilities.[125]
South Ossetian separatists began intensively shelling Georgian villages on 1 August. This caused Georgian peacekeepers and servicemen in the area to return fire.[31][32][33][34][126][127] Grenade launcher and mortar fire were exchanged during the night of 1/2 August. The total Ossetian fatalities became six and the total wounded were now fifteen, among them several civilians; the Georgian casualties were six wounded civilians and one wounded policeman.[124] According to the OSCE mission, the incident was the worst outbreak of violence since 2004.[128] On 2–3 and again on 3–4 August, firing recommenced during the night.[128] A 1992 ceasefire agreement was breached by Ossetian artillery attacks.[36][37]
Nikolay Pankov, the Russian deputy defence minister, had a confidential meeting with the separatist authorities in Tskhinvali on 3 August.[129] An evacuation of Ossetian women and children to Russia began on the same day.[102] According to researcher Andrey Illarionov, the South Ossetian separatists evacuated more than 20,000 civilians, which represented more than 90 percent of the civilian population of the future combat zone.[130] On 4 August, South Ossetian president Eduard Kokoity said that about 300 volunteers had arrived from North Ossetia to help fight the Georgians and thousands more were expected from the North Caucasus.[131] On 5 August, South Ossetian presidential envoy to Moscow, Dmitry Medoyev, declared that South Ossetia would start a "rail war" against Georgia.[132] The razing of the village of Nuli was ordered by South Ossetian interior minister Mindzaev.[133] Georgian authorities organised a tour for diplomats and journalists to demonstrate the damage supposedly caused by separatists. That day, Russian Ambassador-at-Large Yuri Popov declared that his country would be involved in the conflict on the side of South Ossetia.[134] About 50 Russian journalists had come to Tskhnivali for "something to happen".[102] A pro-government Russian newspaper reported on 6 August: "Don Cossacks prepare to fight in South Ossetia".[135][136]Nezavisimaya Gazeta reported that Russian military was being deployed to the Georgian border on 6 August and that "there is no doubt that Russia thus demonstrates determination to protect its citizens in South Ossetia. Up until the operation to enforce peace is carried out."[137] On the evening of 6 August, an attempt by Saakashvili to contact the President of Russia about the conflict was curbed by the Russian Foreign Ministry, which said: "the time for presidential negotiations has not yet arrived."[138][139]
Mortar and artillery exchange between the South Ossetian and Georgian forces erupted in the afternoon of 6 August across almost the entire front line, which lasted until the dawn of 7 August. Exchanges resumed following a brief gap in the morning.[128][133] South Ossetian leader Eduard Kokoity announced that the South Ossetian armed forces were ready to go on the offensive in the next few hours.[140] At 14:00 on 7 August, two Georgian peacekeepers in Avnevi became casualties of Ossetian shelling.[141][142] At about 14:30, Georgian tanks, 122 mm howitzers and 203 mm self-propelled artillery began heading towards South Ossetia to dissuade separatists from additional attacks.[143] During the afternoon, OSCE monitors noted Georgian military traffic, including artillery, on roads near Gori.[141] In the afternoon, Georgian personnel left the Joint Peacekeeping Force headquarters in Tskhinvali.[144]
At 16:00, Temur Iakobashvili (the Georgian Minister for Reintegration) arrived in Tskhinvali for a previously-arranged meeting with South Ossetians and Russian diplomat Yuri Popov;[143] however, Russia's emissary, who blamed a flat tire, did not appear;[31] and neither did the Ossetians.[144] One day earlier the South Ossetians rejected direct negotiations with Georgian authorities, demanding a meeting of the Joint Control Commission for Georgian–Ossetian Conflict Resolution.[145] Tbilisi had left the Commission in March, demanding that a new mediation scheme includes the European Union, the OSCE and the Provisional Administrative Entity of South Ossetia.[102] Iakobashvili contacted General Marat Kulakhmetov (the Russian commander of the Joint Peacekeeping Force) who said that Ossetians could not be restrained by Russian peacekeepers and Georgia should implement a ceasefire.[143][146] "Nobody was in the streets – no cars, no people," Iakobashvili later told journalists.[141]
.mw-parser-output .quotebox{background-color:#F9F9F9;border:1px solid #aaa;box-sizing:border-box;padding:10px;font-size:88%}.mw-parser-output .quotebox.floatleft{margin:0.5em 1.4em 0.8em 0}.mw-parser-output .quotebox.floatright{margin:0.5em 0 0.8em 1.4em}.mw-parser-output .quotebox.centered{margin:0.5em auto 0.8em auto}.mw-parser-output .quotebox.floatleft p,.mw-parser-output .quotebox.floatright p{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .quotebox-title{background-color:#F9F9F9;text-align:center;font-size:larger;font-weight:bold}.mw-parser-output .quotebox-quote.quoted:before{font-family:"Times New Roman",serif;font-weight:bold;font-size:large;color:gray;content:" “ ";vertical-align:-45%;line-height:0}.mw-parser-output .quotebox-quote.quoted:after{font-family:"Times New Roman",serif;font-weight:bold;font-size:large;color:gray;content:" ” ";line-height:0}.mw-parser-output .quotebox .left-aligned{text-align:left}.mw-parser-output .quotebox .right-aligned{text-align:right}.mw-parser-output .quotebox .center-aligned{text-align:center}.mw-parser-output .quotebox cite{display:block;font-style:normal}@media screen and (max-width:360px){.mw-parser-output .quotebox{min-width:100%;margin:0 0 0.8em!important;float:none!important}}
—A confidential report sent on August 8, 2008, by the US Embassy in Tbilisi, leaked by WikiLeaks.[147]
At around 19:00, Georgian President Saakashvili announced a unilateral ceasefire and no-response order.[148] The ceasefire reportedly held for about three hours.[149] The separatists bombarded Tamarasheni and Prisi. They razed Avnevi and a police building in Kurta, the centre of the Provisional Administrative Entity of South Ossetia. The escalated assaults forced Georgian civilians to flee their homes.[150][151] A high-ranking officer of the Georgian Ministry of Defence said late on 7 August that his country was going to "restore constitutional order" in response to the shelling.[152]Georgian Interior Ministry official later told Russian newspaper Kommersant on 8 August that after Ossetians had responded to the ceasefire by shelling, "it became clear" that South Ossetians wouldn't stop firing and that the Georgian casualties were 10 killed and 50 wounded.[153] According to Pavel Felgenhauer, the Ossetians intentionally provoked the Georgians, so Russia would use the Georgian response as a pretext for premeditated military invasion.[154] Russian military was participating in the attacks on Georgian villages.[155]
According to Georgian intelligence,[156] and several Russian media reports, parts of the regular (non-peacekeeping) Russian Army had already moved to South Ossetian territory through the Roki Tunnel before the Georgian military operation.[157] Even the state-controlled Russian TV aired Abkhazia's de facto president Sergei Bagapsh on 7 August as saying: "I have spoken to the president of South Ossetia. It has more or less stabilized now. A battalion from the North Caucasus District has entered the area."[39] Georgian authorities did not announce Russian military incursion in public on 7 August since they relied on the Western guidance and did not want to aggravate tensions.[158] The entrance of second batch of Russian military through the Roki Tunnel during the night of 7/8 August pressured Georgian president Saakashvili to respond militarily around 23:00 in order to check Russian all-out incursion near the Roki Tunnel before the Western response would be late.[159]
Large-scale conflict
Battle of Tskhinvali

Russian BMP-2 from the 58th Army in South Ossetia

Destroyed Georgian tank in Tskhinvali
Georgian artillery launched smoke bombs into South Ossetia at 23:35 on 7 August. This was followed by a 15-minute intermission, which purportedly enabled the civilians to escape, before the Georgian forces began bombarding hostile positions.[149] Georgian military intentionally targeted South Ossetian military objects, not civilian ones. Although Georgian military had pledged safety to the Russian peacekeepers for their neutrality, the Russian peacekeepers had to follow the Russian command to attack the Georgian troops.[160]
The Georgian 4th Brigade of Vaziani Military Base advanced on the left side of Tskhinvali early in the morning on 8 August; the 3rd Brigade advanced on the right side. The purpose of these actions was to advance to the north after capturing key positions. The Georgian troops would secure the Gupta bridge and the road to the Roki Tunnel, barring the Russian military from moving southward.[149]
Georgian forces started moving in the direction of Tskhinvali following several hours of bombardment and engaged South Ossetian forces and militia near the town at 04:00 on 8 August, with Georgian tanks remotely shelling South Ossetian positions. An attempt to take the village of Kvaysa from the west of South Ossetia by a Georgian armed police unit was thwarted by South Ossetian troops occupying reinforced positions. Several Georgians were wounded and the attack was called off.[161] By the morning, the South Ossetian authorities had reported that the Georgian shelling had killed at least 15 civilians.[162]
Georgian forces, among them special troops of the Ministry of Internal Affairs, entered Tskhinvali after taking the high points near the town.[149] The centre of the town was reached by 1,500 men of Georgian infantry by 10:00.[141] The Russian air force began raiding targets inside South Ossetia and Georgia proper after 10:00 on 8 August.[163] According to Russia, it suffered its first casualties at around 12:00 when two servicemen were killed and five injured following an attempt by the Georgian troops to storm the northern peacekeeping base in Tskhinvali.[164] Georgia has stated that it only targeted Russian peacekeepers in self-defence, after coming under fire from them.[165] Most of Tskhinvali and several villages had been secured by Georgian troops by the afternoon;[149] however, they failed to blockade the Gupta bridge and the key roads linking Tshkinvali with the Roki Tunnel and the Russian military base in Java.[166] One Georgian diplomat told Kommersant on the same day that by taking control of Tskhinvali, Tbilisi wanted to demonstrate that Georgia wouldn't tolerate killing of Georgian citizens.[153]
By 15:00 MSK, an urgent session of Security Council of Russia had been convened by Russian president Dmitry Medvedev and Russia's options regarding the conflict had been discussed.[167] Russia accused Georgia of "aggression" against South Ossetia.[38] Russia stated it was defending both peacekeepers and South Ossetian civilians who were Russian citizens.[43] While Russia claimed that it had to conduct peacekeeping operations according to the international mandates, in reality such accords had only arranged the ceasefire observer status; according to political scientist Roy Allison, Russia could evacuate its peacekeepers if attacked.[43] At around 16:00 MSK, it became known that two heavy armoured columns of the 58th Army passed the Roki Tunnel and Java and were on the road to Tskhinvali. According to Kommersant, the column had begun moving towards South Ossetia at the same time as President Medvedev was giving a televised speech. At around 17:00 MSK, Russian tank columns surrounded Tskhinvali and began bombing the Georgian positions.[153] The Russian Air Force mounted attacks on Georgian infantry and artillery on 8 August, but suspended sorties for two days after taking early losses from anti-aircraft fire.[168][169] Georgian troops left the centre of the town in the evening.[166] Military expert Ralph Peters later noted that anyone "above the grade of private" knew that such a large-scale Russian "response" was not spontaneous since it was impossible "even to get one armored brigade over the Caucasus Mountains" without lengthy planning.[170]
In the afternoon of 9 August, a Georgian effort to push deeper into Tskhinvali was repulsed with Georgian losses and they withdrew.[166] According to the Georgian Defence Minister, the Georgian military had tried to push into Tskhinvali three times by 9 August. During the last attempt they were met with a serious counterattack, which Georgian officers described as "something like hell."[141] On the same day a Russian advance column, led by Lieutenant-General Anatoly Khrulyov, was ambushed by Georgian special forces near Tskhinvali; Khrulyov was wounded in the leg.[171] The number of Russian forces deployed in South Ossetia exceeded the number of Georgians by 9 August.[102]
A ceasefire was unilaterally announced on 10 August by Georgian authorities. An aim to pull out Georgian troops from South Ossetia was stated by the Georgians. However, Russia did not embrace this truce offer.[172] After the ceasefire agreement was negotiated by French president Nicolas Sarkozy on 12 August, 15:00 on 12 August was set as a deadline for the cessation of military action; however, Russian forces didn't stop to push forward.[173]
Bombing and occupation of Gori

Nearly-intact Russian missile booster in the bedroom of a Gori house
Gori is an important city in the centre of Georgia,[174] located about 25 km (16 mi) from Tskhinvali.[175] On 9 August, a Russian air attack targeted military garrisons in Gori, damaging the garrison, several apartment buildings and a school. Russians did not admit that non-combatants were intentionally attacked.[176] The Georgian government reported that the air raid had killed 60 civilians.[177] No less than 5 Georgian cities had been bombed by 9 August.[178]
After Georgian troops had left Tskhinvali on 10 August, the Russians indiscriminately bombed the civilian areas in Gori on 11 August.[179] The Georgian forces withdrew from Gori on 11 August. A Georgian official said that the troops were ordered to secure Tbilisi, the capital of Georgia.[180] By late 11 August, majority of inhabitants and Georgian troops had abandoned Gori.[181] Georgian president Saakashvili stated that Russians had split Georgia into two by occupying an important intersection near Gori.[182]

A memorial on the wall of a residential building, damaged during the war, in downtown Gori (2016).
Russian bombers attacked Gori on 12 August,[181] killing a seven people and wounding over thirty.[183] Dutch TV journalist Stan Storimans was among those killed and another foreign reporter was injured.[181] According to Georgian authorities, the Russians aimed at the city's administrative offices. The air raids set the post office and the Gori University on fire.[181] The Gori Military Hospital carrying a Red Cross flag was struck by a rocket,[184] and one doctor was killed.[185]
Russian military was warning during the march towards Gori on 13 August that they would not spare ethnic Georgian civilians in villages if the latter did not demonstrate signs of surrender. Escaping Georgians blamed Russian president Medvedev for their suffering because they, trusting Medvedev's statement on ceasefire, had remained in their homes before the Russian advance.[186] Russian military captured Gori on 13 August.[187] The destruction of Georgian military bases began.[188] On 14 August, Major General Vyacheslav Borisov (the commander of the Russian occupying troops) told Aleksandre Lomaia, secretary of Georgia's National Security Council, that the Russian company did not upset the locals of Gori.[189] That day, Borisov stated that the Georgian police and Russian forces were in charge of Gori together. He also said that Russian troops would begin leaving Gori in two days.[190] Combined guard efforts by the Russian Army and Georgian police in Gori soon broke down.[187] The next day, Russian forces pushed to about 40 kilometres (25 mi) from Tbilisi, the nearest during the war, and stopped in Igoeti at the same time as Condoleezza Rice was received by Saakashvili.[191] In 2014, Anatoly Khrulyov, the commander of the 58th Army, said that Russian troops had to act in accordance with operational objective and plan issued before 8 August 2008. If Khrulyov had not contacted the General Staff during the war and received new order, the 58th Army would have taken Tbilisi.[192]
The humanitarian conditions in Gori by 16 August was assessed as "desperate" by the United Nations. Human Rights Watch (HRW) reported that following Russian takeover of Georgian areas, Georgians from Gori and the adjacent villages reported South Ossetian militias pillaging and assaulting Georgian properties and abducting civilians.[193]The Times reported from Gori on 18 August that Russian troops reportedly had told Georgian civilians fleeing South Ossetia: "Putin has given us an order that everyone must be either shot or forced to leave".[194]
The occupation lasted until 22 August, when Russian troops departed and Georgian police re-entered the city.[195] Georgia's principal highway connecting east with west was now free for transit.[196]
Abkhaz front

Russian guided-missile ship 12341 Mirazh (Mirage) in Sevastopol
A naval confrontation occurred between Russian and Georgian vessels on 10 August.[197] According to the Russian Ministry of Defence, the Russian fleet sank one Georgian ship after four Georgian missile boats had attacked the Russian Navy ships near the coast of Abkhazia.[198] The Russian patrol ship Mirazh was probably responsible for the sinking.[199] The Georgian coast was blockaded by vessels of the Russian Black Sea Fleet on 10 August.[200][201] This was first activity since 1945 for the Black Sea Fleet, which had probably departed from Sevastopol before full-scale hostilities between Russia and Georgia began.[202]
Abkhaz forces opened a second front by attacking the Kodori Gorge, held by Georgia.[203] Abkhaz artillery and aircraft began a bombardment against Georgian troops in the upper Kodori Gorge on 9 August.[204] Three days later, a military offensive against the Kodori Gorge was officially initiated by Abkhaz separatists.[201] Abkhaz defence officer said that Georgian forces were driven out of the Kodori Gorge. Although he claimed that Russians did not participate in the battle, Russian military traffic headed for the gorge was witnessed by an Associated Press correspondent.[205] Casualties were light on both sides; Abkhaz fighters accidentally killed one of their comrades,[20] and two Georgian soldiers were also killed.[206] About 2,000 people living in the Kodori Gorge fled.[2]
Russian forces advanced into western Georgia from Abkhazia on 11 August.[180] This marked the opening of another front. Russian troops captured the police buildings in Zugdidi in spite of earlier Russian official claims of not intending to expand assault to Georgia proper.[182] Russian forces arrived in the town of Senaki that day and took a military base there.[174]
Occupation of Poti
Poti is the crucial seaport of Georgia on the Black Sea and serves as an essential entrance for Transcaucasia and the landlocked Central Asia.[207] Russian aircraft attacked the town of Poti on 8 August, causing a two-day shutdown of the seaport.[207] Russia positioned ships in the vicinity of Poti and other Georgian ports on 10 August 2008.[201] The next day, Georgian and Russian representatives said that Russian troops were in Poti. However, Russia claimed it had only sent a task force for surveying the area.[208] On 13 August, six Georgian watercraft were submerged by Russian troops in Poti.[209]Anatoliy Nogovitsyn, Russian deputy chief of the General staff, denied the Russian presence in Poti the following day.[210] One day after Russia's declaration of the beginning of the withdrawal from Georgia, 70 Russian soldiers moved into the seaport on the morning of 19 August.[207] Russian soldiers took twenty-one Georgian troops prisoner and grabbed five US Humvees in Poti, taking them to a Russian-occupied military base in Senaki.[211]The Wall Street Journal said that Russian actions in Poti constituted an additional attack on the Georgian economy.[207] Russian military was accused of plundering and damaging properties during their presence in Poti, even ransacking toilets.[212][213]
Bombing of Tbilisi and surroundings
During the fighting in South Ossetia, the Russian Air Force repeatedly attacked Tbilisi and its surrounding areas.[214] On 8 August, the Georgian Interior Ministry reported that Vaziani Military Base near the city was hit by two bombs.[215] Prior to the war, the bombed base near Tbilisi had housed the Russian military before the government of Georgia forced their withdrawal. The Daily Telegraph described this bombing as "Russia's revenge".[216] A Georgian military airstrip in Marneuli was attacked and three persons were killed.[217] The Georgian government vacated their offices on 9 August.[218] Georgian authorities reported on 9 August that Russian air attacks had targeted the Baku–Tbilisi–Ceyhan pipeline, but missed.[178] Reporters for Reuters in Tbilisi reported hearing three explosions in the early-morning hours of 10 August and a Georgian Interior Ministry representative said that three bombs were dropped on Tbilisi International Airport by Russian warplanes.[219] A military manufacturing plant near the airport was also attacked by Russia that day.[220] A civilian radar station in Tbilisi was bombed the following day.[179] Although an end to hostilities was declared on 12 August, Russian warplanes did not stop dropping bombs in Georgia throughout 12 August.[221]The Wall Street Journal reported on 14 August that reporter had witnessed 45 craters near intersection of Baku–Tbilisi–Ceyhan pipeline and Baku–Supsa Pipeline south of Tbilisi.[222]
Media and cyber war
The war was accompanied by a media battle between Russia and Georgia.[223] The Russian military took Russian journalists to the combat zone to report news discrediting Georgia and portraying Russia as the saviour of Russian citizens in the conflict zone. Russia also aired records on TV supporting its actions which had a strong effect on the local populations of South Ossetia and Abkhazia. For the first time, a Russian Armed Forces spokesman was provided by the Russian authorities to give TV interviews about the war. Despite these tactics and domestic success, the Russian information operation against Georgia was not successful internationally.[224] In response to the information war, the Georgian government halted the broadcasting of Russian television channels in Georgia and blocked access to Russian websites.[225] The information skirmishes between Georgia and Russia continued after armed hostilities had ended.[223] According to political scientist Svante Cornell, the Kremlin spent millions in an international information campaign to blame Georgia for the war;[226] however, there is evidence, including some in Russian media, that Russia actually started the war.[41][226]
During the war, hackers attacked Georgian government and news websites and disabled host servers.[227] Some Russian news websites were also attacked.[228][229] Some experts noted this as the first time in history that a notable cyberattack and an actual military engagement happened at the same time.[230]
Ceasefire agreement

Joint press conference by Russian president Dmitry Medvedev and French President Nicolas Sarkozy after negotiations on the plan
On 12 August, Russian President Dmitry Medvedev announced the cessation of the "peace enforcement" operation in Georgia. "The operation has achieved its goal, security for peacekeepers and civilians has been restored. The aggressor was punished, suffering huge losses."[231] Later that day he met French President Nicolas Sarkozy (the President-in-Office of the European Union) and approved a six-point proposal.[232] The proposal originally had four points, but Russia firmly requested to add two more. Georgia requested that the additions be parenthesised; Russia objected and Sarkozy prevailed upon Saakashvili to accept the agreement.[233] According to Sarkozy and Saakashvili, a sixth point in the Sarkozy proposal was removed with Medvedev's consent.[234] On 14 August, South Ossetian President Eduard Kokoity and Abkhaz President Sergei Bagapsh also endorsed the plan.[235] The following day Condoleezza Rice travelled to Tbilisi, where Saakashvili signed the document in her presence.[236] On 16 August, Russian President Dmitry Medvedev signed the agreement.[237]
The plan embodied the following statutes (dismissed additions are parenthesised):[233]
.mw-parser-output .templatequote{overflow:hidden;margin:1em 0;padding:0 40px}.mw-parser-output .templatequote .templatequotecite{line-height:1.5em;text-align:left;padding-left:1.6em;margin-top:0}
- No recourse to the use of force
- Definitive cessation of hostilities
- Free access to humanitarian aid (and to allow the return of refugees)
- Georgian military forces must withdraw to their normal bases of encampment
- Russian military forces must withdraw to the lines prior to the start of hostilities. While awaiting an international mechanism, Russian peacekeeping forces will implement additional security measures (six months)
- Opening of international discussions on the modalities of lasting security in Abkhazia and South Ossetia (based on the decisions of the U.N. and the OSCE)
After the ceasefire was signed, hostilities did not immediately end.[173] Noting that civilians were fleeing before advancing Russian armour, troops and mercenaries, a reporter for The Guardian wrote on 13 August that "the idea there is a ceasefire is ridiculous".[238]
On 8 September, Sarkozy and Medvedev signed another agreement on a Russian pullback from Georgia. After meeting with the French president, Medvedev said the withdrawal depended on assurances that Georgia would not use force;[239] Russian forces would withdraw "from the zones adjacent to South Ossetia and Abkhazia to the line preceding the start of hostilities". However, a military withdrawal from South Ossetia and Abkhazia was not proclaimed.[240]
Aftermath
Russian withdrawal
@media all and (max-width:720px){.mw-parser-output .tmulti>.thumbinner{width:100%!important;max-width:none!important}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsingle{float:none!important;max-width:none!important;width:100%!important;text-align:center}}
On 17 August, Medvedev announced that Russian military would start to pull out of Georgia the following day.[241]Prisoners of war were swapped by the two countries on 19 August. A Georgian official said that although his country swapped five Russian soldiers for fifteen Georgians, among them two non-combatants, Georgia suspected that Russia kept two more Georgians.[242] On 22 August, Russian forces withdrew from Igoeti and the Georgian police proceeded in the direction of Gori.[243] Russia claimed that withdrawal of Russian forces was finished; however, Russian checkpoints stayed near Gori and two Russian lookout stations stayed near Poti.[244] On 13 September, Russian troops began withdrawing from western Georgia and by 11:00 Moscow Time, the posts near Poti were abandoned. Withdrawals from Senaki and Khobi also took place.[245] Russian forces pulled back from the buffer areas bordering Abkhazia and South Ossetia on 8 October and the European Union monitoring mission in Georgia would now oversee the areas.[246]
Russia continued to maintain a single station in the border village of Perevi. On 12 December, Russian forces withdrew; eight hours later they re-entered the village and Georgian police withdrew after the Russians warned they would fire.[247] Russian forces then set up three stations in the village. On 18 October 2010, all Russian forces in Perevi withdrew to South Ossetia and Georgian soldiers entered.[248]
On 9 September 2008, Russia announced that Russian forces in South Ossetia and Abkhazia would remain under bilateral agreements with their respective de facto governments. Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov said that a Russian deployment in Abkhazia and South Ossetia would prove decisive in preventing Georgia from recovering territories.[4] Georgia considers Abkhazia and South Ossetia Russian-occupied territories.[249] In November 2011, the European Parliament passed a resolution acknowledging Abkhazia and South Ossetia as occupied Georgian territories.[250]
Recognition of Abkhazia and South Ossetia by Russia

Sergey Bagapsh (left), Dmitry Medvedev (middle) and Eduard Kokoity (right) shortly after the recognition of Abkhazia and South Ossetia
On 25 August 2008, the Russian parliament passed a motion, with no one voting against. The motion called for the diplomatic recognition of Abkhazia and South Ossetia by President Medvedev.[251] On 26 August, Medvedev issued orders recognising the two states,[252] saying that recognising the independence of the two entities "represents the only possibility to save human lives."[3]
The recognition by Russia was condemned by the United States, France, the secretary-general of the Council of Europe, the president of the Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe, the OSCE chairman, NATO and the G7 on the grounds that it violated Georgia's territorial integrity, United Nations Security Council resolutions and the ceasefire agreement.[253][254][255][256][257] In response to Russia's action, the Georgian government severed diplomatic relations with Russia.[258]
Russia sought approval for its recognition from the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation. However, because of anxiety about secessionist areas in SCO states, especially in China, the organisation did not endorse recognition.[259]
International monitors
The mandate of the OSCE mission in Georgia expired on 1 January 2009, after Russia refused to support its continuation. OSCE monitors had been denied access to South Ossetia since the war.[260] The mandate of the UNOMIG ended on 16 June 2009; its extension was also blocked by Russia, which argued that the mandate did not properly reflect Russia's position on recognition of Abkhazia's independence. According to UN mission head Johan Verbeke, about 60,000 ethnic Georgians in Abkhazia became vulnerable after the mission's end.[261]
As of 5 January 2015, 259 European Union Monitoring Mission (EUMM) monitors operate in Georgia and 2 in Brussels.[262] EUMM observers are not admitted into Abkhazia and South Ossetia by Russia.[263]
Geopolitical impact

BTC pipeline (green) and planned Nabucco gas pipeline (tangerine)
The 2008 war was the first time since the fall of the Soviet Union that the Russian military had been used against an independent state, demonstrating Russia's willingness to wage an all-out military campaign to attain its political objectives.[264] The failure of the Western security organisations to react swiftly to Russia's attempt to violently revise the borders of an OSCE country revealed its deficiencies. The division between Western European and Eastern European nations also became apparent over the relationship with Russia. Ukraine and other ex-Soviet countries received a clear message from the Russian leadership that the possible accession to NATO would cause a foreign incursion and the break-up of the country. Effective takeover of Abkhazia was also one of Russia's geopolitical goals.[265] The construction of the EU-sponsored Nabucco pipeline linking Europe with Central Asian reserves through Transcaucasia was averted.[266]
The war in Georgia showed Russia's assertiveness in revising international relations and undermining the hegemony of the United States. Shortly after the war, Russian president Medvedev unveiled a five-point Russian foreign policy. The Medvedev Doctrine stated that "protecting the lives and dignity of our citizens, wherever they may be, is an unquestionable priority for our country". The presence of Russian citizens in foreign countries would form a doctrinal foundation for invasion. Medvedev's statement on the existence of territories with Russian "privileged interests" attached to them underlined Russia's particular stake in the Post-Soviet states and the fact that Russia would feel endangered by subversion of local Russia-friendly administrations.[267]
The war eliminated Georgia's prospects for joining NATO.[75][268] Russian President Dmitry Medvedev stated in November 2011 that NATO would have accepted former Soviet republics if Russia had not attacked Georgia. "If you ... had faltered back in 2008, the geopolitical situation would be different now," Medvedev told the officers of a Vladikavkaz military base.[269]
Humanitarian impact and war crimes

South Ossetian refugees in a camp in Alagir, North Ossetia

A burning house in the Georgian village of Kekhvi, on the road from Tskhinvali to Java.
Human Rights Watch (HRW) states that all parties to the war seriously breached international laws governing war and caused many fatalities among civilians.[270] HRW reported that no proof of intentional attacks on non-combatants by Georgian troops had been discovered.[271] The South Ossetian parliament and several schools and nurseries were used as military posts by South Ossetian troops and volunteer militias and targeted by Georgian artillery fire. Georgia stated that its strikes only intended to "neutralize firing positions from where Georgian positions were being targeted". HRW documented witness accounts of the usage of civilian objects by South Ossetian fighters. Such usage made civilian objects permissible military aims, and HRW concluded that South Ossetian fighters put non-combatant population at risk by setting up military positions near or in civilian structures. Georgia was responsible for the indiscriminate use of force by using inaccurate weapons to target military targets in civilian areas.[272]
Russia deliberately attacked fleeing civilians in South Ossetia and the Gori district of Georgia.[273] Russian warplanes bombed civilian population centres in Georgia proper and villages of ethnic Georgians in South Ossetia.[273] Armed militias engaged in plundering, burning and kidnappings. Attacks by militias compelled Georgian civilians to run away.[273]
The use of M85S cluster bombs by the Georgians and RBK 250 cluster bombs by the Russians caused fatalities among civilians. Georgia reportedly used cluster munitions twice to hit non-combatants escaping via the important Dzara road and confessed attacking Russian forces and the vicinity of the Roki Tunnel by cluster bombs.[274] Russia denied using cluster bombs.[275]
HRW reported that during the war, ethnic-Georgian villages in South Ossetia were set on fire and pillaged by South Ossetian militias. This impeded the comeback of 20,000 uprooted people after the conflict.[276] According to the Memorial society, the villages of Kekhvi, Kurta, Achabeti, Tamarasheni, Eredvi, Vanati and Avnevi were "virtually fully burnt down".[277] South Ossetian president Eduard Kokoity said in an interview that Georgian villages had been demolished and no Georgian refugees would be allowed to return.[278] The Georgian civilians, who resided in the Akhalgori district and were willing to live in South Ossetia, were coerced into obtaining a Russian passport.[279] The EU commission said it was likely that during the hostilities and in the aftermath of the war, an ethnic cleansing of Georgians was committed in South Ossetia.[280]

Tserovani, one of the villages built by the Georgian government for IDPs from the conflict zone
Russia accused Georgia of committing "genocide" in South Ossetia.[281] Russian authorities initially claimed that up to 2,000 ethnic Ossetian civilians of Tskhinvali were killed by Georgian forces; according to Russia, the reason for the Russian involvement in the conflict in Georgia was this large number of fatalities.[282] Public opinion among Ossetians was impacted by claims of high casualties; according to HRW, some Ossetian civilians said in interviews that they approved of burning and pillaging of Georgian villages because of the "thousands of civilian casualties in South Ossetia" announced by Russian television.[282] In December 2008, the figures were revised down to a total of 162 South Ossetian casualties by the Investigative Committee of the Prosecutor's Office of the Russian Federation.[282]
Georgia and South Ossetia have filed complaints about alleged war crimes committed by the other side with international courts, including the International Criminal Court,[283] the International Court of Justice,[284] and the European Court of Human Rights.[285]
The war displaced a 192,000 people including both Ossetians and Georgians.[27] Many were able to go back to their homes after the war, but a year later around 30,000 ethnic Georgians were still uprooted.[286] As of May 2014, 20,272 persons were still displaced, with their return being blocked by de facto authorities.[287]
Reactions
International reactions

US Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice and President of Georgia Mikheil Saakashvili at a Tbilisi press conference, August 2008

Georgian Coast Guard patrol boat P-24 Sokhumi passes the USS McFaul on its arrival at the port of Batumi
Russian actions during the war were heavily criticised by several Western countries:
 Sweden – On 8 August 2008, Swedish Minister for Foreign Affairs Carl Bildt said that the crisis was due to provocations from the South Ossetian side and that Georgian forces were trying to restore the constitutional order.[288] On 9 August, Bildt compared Russia's reason for going to war with Georgia to Adolf Hitler's actions, "No state has the right to intervene militarily in the territory of another state simply because there are individuals there with a passport issued by that state or who are nationals of the state. Attempts to apply such a doctrine have plunged Europe into war in the past... And we have reason to remember how Hitler used this very doctrine little more than half a century ago to undermine and attack substantial parts of central Europe".[289]
Sweden – On 8 August 2008, Swedish Minister for Foreign Affairs Carl Bildt said that the crisis was due to provocations from the South Ossetian side and that Georgian forces were trying to restore the constitutional order.[288] On 9 August, Bildt compared Russia's reason for going to war with Georgia to Adolf Hitler's actions, "No state has the right to intervene militarily in the territory of another state simply because there are individuals there with a passport issued by that state or who are nationals of the state. Attempts to apply such a doctrine have plunged Europe into war in the past... And we have reason to remember how Hitler used this very doctrine little more than half a century ago to undermine and attack substantial parts of central Europe".[289]
 United Kingdom – British Foreign Secretary David Miliband said on 9 August, "Russia has extended the fighting today well beyond South Ossetia, attacking the Georgian port of Poti, and the town of Gori, while Abkhaz forces have been shelling Georgian positions in the Upper Kodori valley. I deplore this."[290]
United Kingdom – British Foreign Secretary David Miliband said on 9 August, "Russia has extended the fighting today well beyond South Ossetia, attacking the Georgian port of Poti, and the town of Gori, while Abkhaz forces have been shelling Georgian positions in the Upper Kodori valley. I deplore this."[290]
 United States – US president George W. Bush said on late 11 August, "Russia has invaded a sovereign neighbouring state and threatens a democratic government elected by its people. Such an action is unacceptable in the 21st century." Bush also said, "There’s evidence that Russian forces may soon begin bombing the civilian airport in the capital city." Bush urged Russia to sign the EU-mediated ceasefire agreement, otherwise Russia would "jeopardise" its standing with the West.[291] Although the Bush administration contemplated a military reaction to defend Georgia, it decided against it so as to not provoke a conflict with Russia. Instead, the US sent humanitarian assistance to Georgia on military aircraft.[292]
United States – US president George W. Bush said on late 11 August, "Russia has invaded a sovereign neighbouring state and threatens a democratic government elected by its people. Such an action is unacceptable in the 21st century." Bush also said, "There’s evidence that Russian forces may soon begin bombing the civilian airport in the capital city." Bush urged Russia to sign the EU-mediated ceasefire agreement, otherwise Russia would "jeopardise" its standing with the West.[291] Although the Bush administration contemplated a military reaction to defend Georgia, it decided against it so as to not provoke a conflict with Russia. Instead, the US sent humanitarian assistance to Georgia on military aircraft.[292]
 Poland – The presidents of Poland, Lithuania, Estonia, Ukraine and the prime minister of Latvia (Lech Kaczyński, Valdas Adamkus, Toomas Hendrik Ilves, Viktor Yushchenko and Ivars Godmanis), who met with Georgian president Mikheil Saakashvili at Kaczyński's initiative, appeared at a 12 August 2008 Tbilisi rally held in front of the parliament which was attended by nearly 150,000 people. The crowd responded enthusiastically to the Polish president's speech, chanting "Poland, Poland", "Friendship, Friendship" and "Georgia, Georgia".[293]
Poland – The presidents of Poland, Lithuania, Estonia, Ukraine and the prime minister of Latvia (Lech Kaczyński, Valdas Adamkus, Toomas Hendrik Ilves, Viktor Yushchenko and Ivars Godmanis), who met with Georgian president Mikheil Saakashvili at Kaczyński's initiative, appeared at a 12 August 2008 Tbilisi rally held in front of the parliament which was attended by nearly 150,000 people. The crowd responded enthusiastically to the Polish president's speech, chanting "Poland, Poland", "Friendship, Friendship" and "Georgia, Georgia".[293]
 Hungary – Hungarian opposition leader Viktor Orbán drew parallels between the Russian intervention and the crushing of the Hungarian Revolution of 1956.[294]
Hungary – Hungarian opposition leader Viktor Orbán drew parallels between the Russian intervention and the crushing of the Hungarian Revolution of 1956.[294]
 Ukraine – President Yushchenko suggested that the contract between Ukraine and Russia regarding the Sevastopol naval base would not be extended in 2017. Ukrainians suspected that pro-Russian Crimea would become a cause for military incursion by Russia.[295]
Ukraine – President Yushchenko suggested that the contract between Ukraine and Russia regarding the Sevastopol naval base would not be extended in 2017. Ukrainians suspected that pro-Russian Crimea would become a cause for military incursion by Russia.[295]
France and Germany took an intermediate position, abstaining from naming a guilty party:[296]
 European Union – On 8 August, France (who held the rotating presidency of the European Union) announced that the EU and the US would send a joint delegation to negotiate a ceasefire.[297]
European Union – On 8 August, France (who held the rotating presidency of the European Union) announced that the EU and the US would send a joint delegation to negotiate a ceasefire.[297]
 Germany – German chancellor Angela Merkel conveyed her concern about the humanitarian situation in Georgia and urged to cease war.[298]
Germany – German chancellor Angela Merkel conveyed her concern about the humanitarian situation in Georgia and urged to cease war.[298]
A few leaders supported Russia's position:
 Italy – Italian Minister of Foreign Affairs Franco Frattini said, "We cannot create an anti-Russia coalition in Europe, and on this point we are close to Putin's position." He emphasised that Vladimir Putin and Italian Prime Minister Silvio Berlusconi were near partners.[296]
Italy – Italian Minister of Foreign Affairs Franco Frattini said, "We cannot create an anti-Russia coalition in Europe, and on this point we are close to Putin's position." He emphasised that Vladimir Putin and Italian Prime Minister Silvio Berlusconi were near partners.[296]
 Belarus – President of Belarus Alexander Lukashenko said on 19 August, "Russia acted calmly, wisely and beautifully."[299]
Belarus – President of Belarus Alexander Lukashenko said on 19 August, "Russia acted calmly, wisely and beautifully."[299]
Georgia proclaimed on 12 August 2008 that it would quit the Commonwealth of Independent States, which it held responsible for not avoiding the war. Its departure became effective in August 2009.[300]
According to academic Martin Malek, western countries did not feel it was necessary to aggravate tensions with Russia over "tiny and insignificant" Georgia. He wrote in the Caucasian Review of International Affairs that western policy makers did not want to alienate Russia because its support was necessary to solve "international problems".[135] The May 2015 report by the Committee on Foreign Affairs of the European Parliament stated that "the reaction of the EU to Russia’s aggression towards, and violation of the territorial integrity of, Georgia in 2008 may have encouraged Russia to act in a similar way in Ukraine".[301]
NATO reaction in the Black Sea
NATO increased its naval presence in the Black Sea significantly following the Russian invasion, with ships dropping anchors in Georgian ports,[302] and according to the US Navy, bringing humanitarian assistance.[303] NATO said that its presence in the Black Sea was not related to the Georgian crisis; its vessels were carrying out typical visits and preplanned naval trainings with Romania and Bulgaria.[304] Russian General Anatoliy Nogovitsyn recalled the limit on the number of vessels admitted into the Black Sea under the 1936 Montreux convention.[305] Russian President Dmitry Medvedev questioned the claim that ships going to Georgia were bringing only humanitarian assistance, alleging the delivery of military material.[306] According to political analyst Vladimir Socor, in spite of the limits on vessel's weight and length of visits set by the Montreux Convention, the US kept a continual presence in the Black Sea by alternating vessels from time to time.[307]
Combatants
Georgian order of battle
According to the Moscow Defence Brief, an English-language magazine published by the Russian non-governmental organisation the Centre for Analysis of Strategies and Technologies, the Georgian troops included the 2nd, 3rd and 4th Infantry Brigades, the Artillery Brigade, part of the 1st Infantry Brigade and the standalone Gori Tank Battalion. Additionally, special forces and Ministry of Internal Affairs troops were deployed. The total number of troops was 16,000 according to the magazine.[7] According to the International Institute for Strategic Studies, ten light infantry battalions of the 2nd, 3rd and 4th infantry brigades, special forces and an artillery brigade, totalling approximately 12,000 troops, had been concentrated by the start of the conflict.[8] The primary task of securing Tskhinvali was accomplished by the 4th Brigade with support from the 2nd and 3rd Brigades.[8] According to the EU fact-finding mission, 10,000–11,000 soldiers took part in the war.[11]
The 1st Infantry Brigade, the only one instructed to NATO standards, was serving in Iraq at the beginning of the war;[308] on 11 August, the United States Air Force flew it to Georgia.[309] The best Georgian troops were overdue from Iraq and could not participate in the fighting.[11] The presence of prime 2,000 Georgian military and the bulk of Georgian high-level government officials abroad before the war meant that Georgia did not intend to begin hostilities.[310]
| Deployed units | |
|---|---|
| Affiliation | Units |
| Ministry of Defence[21] | Special Operations Forces |
| 1st Infantry Brigade | |
| 2nd Infantry Brigade | |
| 3rd Infantry Brigade | |
| 4th Infantry Brigade | |
| 5th Infantry Brigade | |
| Military Engineering Brigade | |
| Separate Light Infantry Battalion | |
| Separate Tank Battalion | |
| Naval Forces | |
| Air Forces | |
| Logistic Support Department of Army | |
| National Guard | |
| M/R Department, I Operative Division | |
| Ministry of Internal Affairs[13] | Special Tasks Main Division |
| Regional Police units in the regions near the conflict areas | |
| Special Operations Department | |
| Constitutional Security Department | |
| Special Operations Centre | |
Russo-South Ossetian-Abkhaz order of battle
A sizeable portion of the Russian 58th Army, one of the foremost military units in Russia, was included in the Russian order of battle.[311] It exceeds the Georgian Army in the number of forces, heavy hardware and planes.[311] The 58th Army fought in Second Chechen War.[312]
| Deployed units: South Ossetian sector | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Allegiance | Units | Subunits |
| Initially present | South Ossetia | 2,500 South Ossetian troops[313] | |
| Russia | Russian peacekeeping forces | 496 from Russian battalion[314] | |
| 488 from North Ossetia[314] | |||
| Reinforcement | Russia | 58th Army | Two battalions of the 135th Separate Motorised Rifle Regiment[156] |
| 503rd Motorised Rifle Regiment of the 19th Motorised Rifle Division[7] | |||
| 693rd Motorised Rifle Regiment of the 19th Motorised Rifle Division[7] | |||
| 42nd Motorised Rifle Division | 70th Motorised Rifle Regiment[7] | ||
| 71st Motorised Rifle Regiment[7] | |||
| Chechen units | One company of Special Battalion Vostok[315] | ||
| One company of Special Battalion Zapad[315] | |||
Airborne Troops (VDV) | 104th and 234th Paratroop Regiments of the 76th Guards Air Assault Division (Pskov)[7][316] | ||
| Units of 98th Guards Airborne Division (Ivanovo)[316] | |||
| Units of GRU | One Battalion of the Spetsnaz of 45th Detached Reconnaissance Regiment of VDV (Moscow)[316] | ||
| Units of the 10th Special Forces Brigade[7] | |||
| Units of the 22nd Special Forces Brigade[7] | |||
| Deployed units: Abkhaz sector | |
|---|---|
| Allegiance | Units |
| Russia | 7th Novorossiysk Air Assault Division[7] |
| 76th Pskov Air Assault Divisions[7] | |
| Elements of the 20th Motorised Rifle Division[7] | |
| Two battalions of Black Sea Fleet Marines[7] | |
| Abkhazia | Armed Forces (land and air forces) of Abkhazia[20][204] |
| Deployed units: Air | |
|---|---|
| Allegiance | Units |
| Russia | 4th Air Army[9] |
Military analysis
Georgia

Buk-M1 air defence system
United States officials said that "one of the few effective elements of the [Georgia]'s military" was air defence, with the analysts crediting the SA-11 Buk-1M with shooting down a Tupolev-22M bomber and contributing to the loss of some Su-25s.[317] This view was supported by independent Russian analysis.[168] Colonel-General Anatoliy Nogovitsyn, Russian deputy chief of general staff, said the Soviet-made Tor and Buk anti-aircraft missile systems, bought by Georgia from Ukraine, were responsible for downing Russian aircraft during the war.[318] A Russian assessment, reported by Roger McDermott, said that Russian losses would have been significantly higher if the Georgians had not left behind a portion of their Buk-M1 systems near Senaki in western Georgia and several Osa missile launchers in South Ossetia.[319] According to some reports, Georgia also possessed a battery of the Israeli-made SPYDER-SR short-range self-propelled anti-aircraft system.[320] The Georgian air-defence early-warning and command-control tactical system was linked via Turkey to a NATO Air Situation Data Exchange (ASDE), which provided Georgia with intelligence during the conflict.[320]
Georgia has said that its key deficiencies were ineffective communication during action and its lacking air strength.[321] Konstantin Makienko of CAST saw substandard instruction of pilots as the primary reason for the paltry conduct of Georgian air sorties.[168] According to Georgian first deputy defence minister Batu Kutelia, Georgia was required to have a complex, multi-layered air-defence system to protect its airspace.[321] However, Western officers involved with Georgia's military indicated that Georgia's military deficiencies were too great to be eliminated by new weaponry acquisitions.[321] According to a 2 September 2008 New York Times article, "Georgia's Army fled ahead of the Russian Army's advance, turning its back and leaving Georgian civilians in an enemy's path. Its planes did not fly after the first few hours of contact. Its navy was sunk in the harbor, and its patrol boats were hauled away by Russian trucks on trailers."[321]
Georgia did not prepare for confronting an all-out incursion by Russia.[322] Many managerial and procedural problems surfaced during the war.[323] According to a Western officer, Georgian logistical readiness was mediocre; there was interference between subdivisions during the action.[321] Trainings simulating combat against a probable enemy, the 58th Army, had never been organised by the Georgian Army. During the war, communications broke down in the mountains and troops had to resort to mobile phones. There was insufficient planning; according to Giorgi Tavdgiridze, nobody thought about sealing the Roki Tunnel. There was a dismal organisation of the delivery of 10,000 Georgian reservists in Gori on 9 August; they had no specific targets and went back to Tbilisi the following day. The conflict was named by Georgian journalists as the war "that was hidden from history" because there was very little video recording of the fighting.[5] According to their American trainers, Georgian soldiers were unprepared for fighting despite having "warrior spirit".[308] There was a small number of disciplined and knowledgeable officers in high ranking positions,[324] and Saakashvili's government had no military background.[325]
Russia
The Russian Command, Control, Communications and Intelligence (C³I) performed poorly during the conflict.[319] The Russian communication systems were outdated, with a 58th Army commander allegedly making contact with his combat troops via a journalist-owned satellite phone.[319] Without the modern GLONASS, precision-guided munitions could not be used; the US-controlled GPS was unavailable, since the war zone was blacked out.[319] Due to the negligence of Russian defence minister, the use of unmanned aerial vehicles was not sanctioned;[319] an RIA Novosti editorial said that Russian forces were without reliable aerial-reconnaissance systems, once using a Tupolev Tu-22M3 bomber instead.[326] However, Russian reconnaissance battalions and regiments were also deployed during the war.[327] Deputy chief of the General staff of Russia, General Anatoly Nogovitsyn, said that in the conflict new weapons were not tried out.[328]
The RIA Novosti editorial also said that Russian Su-25 ground-attack jets did not have radar vision and ground-target coordinate computing. They also did not have long-range surface-to-air missiles that could be fired beyond the air-defence zones of an adversary.[326] Opposition-affiliated Russian analyst Konstantin Makienko observed the substandard conduct of the Russian Air Force: "It is totally unbelievable that the Russian Air Force was unable to establish air superiority almost to the end of the five-day war, despite the fact that the enemy had no fighter aviation."[168]
According to Russian expert Anton Lavrov, on 8 August, Russian and South Ossetian troops deployed in South Ossetia were unaware that Russian aviation was involved in the war. Russian troops and South Ossetians often assessed Russian aircraft as enemy and shot at them before precise identification took place.[329] On 8 August, the air force performed 63 flights in support of Russian ground troops.[330] A total of six Russian warplanes were lost during the war: one Su-25SM, two Su-25BMs, two Su-24Ms and one Tu-22M3; friendly fire was the cause of the downing of three planes.[331] Lavrov denies that the downed Tu-22M was used for reconnaissance.[332]
The communication between the North Caucasus Military District commander and the air force was poor and their roles in commanding were unclear. Colonel-General Aleksandr Zelin, commander-in-chief of the Air Force, did not set foot in the command post, instead running Air-force operations on a mobile phone from his workroom without any help from his air-defence aides. The air force was blamed of rendering no assistance to land campaign.[319]
Swedish analysts Carolina Vendil Pallin and Fredrik Westerlund said that although the Russian Black Sea Fleet did not meet significant resistance, it proved effective at implementing elaborate operations.[333] Mechanised infantry opened a new front in Abkhazia, which contributed to the rapidity of Russia's winning.[319]
Heritage Foundation researchers said in their assessment of the preparation of Russian general-staff that the manoeuvres were planned and implemented effectively, with a crucial confusion being engineered by the Russians.[312] A Reuters analyst described Russia's army as "strong but flawed"; the war demonstrated that Russia's "armed forces have emerged from years of neglect as a formidable fighting force, but revealed important deficiencies." He stated that Russia fell short of its role of a first-rate military power due to these faults.[334] Unlike the Second Chechen War, Russia's force in Georgia was composed primarily of professional soldiers instead of conscripts.[335] Reuters journalists in Georgia stated that they detected the Russian forces to be well-outfitted and orderly forces. CAST director Ruslan Pukhov said that "the victory over the Georgian army ... should become for Russia not a cause for euphoria and excessive joy, but serve to speed up military transformations."[334] Roger McDermott wrote that slight dissimilarity in criticism by civilian and official references after the conflict was "an orchestrated effort by the government to 'sell' reform to the military and garner support among the populace."[319]
However, the Russian Army's transformation into a professional army was not deemed as fruitful. In September 2008, General Vladimir Boldyrev acknowledged that many of the professional soldiers did not have better training than the conscripts. Most of the land combat warfare was conducted by Russian Airborne Troops and special troops. Due to the failure of the Russian Air Force to penetrate Georgian air defence, airborne troops could not be airlifted behind Georgian lines. A surprise attack on a land-forces commander, in which only five of thirty vehicles in his convoy made it, demonstrated information-gathering negligence. Many Russian land units reportedly had a scarce ammo supply.[324]
Equipment losses and cost
Georgia

Georgian DANA howitzer
After the ceasefire agreement Stratfor states that Russia "has largely destroyed Georgia's war-fighting capability".[336] After the ceasefire was signed on 12 August, in Georgia proper, Russian troops attempted to seize and destroy Georgian armament, a process termed by the Moscow Defence Brief as the "demilitarization of the Georgian Armed Forces".[7] Most losses of armaments were sustained after the ceasefire.[337]
About 20 armoured fighting vehicles, including tanks, were destroyed in the fighting.[338] Before the conflict, Georgia possessed 230–240 tanks in total.[339] At the time of the conflict, Georgia operated 191 T-72 tanks,[340] of which 75 were deployed into South Ossetia.[341] Georgia lost at least 10 T-72 tanks destroyed in and near Tskhinvali.[342] After the end of hostilities, the Russian military seized a total of 65 Georgian tanks. About 20 of those were subsequently destroyed.[337]
The Georgian army possessed 154 IFVs, 16 reconnaissance vehicles, 66 APCs and 86 multi-purpose tracked armoured vehicles before the conflict.[340] Less than 10 armoured vehicles were destroyed in combat.[338] Two BMP-2s were destroyed in combat and two were captured.[342] At least 20 BMPs were captured after the hostilities,[337] including several BMP-1s that were upgraded to BMP-1U.[343] Georgia lost two Otokar Cobra armoured vehicles. Dozens of automobiles and lorries were also lost.[337]
Two DANA self-propelled howitzers of the Georgian army were destroyed in combat and two DANAs were captured in and near Gori.[342] Further 20 artillery pieces, including 120 mm mortars, were left behind. Six 2S7 Pions were captured after the hostilities.[344] Two Buk-M1s launch vehicles and their transport loaders, as well as up to five OSA-AKM SAMs were also captured.[345] The Russian military seized 1,728 firearms at the Senaki Second Infantry Brigade base.[346]
The Georgian Navy lost one boat at sea according to Russia.[347] In Poti, four boats were submerged. Nine rigid-hull inflatables were captured.[348][337]
The Air Force sustained limited damage as only three transport planes and four helicopters were confirmed lost.[345] The Georgian air force ceased all sorties after 8 August.[345] Instead all fighter and training aircraft, including the Su-25s, were tucked away.[345] Russian bombers impaired the airstrips in Georgia.[347] A Russian air attack on Marneuli Air Force Base destroyed three AN-2 aircraft. Russian airborne forces set fire to two Mi-24 helicopters and one Mi-14 on 11 August.[349]
Georgian Defence Minister Davit Kezerashvili said that Georgia lost materiel worth $250 million.[5] According to Georgian president Mikheil Saakashvili, his country saved 95 percent of its armed forces.[5]
In 2009, Russian Army Chief of General Staff Nikolai Makarov stated that Georgia was rearming, although the armament was not directly provided by the United States. According to Makarov, the Georgian Armed Forces had exceeded their pre-war strength by 2009.[350]
Russia and South Ossetia

Russian Tu-22M3
Russia admitted that three of its Su-25 strike aircraft and one Tu-22 long-range bomber were lost. Georgia at that time claimed it had downed no less than 21 Russian aircraft.[318]Moscow Defence Brief provided a higher estimate for air force losses, saying that Russian Air Force total losses during the war were one Tu-22M3 long-range bomber, one Su-24M Fencer fighter-bomber, one Su-24MR Fencer E reconnaissance plane and four Su-25 attack planes.[7] Anton Lavrov listed one Su-25SM, two Su-25BM, two Su-24M and one Tu-22M3 lost.[331] Two helicopters, a Mi-8MTKO and a Mi-24, were wrecked in an accident after the hostilities.[351]
While there are no official figures, Russian ground equipment losses in the war are estimated to be three tanks, at least 20 armoured and 32 non-armoured vehicles lost in combat. Several more vehicles were impaired in accidents.[351] During one engagement, Georgian forces destroyed 25 out of 30 vehicles of a Russian military unit commanded by General Anatoly Khrulyov.[352] The Russian military had no losses in the artillery, air defence and naval forces.[351] According to Nezavisimaya Gazeta, the five-day war cost Russia an estimated 12.5 billion rubles, a daily cost of 2.5 billion rubles.[353]
South Ossetian forces lost two BMP-2s.[17]
See also
- Tom Clancy's Ghost Recon (2001 video game)
- Kosovo independence precedent
- For Enforcing Peace
Olympus Inferno – a 2009 Russian war drama film and the first feature film on the South Ossetian conflict
5 Days of War – a 2011 film depicting the war
August Eighth – a 2012 Russian war drama film depicting the war
Notes
^ South Ossetia's status is disputed. It considers itself to be an independent state, but this is recognised by only a few other countries. The Georgian government and most of the world's other states consider South Ossetia de jure a part of Georgia's territory.
^ Abkhazia is the subject of a territorial dispute between the Republic of Abkhazia and Georgia. The Republic of Abkhazia unilaterally declared independence on 23 July 1992, but Georgia continues to claim it as part of its own sovereign territory. Abkhazia has received formal recognition as an independent state from 7 out of 193 United Nations member states, 2 of which have subsequently withdrawn their recognition.
^ The war is known by a variety of other names, including Five-Day War, August War and Russian invasion of Georgia.
References
^ Hider, James (27 August 2008). "Russian-backed paramilitaries 'ethnically cleansing villages'". The Times. Archived from the original on 27 August 2008..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ ab Irma Choladze (22 January 2009). "Kodori Gorge Refugees in Limbo". Institute for War and Peace Reporting. Archived from the original on 11 October 2014.
^ ab "Statement by President of Russia Dmitry Medvedev". The Kremlin. 26 August 2008. Archived from the original on 2 September 2008.
^ ab Harding, Luke; Percival, Jenny (9 September 2008). "Russian troops to stay in Abkhazia and South Ossetia". The Guardian.
^ abcde Liklikadze, Koba (26 September 2008). "Lessons and losses of Georgia's five-day war with Russia". The Jamestown Foundation. Archived from the original on 6 September 2009.
^ Donovan 2009, p. 11.
^ abcdefghijklmno Barabanov, Mikhail (2009). "The August War between Russia and Georgia". Moscow Defence Brief. Centre for Analysis of Strategies and Technologies. 3 (13). Archived from the original on 4 April 2009.
^ abc Alexander Nicoll; Sarah Johnstone (September 2008). "Russia's rapid reaction". International Institute for Strategic Studies. Archived from the original on 21 October 2008.
^ ab Krasnogir, Sergey (8 August 2008). Расстановка сил (in Russian). Lenta.Ru. Archived from the original on 9 August 2008.
^ Luke Harding (11 August 2008). "Abkhazia: Moscow sends troops into second enclave". The Guardian.
^ abc Volume II 2009, p. 214.
^ Misha Dzhindzhikhashvili (9 August 2008). "Full scale war: Georgia fighting continues over South Ossetia". Die Welt.
^ abcde "Human Rights Watch – Appendix" (PDF). Human Rights Watch.
^ ab Tanks 2010, pp. 130–135.
^ "Russia lost 64 troops in Georgia war, 283 wounded". Reuters. 21 February 2009.
^ Volume II 2009, p. 224.
^ abc Tanks 2010, p. 137.
^ abc Tanks 2010, pp. 136–137.
^ Юрий ТАНАЕВ: "Грузинская сторона по моральному духу и боеготовности не готова к активным действиям" (in Russian). "Южная Осетия". 11 April 2009. Archived from the original on 28 July 2013.
^ abc Inal Khashig (14 August 2008). "Abkhaz Open 'Second Front'". Institute for War and Peace Reporting. Archived from the original on 14 August 2008.
^ abc "List of Casualties among the Georgian Military Servicemen". Ministry of Defence of Georgia. Archived from the original on 7 June 2012.
^ abcde "BASIC FACTS: CONSEQUENCES OF RUSSIAN AGGRESSION IN GEORGIA". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Georgia. Archived from the original on 2 August 2014.
^ ab Мы полагаем, что мы в полной мере доказали состав преступления (in Russian). Interfax. 3 July 2009. Archived from the original on 16 May 2011.
^ "Deceased victims list". Ossetia-war.com. Archived from the original on 28 May 2009.
^ Список погибших граждан Южной Осетии на 04.09.08 (in Russian). osetinfo.ru. 4 September 2008. Archived from the original on 5 September 2008.
^ "A Summary of Russian Attack". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Georgia. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 August 2014.
^ ab "Civilians in the line of fire: The Georgia-Russia conflict". Amnesty International. 18 November 2008. Archived from the original on 11 December 2008.
^ "UNHCR secures safe passage for Georgians fearing further fighting". UNHCR. 15 August 2008.
^ Fawkes, Helen (20 August 2008). "Despair among Georgia's displaced". BBC News.
^ Michael Emerson (August 2008). "Post-Mortem on Europe's First War of the 21st Century" (PDF). Centre for European Policy Studies.
^ abc Brian Whitmore (12 September 2008). "Is The Clock Ticking For Saakashvili?'". Radio Free Europe / Radio Liberty.
^ ab Marc Champion; Andrew Osborn (16 August 2008). "Smoldering Feud, Then War". The Wall Street Journal.
^ ab Luke Harding (19 November 2008). "Georgia calls on EU for independent inquiry into war". The Guardian.
^ ab Jean-Rodrigue Paré (13 February 2009). "The Conflict Between Russia and Georgia". Parliament of Canada.
^ Andrew Rettman (24 February 2016). "West told Ukraine to abandon Crimea, document says". EUobserver.
^ ab Eka Tsamalashvili; Brian Whitmore (14 November 2008). "Eyewitness Accounts Confirm Shelling Of Georgian Villages". Radio Free Europe / Radio Liberty.
^ abc Håkan Karlsson (12 September 2016). "Competing Powers: U.S.-Russian Relations, 2006–2016" (PDF). Swedish Defence University. p. 50. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 January 2017.
^ abcd Peter Roudik. "Russian Federation: Legal Aspects of War in Georgia". Library of Congress.
^ ab Nikolaus von Twickel (17 November 2008). "Moscow Claims Media War Win". The Moscow Times. Archived from the original on 23 May 2012.
^ Chifu 2009, pp. 53–54.
^ ab Laaneots 2016, pp. 56–57.
^ ""Little Green Men": A Primer on Modern Russian Unconventional Warfare, Ukraine 2013–2014" (PDF). The United States Army Special Operations Command. 2016. p. 14. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 April 2016. Retrieved 7 August 2018.
^ abcd Roy Allison (2008). "Russia resurgent? Moscow's campaign to 'coerce Georgia to peace'" (PDF). International Affairs. 84 (6): 1145–1171. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2346.2008.00762.x. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 September 2009.
^ Andrew North (14 July 2015). "Georgia accuses Russia of violating international law over South Ossetia". The Guardian.
^ Cornell 2001, pp. 131–135.
^ Cornell 2001, p. 130.
^ Julie 2009, pp. 97–99.
^ Julie 2009, p. 105.
^ ab Souleimanov, Emil (2013). Understanding Ethnopolitical Conflict: Karabakh, South Ossetia, and Abkhazia Wars Reconsidered. Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 112–113.
^ Saparov 2014, p. 74.
^ Saparov 2014, p. 82.
^ Stephen F. Jones (10 June 2014). "South Ossetia's unwanted independence". openDemocracy.
^ Saparov 2014, p. 148.
^ Saparov 2014, p. 77.
^ Stephen Jones (November 2008). "Clash in the Caucasus: Georgia, Russia, and the Fate of South Ossetia" (PDF). Origins: Current Events in Historical Perspective. 2 (2).
^ ab Lieven, Anatol (11 August 2008). "Analysis: roots of the conflict between Georgia, South Ossetia and Russia". The Times. Archived from the original on 12 August 2008.
^ Cornell 2001, pp. 154–155.
^ ab International Crisis Group (7 June 2007). "Georgia's South Ossetia Conflict: Make Haste Slowly" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 June 2007.
^ "March 31: Georgia moves towards independence, first president's birthday". Agenda.ge. 31 March 2015.
^ ab Charles King. "The Five-Day War" (PDF). Georgetown University.
^ Alexei Zverev (1996). "Ethnic Conflicts in the Caucasus 1988–1994". Vrije Universiteit Brussel.
^ Cornell 2001, pp. 157–158.
^ Hooman Peimani (2009). Conflict and Security in Central Asia and the Caucasus. ABC-CLIO.
^ Giorgi Sepashvili; Nino Khutsidze (5 February 2006). "S.Ossetia: Mapping Out Scenarios". Civil.Ge.
^ Luke Harding (1 September 2008). "Russia's cruel intention". The Guardian.
^ Oleksandr Kramar (16 April 2014). "Self-Determination for the Kremlin". The Ukrainian Week.
^ ab Giorgi Kupatadze (26 September 2006). "Georgian-Abkhaz Tensions Rise Over Kodori Gorge". Institute for War and Peace Reporting. Archived from the original on 20 October 2014.
^ Cornell 2001, pp. 331–332.
^ Cornell 2001, p. 334.
^ ab Van Herpen 2014, pp. 206–209.
^ ab Van Herpen 2014, pp. 233–235.
^ "FACTBOX-What is Georgia's rebel South Ossetia region?". Reuters. 8 August 2008.
^ Volume II 2009, p. 132.
^ ab "Q&A: Conflict in Georgia". BBC News. 11 November 2008.
^ ab "Profile: President Mikheil Saakashvili of Georgia". BBC. 27 September 2012.
^ ab Charles King (25 August 2004). "Tbilisi Blues". Foreign Affairs.
^ Sergey Markedonov (16 November 2008). "Regional Conflicts Reloaded". Russia in Global Affairs.
^ "Chronicle of the Georgian-Ossetian conflict: Fact sheet". RIA Novosti. 13 August 2008.
^ "Russia Warns Against Tbilisi's 'S.Ossetia Administration' Plan". Civil.Ge. 29 March 2007.
^ The Associated Press (11 March 2008). "Russia's NATO envoy says offering Georgia membership track would bolster separatists". International Herald Tribune. Archived from the original on 17 September 2008.
^ Marina Perevozkina (24 March 2008). Дума разочаровала непризнанных (in Russian). Nezavisimaya Gazeta.
^ Cohen 2011, p. 15.
^ James Rodgers (28 November 2006). "Georgia's Nato bid irks Russia". BBC News.
^ Pagnamenta, Robin (8 August 2008). "Analysis: energy pipeline that supplies West threatened by war Georgia conflict". The Times. Archived from the original on 3 September 2008.
^ Emin Makhmudov; Mikhail Zygar (25 May 2005). "Revolutions in the Pipeline". Kommersant. Archived from the original on 23 July 2009.
^ Anne Gearan (9 August 2008). "Georgia's oil pipeline is key to U.S. support". San Francisco Chronicle.
^ Steven Erlanger; Steven Lee Myers (3 April 2008). "NATO Allies Oppose Bush on Georgia and Ukraine". The New York Times.
^ "What NATO Summit Declaration Says on Georgia". Civil.Ge. 4 April 2008.
^ Evans, Michael (5 April 2008). "Vladimir Putin tells summit he wants security and friendship". The Times. Archived from the original on 24 July 2008.
^ Van Herpen 2014, p. 210.
^ "Russia army vows steps if Georgia and Ukraine join NATO". Reuters. 11 April 2008.
^ Cables Track US Diplomatic Efforts to Avert Russian-Georgian Conflict, Der Spiegel
^ DAS BRYZA'S MEETINGS WITH GEORGIA MINISTRY OF INTERNAL AFFAIRS OFFICIALS, 2008 May 16
^ Luke Harding (1 December 2010). "WikiLeaks cables claim Russia armed Georgian separatists". The Guardian. Retrieved 26 October 2018.
^ Vladimir Socor (18 April 2008). "Russia moves toward open annexation of Abkhazia, South Ossetia". The Jamestown Foundation. Archived from the original on 15 August 2009.
^ "Russia Brushes off Western Call to Revoke Abkhaz, S.Ossetia Move". Civil.Ge. 24 April 2008.
^ "Russia 'shot down Georgia drone'". BBC News. 21 April 2008.
^ Finn, Peter (1 May 2008). "Russia's Moves Add To Strains With Georgia". The Washington Post.
^ "UN Probe Says Russian Jet Downed Georgian Drone". Civil.Ge. 26 May 2008.
^ "Georgia 'plans war in Abkhazia'". BBC News. 29 April 2008.
^ "Georgia-Russia tensions ramped up". BBC News. 30 April 2008.
^ abcdefg Svante E. Cornell; Johanna Popjanevski; Niklas Nilsson (August 2008). "Russia's War in Georgia: Causes and Implications for Georgia and the World" (PDF). Central Asia-Caucasus Institute & Silk Road Studies Program. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 February 2014.
^ "UNOMIG Denies Military Buildup in Abkhaz Conflict Zone". Civil.Ge. 8 May 2008.
^ "Russia Gives Some Details on Troop Increase in Abkhazia". Civil.Ge. 8 May 2008.
^ "Georgia condemns Russian actions". BBC News. 18 May 2008.
^ "General Assembly recognizes right of return of displaced to Abkhazia, Georgia". UN News Centre. 15 May 2008.
^ "Russia says UN Abkhazian refugee resolution counterproductive". RIA Novosti. 16 May 2008.
^ "Russia army unit sent to Abkhazia". BBC News. 31 May 2008.
^ "European Parliament resolution of 5 June 2008 on the situation in Georgia". European Parliament. 5 June 2008.
^ "Russia railway soldiers leave Georgian rebel region". Reuters. 2 August 2008.
^ "RUSSIA VS GEORGIA: THE FALLOUT" (PDF). International Crisis Group. 22 August 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016.
^ Россия начнет войну против Грузии предположительно в августе – П. Фельгенгауер (in Russian). Gruziya Online. 20 June 2008.
^ Чеченцы расписали сценарий войны России против Грузии (in Russian). MIGnews. 5 July 2008.
^ Volume II 2009, p. 204.
^ Margarita Antidze (8 July 2008). "Georgia plans operation to free detained soldiers". Reuters.
^ ab Mikheil Svanidze (11 July 2008). "Russia says it sent warplanes over South Ossetia to 'prevent bloodshed'". The Messenger.
^ "Russia admits Georgia overflights". BBC News. 10 July 2008.
^ "Overflights question Russia's Georgia role: NATO". Reuters. 15 July 2008.
^ "Russia, U.S. hold war games on opposite sides of Caucasus: officials". Canada.com. Agence France-Presse. 15 July 2008. Archived from the original on 26 February 2015.
^ Tea Kerdzevadze (1 August 2008). "International Large-Scale Military Exercise 'Immediate Response 2008'". Georgian Daily. Archived from the original on 13 August 2008.
^ ab Shanker, Thom (16 August 2008). "Russians Melded Old-School Blitz With Modern Military Tactics". The New York Times.
^ "Russian paratroopers arrive in North Caucasus for combat drills". RIA Novosti. 16 July 2008.
^ Svante E. Cornell; S. Frederick Starr, eds. (2009). The Guns of August 2008: Russia's War in Georgia. M.E. Sharpe. p. 71.
^ ab Tanks 2010, p. 44.
^ "Countdown in the Caucasus: Seven days that brought Russia and Georgia to war". Financial Times. 26 August 2008. Archived from the original on 20 September 2008.
^ Chifu 2009, p. 53.
^ Laaneots 2016, p. 35.
^ abc Volume II 2009, p. 208.
^ Van Herpen 2014, p. 214.
^ Dunlop 2012, p. 93.
^ В Цхинвали прибыли 300 добровольцев из Северной Осетии (in Russian). Lenta.ru. 4 August 2008.
^ Южная Осетия может начать против Грузии "рельсовую войну" (in Russian). Regnum. 5 August 2008.
^ ab Dunlop 2012, p. 95.
^ "Russia vows to defend S Ossetia". BBC News. 5 August 2008.
^ ab Martin Malek (March 2009). "Georgia & Russia: The 'Unknown' Prelude to the 'Five Day War'". Caucasian Review of International Affairs. 3 (2): 227–232.
^ Maria Bogdarenko (6 August 2008). Шашки наголо (in Russian). Nezavisimaya Gazeta. Archived from the original on 30 May 2009.
^ Marina Perevozkina (8 August 2008). Это не конфликт, это – война (in Russian). Nezavisimaya Gazeta.
^ Laaneots 2016, p. 37.
^ Chifu 2009, p. 58.
^ Конфликт в Южной Осетии: переговоров не будет (in Russian). Radio Svoboda. 7 August 2008.
^ abcde Peter Finn (17 August 2008). "A Two-Sided Descent into Full-Scale War". The Washington Post.
^ Tanks 2010, p. 46.
^ abc "On the eve of war: The Sequence of events on august 7, 2008" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 July 2009.
^ ab "Spot Report: Update on the situation in the zone of the Georgian-Ossetian conflict" (PDF). OSCE. 7 August 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 March 2009.
^ "S.Ossetia Rejects Talks". Civil.Ge. 6 August 2008.
^ Van Herpen 2014, p. 222.
^ "GEORGIA: SOUTH OSSETIA SITREP 2: GEORGIA CLAIMS TO CONTROL MUCH OF SOUTH OSSETIA, FIGHTING CONTINUES". WikiLeaks.
^ "Saakashvili Appeals for Peace in Televised Address". Civil.Ge. 7 August 2008.
^ abcde Volume II 2009, p. 209.
^ Vladimir Socor (8 August 2008). "THE GOALS BEHIND MOSCOW'S PROXY OFFENSIVE IN SOUTH OSSETIA". The Jamestown Foundation.
^ Alex Rodriguez; Bay Fang (9 August 2008). "Georgian conflict puts U.S. in middle". Chicago Tribune.
^ "'Georgia Decided to Restore Constitutional Order in S.Ossetia' – MoD Official". Civil.Ge. 8 August 2008. Archived from the original on 6 September 2009.
^ abc Allenova, Olga (8 August 2008). Первая миротворческая война (in Russian). Kommersant.
^ Pavel Felgenhauer (14 August 2008). Это была не спонтанная, а спланированная война (in Russian). Novaya Gazeta.
^ Laaneots 2016, p. 57.
^ ab Chivers, C.J. (15 September 2008). "Georgia Offers Fresh Evidence on War's Start". The New York Times.
^ СМИ: российские войска вошли в Южную Осетию еще до начала боевых действий (in Russian). NEWSru.com. 11 September 2008.
^ Chifu 2009, p. 60.
^ Chifu 2009, p. 59.
^ Laaneots 2016, pp. 58–59.
^ Tanks 2010, pp. 50–51.
^ "Heavy fighting as Georgia attacks rebel region". Agence France-Presse. 7 August 2008. Archived from the original on 22 August 2008.
^ Tanks 2010, p. 54.
^ Volume III 2009, pp. 370–371.
^ Volume III 2009, p. 69.
^ abc Volume II 2009, p. 210.
^ "Dmitry Medvedev held an emergency meeting with permanent members of the Security Counsil on the situation in South Ossetia". The Kremlin. 8 August 2008. Archived from the original on 10 February 2015.
^ abcd Konstantin Makienko (15 November 2008). "The Russian Air Force didn't perform well during the conflict in South Ossetia". Centre for Analysis of Strategies and Technologies. Archived from the original on 27 March 2009.
^ Tanks 2010, p. 55.
^ Ralph Peters (12 August 2008). "Russia Goes Rogue". New York Post.
^ Герой (in Russian). Lenta.ru. 15 August 2008. Archived from the original on 28 May 2009.
^ Volume I 2009, p. 21.
^ ab Volume II 2009, p. 219.
^ ab Schwirtz, Michael; Barnard, Anne; Kramer, Andrew E. (11 August 2008). "Russian Forces Capture Military Base in Georgia". The New York Times.
^ Elizabeth Owen; Giorgi Lomsadze (8 August 2008). "Georgia: All-Out War Looms in South Ossetia". EurasiaNet. Archived from the original on 6 May 2009. Retrieved 25 November 2008.
^ Adrian Blomfield (9 August 2008). "Georgia conflict: Screams of the injured rise from residential streets". The Telegraph.
^ "Russian jets attack Georgian town". BBC News. 9 August 2008.
^ ab Barnard, Anne (9 August 2008). "Georgia and Russia Nearing All-Out War". The New York Times.
^ ab Harding, Luke (11 August 2008). "'I got my children out minutes before the bombs fell'". The Guardian.
^ ab Damien McElroy; Adrian Blomfield; Jon Swaine (11 August 2008). "Georgia: Russia fighting on several fronts as Georgian troops withdraw to defend Tbilisi". The Telegraph.
^ abcd "Dutch journalist killed in Russian bombing of Gori". International Herald Tribune. The Associated Press. 12 August 2008. Archived from the original on 13 August 2008.
^ ab Christopher Torchia; David Nowak (11 August 2008). "Russia opens new front, drives deeper into Georgia". Associated Press. Archived from the original on 14 August 2008.
^ Goga Aptsiauri (12 August 2009). "Victims of Last Year's Tragedy Remembered in Gori". Media.ge. Archived from the original on 15 August 2009.
^ Kim Sengupta; Shaun Walker; Rupert Cornwell (17 August 2008). "The new Cold War: Crisis in the Caucasus". The Independent.
^ Greenhill, Sam (13 August 2008). "The innocent babies covered in blood after Russia's blitzkrieg in Georgia". Daily Mail.
^ Luke Harding (14 August 2008). "Amid promise of peace, Georgians live in terror". The Guardian.
^ ab Levy, Clifford J. (14 August 2008). "Russia Vows to Support Two Enclaves, in Retort to Bush". The New York Times.
^ "Violence flares in Georgian town". BBC News. 13 August 2008.
^ Bahrampour, Tara (14 August 2008). "A Convoy Heads for Gori to Investigate Rumors of Plunder". The Washington Post.
^ "Russian Military Will Leave Gori in 2 Days". redOrbit. 14 August 2008. Archived from the original on 30 March 2014. Retrieved 29 March 2014.
^ C. J. Chivers (15 August 2008). "For Russian Armor, Even With Rice in Georgia, Cease-Fire Is Not a Red Light". The New York Times.
^ Viktor Baranets (8 August 2014). Генерал-лейтенант Анатолий Хрулев: Мои войска могли взять Тбилиси, но не было приказа (in Russian). Komsomolskaya Pravda.
^ "Russia/Georgia: Militias Attack Civilians in Gori Region". Human Rights Watch. 16 August 2008.
^ Tony Halpin (18 August 2008). "'Putin has given us an order that everyone must leave or be shot'". The Times. Archived from the original on 18 August 2008.
^ "Police Back in Gori". Civil.Ge. 23 August 2008.
^ C.J. Chivers (22 August 2008). "Russia Pulls the Bulk of Its Forces Out of Georgia". The New York Times.
^ "Russian navy sinks Georgian boat: Defence ministry". Reuters. 10 August 2008.
^ "Russia sinks Georgian boat after attack". RT. 11 August 2008.
^ Dmitry Gorenburg (December 2008). "The Russian Black Sea Fleet After The Georgia War" (PDF). PONARS Eurasia Policy.
^ Ariel Cohen (11 August 2008). "The Russian-Georgian War: A Challenge for the U.S. and the World". The Heritage Foundation. Archived from the original on 28 May 2009.
^ abc "Day-by-day: Georgia-Russia crisis". BBC News. 21 August 2008.
^ Cohen 2011, pp. 11–12.
^ Ilya Kachayev (9 August 2008). "Abkhaz separatists strike disputed Georgia gorge". Reuters.
^ ab "Abkhazia moves to flush out Georgian troops". Associated Press. 9 August 2008. Archived from the original on 12 August 2008.
^ "Abkhazia says Georgian troops pushed from province". International Herald Tribune. The Associated Press. 12 August 2008. Archived from the original on 13 August 2008.
^ "Abchasen räumen Minen und suchen versprengte georgische Truppen im Kodori-Tal" (in German). RIA Novosti. 14 August 2008. Archived from the original on 18 August 2008.
^ abcd Guy Chazan (19 August 2008). "Russia Briefly Seizes Georgian Port". The Wall Street Journal.
^ "Russia moves into Georgian territory as conflict worsens". Agence France-Presse. 11 August 2008. Archived from the original on 17 August 2008.
^ "Russian forces sink Georgian ships". Al Jazeera. 14 August 2008. Archived from the original on 22 March 2014.
^ "Russian tanks in Georgia's Poti: witnesses". Reuters. 14 August 2008.
^ Schwirtz, Michael; Barry, Ellen (19 August 2008). "Russia Sends Mixed Signs on Pullout From Georgia". The New York Times.
^ Adrian Blomfield (24 August 2008). "Georgia conflict: Russian troops accused of selling loot". The Telegraph.
^ Reuben F. Johnson (24 November 2008). "Tennis Shoes and Stolen Toilets". The Weekly Standard.
[permanent dead link]
^ "Russian bombing kills 3 at Georgian airbase-Georgia". Reuters. 8 August 2008.
^ "Georgia Says Russian Jet Bombed Vaziani Base". Civil.Ge. 8 August 2008.
^ Blomfield, Adrian (8 August 2008). "Georgia conflict: Roar of war as jets fill the air". The Telegraph.
^ "MIA: Three Die in Marneuli Airfield Bombing". Civil.Ge. 8 August 2008.
^ "Fighting with Russia spreads to cities across Georgia". CNN. 8 August 2008. Archived from the original on 22 August 2008.
^ "Russia bombs Tbilisi airport, says official". Reuters. 9 August 2008.
^ "Tbilisi civilian airport hit in Russian air strike". Reuters. 10 August 2008.
^ Kramer, Andrew E.; Barry, Ellen (12 August 2008). "Russia, in Accord With Georgians, Sets Withdrawal". The New York Times.
^ Guy Chazan (14 August 2008). "Raids Suggest Russia Targeted Energy Pipelines". The Wall Street Journal.
^ ab Matthew Collin (24 November 2008). "Media war flares over S Ossetia". Al Jazeera.
^ Donovan 2009, p. 21.
^ Рунет вернулся в Грузию (in Russian). Interfax. 21 October 2008.
^ ab Svante Cornell (17 June 2009). "Georgia feels Russia's heavy hand". The Guardian.
^ Asher Moses (12 August 2008). "Georgian websites forced offline in 'cyber war'". The Sydney Morning Herald.
^ "RIA Novosti hit by cyber-attacks as conflict with Georgia rages". RIA Novosti. 10 August 2008.
^ "RT attacked". RT. 12 August 2008.
^
Markoff, John (12 August 2008). "Before the Gunfire, Cyberattacks". The New York Times.
^ "Russia's president says operation in Georgia over". RIA Novosti. 12 August 2008.
^ "Russia Endorses Six-Point Plan". Civil.Ge. 12 August 2008.
^ ab Kramer, Andrew E. (13 August 2008). "Peace Plan Offers Russia a Rationale to Advance". The New York Times. The translation of the six points is by the Times.
^ "Georgia and Russia agree on truce". BBC News. 13 August 2008.
^ "President of Russia". The Kremlin. 14 August 2008. Archived from the original on 5 May 2009.
^ Kilner, James (15 August 2008). "Russian convoy moves deeper inside Georgia: witness". Reuters.
^ "President Medvedev signed a plan to resolve the Georgian-South Ossetia conflict, based on the six principles previously agreed on". The Kremlin. 16 August 2008. Archived from the original on 29 July 2012.
^ Harding, Luke; Meikle, James (13 August 2008). "Georgian villages burned and looted as Russian tanks advance". The Guardian.
^ "New Agreement in Force". Civil.Ge. 8 September 2008.
^ "Russians 'agree Georgia deadline'". BBC News. 8 September 2008.
^ Kunkle, Fredrick (18 August 2008). "Bush, European Leaders Urge Quick Withdrawal From Georgia". The Washington Post.
^ Margarita Antidze; Matt Robinson (19 August 2008). "Russian, Georgian forces exchange prisoners". Reuters.
^ Halpin, Tony (23 August 2008). "Russian troops in partial pullout keeping checkpoints within Georgia". The Times. Archived from the original on 27 August 2008.
^ Schwirtz, Michael (23 August 2008). "Georgia Prepares for Refugees; Russians Declare Pullback Finished". The New York Times.
^ Вывод войск (in Russian). Interfax. 13 September 2008.
^ "Russia hands over control of Georgian buffer zones to EU". RIA Novosti. 9 October 2008.
^ "MIA: Russia's Moves in Perevi Aim at 'Renewal of Military Confrontation'". Civil.Ge. 13 December 2008.
^ "Russian troops withdraw from Georgian town". BBC News. 19 October 2010.
^ "Abkhazia, S.Ossetia Formally Declared Occupied Territory". Civil.Ge. 28 August 2008.
^ "European Parliament resolution of 17 November 2011 containing the European Parliament's recommendations to the Council, the Commission and the EEAS on the negotiations of the EU-Georgia Association Agreement (2011/2133(INI))". European Parliament. 17 November 2011.
^ "Russian MPs back Georgia's rebels". BBC News. 25 August 2008.
^ Mark Tran (26 August 2008). "Russia defies west by recognising Georgian rebel regions". The Guardian.
^ "West condemns Russia over Georgia". BBC News. 26 August 2008.
^ "CoE, PACE Chairs Condemn Russia's Move". Civil.Ge. 26 August 2008.
^ "OSCE Chair Condemns Russia's Recognition of Abkhazia, S.Ossetia". Civil.Ge. 26 August 2008.
^ "Scheffer 'Rejects' Russia's Move". Civil.Ge. 26 August 2008.
^ Jun Okumura (29 August 2008). "The Emergence of an Expanded Forum to Replace the G8: The Silver Lining to the Cloud over Russia and the West". GLOCOM Platform.
^ "Georgia breaks ties with Russia". BBC News. 29 August 2008.
^ Niklas Swanström (3 September 2008). "Georgia: The split that split the SCO". Central Asia-Caucasus Institute Analyst. Archived from the original on 28 May 2009.
^ Parfitt, Tom (22 December 2008). "Security and human rights observers to close South Ossetia mission". The Guardian.
^ Matt Robinson (16 June 2009). "Georgia angry after Russia vetoes U.N. monitors". Reuters.
^ "EUMM Mission Facts And Figures". Retrieved 7 January 2015.
^ Luke Coffey (1 June 2012). "Georgia and Russia: The occupation too many have forgotten". thecommentator.
^ Kaarel Kaas (2009). "The Russian Bear on the Warpath Against Georgia". International Centre for Defense Studies.
^ Cohen 2011, pp. vii–viii.
^ Mohammad Sajjadur Rahman. "Georgia and Russia: What Caused the August War?" (PDF). Identity, Culture & Politics: An Afro-Asian Dialogue. 10 (1): 132–146.
^ George Friedman (2 September 2008). "The Medvedev Doctrine and American Strategy". Stratfor Global Intelligence.
^ Henrik Larsen (March 2012). "The Russo-Georgian war and beyond: towards a European great power concert". European Security. 21 (1): 102–121. doi:10.1080/09662839.2012.656595.
^ Denis Dyomkin (21 November 2011). "Russia says Georgia war stopped NATO expansion". Reuters.
^ "S Ossetia 'war crimes' condemned". BBC News. 23 January 2009.
^ "Executive Summary". Up in Flames. Human Rights Watch. 23 January 2009.
^ "2.2 Indiscriminate Shelling of Tskhinvali and Outlying Villages". Up in Flames. Human Rights Watch. 23 January 2009. Archived from the original on 28 May 2009.
^ abc "Georgia: International Groups Should Send Missions". Human Rights Watch. 18 August 2008.
^ Thomas Hammarberg (8 September 2008). "Human Rights in Areas Affected by the South Ossetia Conflict. Special Mission to Georgia and Russian Federation". Council of Europe.
^ "The human cost of war in Georgia". Amnesty International. 1 October 2008. Archived from the original on 2 October 2008.
^ "Russia: Protect Civilians in Occupied Georgia". Human Rights Watch. 25 November 2008.
^ "Violations of Human Rights and Norms of Humanitarian law in the Conflict Zone in South Ossetia". Memorial. 11 September 2008. Archived from the original on 28 May 2009.
^ Aleksandr Gabuev (15 August 2008). Эдуард Кокойты: мы там практически выровняли все (in Russian). Kommersant. Archived from the original on 28 May 2009.
^ McElroy, Damien (30 August 2008). "South Ossetian police tell Georgians to take a Russian passport, or leave their homes". The Telegraph.
^ Volume I 2009, p. 27.
^ Andrew Osborn; Jeanne Whalen (15 August 2008). "Evidence in Georgia Belies Russia's Claims of 'Genocide'". Wall Street Journal.
^ abc "2.7 The Issue of Civilian Casualties in South Ossetia". Up in Flames. Human Rights Watch. 23 January 2009.
^ "South Ossetia Floods European Rights Court With Georgia Cases". Radio Free Europe / Radio Liberty. 6 October 2008. Archived from the original on 6 August 2009.
^ "Case Concerning Application of the International Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination (Georgia v. Russian Federation) Order of 2 December 2008" (PDF). Reports of Judgments, Advisory Opinions, and Orders. International Court of Justice. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 August 2009.
^ "South Ossetians Complain to Court". The New York Times. Reuters. 7 October 2008.
^ "Georgia marks anniversary of war". BBC News. 7 August 2009.
^ "Status of internally displaced persons and refugees from Abkhazia, Georgia, and the Tskhinvali region/ South Ossetia, Georgia". United Nations. 7 May 2014.
^ "Carl Bildt oroad över utvecklingen" (in Swedish). Aftonbladet. 8 August 2008.
^ "Sweden evokes Hitler in condemning Russian assault". The Local. 9 August 2008. Archived from the original on 10 August 2008.
^ "Foreign Secretary deplores continued fighting in Georgia (09/08/2008)". Foreign and Commonwealth Office. Archived from the original on 28 August 2008.
^ "Moscow threatens Georgia regime, says Bush". Financial Times. 12 August 2008.
^ Ben Smith (2 March 2010). "U.S. pondered military use in Georgia". Politico.com.
^ "Lech Kaczyński: jesteśmy tu po to, by podjąć walkę". Rzeczpospolita (in Polish). 12 August 2008.
^ "Orbánnak 56 jutott eszébe az orosz hadmûveletekrõl" (in Hungarian). index.hu. 14 August 2008. Archived from the original on 26 February 2012.
^ Bridget Kendall (21 August 2008). "Russia's Neighbours Go Their Own Way". BBC News.
^ ab Bennhold, Katrin (12 August 2008). "Differences emerge in Europe of a response to Georgia conflict". International Herald Tribune. Archived from the original on 21 August 2008.
^ "La Géorgie et la Russie s'affrontent pour le contrôle de l'Ossétie du Sud". Le Monde (in French). 8 August 2008.
^ "Angela Merkel calls for immediate ceasefire". Bundeskanzlerin. 11 August 2008. Archived from the original on 31 August 2008.
^ "Belarus leader applauds Russian response to South Ossetia crisis". RIA Novosti. 19 August 2008. Archived from the original on 7 September 2009.
^ "Georgia Finalizes Withdrawal From CIS". RFE/RL. 18 August 2009.
^ Committee on Foreign Affairs (21 May 2015). "REPORT on the strategic military situation in the Black Sea Basin following the illegal annexation of Crimea by Russia (2015/2036(INI))". European Parliament.
^ Kramer, Andrew (27 August 2008). "NATO ships cause alarm in Moscow". International Herald Tribune. Archived from the original on 31 August 2008.
^ Mike Mount (20 August 2008). "Navy ships wait to deliver aid to Georgia". CNN.
^ Tran, Mark (21 August 2008). "Russia suspends military cooperation with Nato". The Guardian.
^ "Black Sea Fleet ships start tracking NATO guests". Regnum. 27 August 2008. Archived from the original on 28 August 2008.
^ Госсовет России формулирует новую внешнеполитическую стратегию страны (in Russian). Pervy Kanal. 6 September 2008. Archived from the original on 12 September 2008.
^ Vladimir Socor (27 November 2008). "Naval Imbalance in the Black Sea After the Russian-Georgian War". Ocnus.Net.
^ ab "US trainers say Georgian troops weren't ready". International Herald Tribune. Associated Press. 19 August 2008. Archived from the original on 19 September 2008.
^ Michael Hoffman (11 August 2008). "U.S. takes Georgian troops home from Iraq". Air Force Times.
^ Chifu 2009, p. 57.
^ ab Hamilton, Robert E. (4 September 2008). "A Resolute Strategy on Georgia" (PDF). Centre for Strategic and International Studies. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 September 2008.
^ ab James Jay Carafano; Ariel Cohen; Lajos F. Szaszdi (20 August 2008). "Russian Forces in the Georgian War: Preliminary Assessment and Recommendations". The Heritage Foundation. Archived from the original on 14 August 2009.
^ "What will be the outcome of the Georgian-Ossetian war?". RIA Novosti. 8 August 2008.
^ ab Volume III 2009, p. 371.
^ ab В зону конфликта переброшены роты чеченских батальонов "Восток" и "Запад" (in Russian). Lenta.ru. 11 August 2008.
^ abc В Цхинвали вошли подразделения Воздушно-десантных войск (in Russian). Russian Ministry of Defence. 9 August 2008. Archived from the original on 12 August 2008.
^ David A. Fulghum; Douglas Barrie; Robert Wall; Andy Nativi (15 August 2008). "Georgian Military Folds Under Russian Attack". Aviation Week. Archived from the original on 21 May 2011.
^ ab Vladimir Isachenkov (18 August 2008). "War Reveals Russia's Military Might and Weakness". Aviation. Archived from the original on 20 November 2008.
^ abcdefgh McDermott, Roger N. (Spring 2009). "Russia's Conventional Armed Forces and the Georgian War" (PDF). Parameters. US Army War College. XXXIX: 65–80.
^ ab Aminov, Said. "Georgia's Air Defense in the War with South Ossetia". Moscow Defence Brief. Centre for Analysis of Strategies and Technologies (#1(15)/2009). Archived from the original on 28 May 2009.
^ abcde Chivers, C. J.; Shanker, Thom (2 September 2008). "Georgia Eager to Rebuild Its Defeated Armed Forces". The New York Times.
^ Chifu 2009, p. 63.
^ Chifu 2009, p. 45.
^ ab Tor Bukkvoll (November–December 2009). "Russia's Military Performance in Georgia" (PDF). Military Review. 89 (6): 58. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 December 2009.
^ Cooper, Helene; Chivers, C.J.; Levy, Clifford J. (17 August 2008). "U.S. Watched as a Squabble Turned into a Showdown". The New York Times.
^ ab "Russian Army's weaknesses exposed during war in Georgia". RIA Novosti. 9 September 2008.
^ Tanks 2010, p. 142.
^ Sebastian Alison (27 August 2008). "Georgia War Shows Russia Army Now a 'Force to Be Reckoned With'". Georgian Daily. Archived from the original on 5 May 2009.
^ Tanks 2010, p. 105.
^ Tanks 2010, p. 57.
^ ab Tanks 2010, p. 104.
^ Tanks 2010, p. 100.
^ Pallin, Carolina Vendil; Fredrik Westerlund (24 July 2009). "Russia's war in Georgia: lessons and consequences". Small Wars & Insurgencies. 20 (2).
^ ab Christian Lowe (20 August 2008). "Georgia war shows Russian army strong but flawed". Reuters.
^ "The Caucasus Crisis". German Institute for International and Security Affairs. November 2008. Archived from the original on 1 December 2008.
^ Sweeney, Conor (13 August 2008). "ANALYSIS-Georgia rebel confidence rises after fighting". Reuters. Archived from the original on 2 September 2008.
^ abcde Tanks 2010, p. 75.
^ ab Tanks 2010, p. 113.
^ Россия забрала себе пятую часть грузинских танков (in Russian). Lenta.ru. 16 August 2008.
^ ab Tanks 2010, p. 19.
^ Tanks 2010, p. 47.
^ abc Tanks 2010, p. 110.
^ Tanks 2010, p. 114.
^ Tanks 2010, pp. 110–111.
^ abcd Tanks 2010, p. 111.
^ ლიკლიკაძე, კობა (24 August 2008). "საქართველოს არმიის დანაკარგები ჯერაც დაუზუსტებელია". radiotavisupleba.ge (in Georgian).
^ ab Tanks 2010, p. 112.
^ Mikaberidze, Alexander (1 February 2015). "ARMED FORCES". Historical Dictionary of Georgia. p. 139. ISBN 978-1442241459.
^ "History of the Air Forces of Georgia". Geo-Army.ge. Archived from the original on 13 October 2013.
^ "Russian Army Chief Says Georgia is Rearming". Civil.Ge. 11 November 2009.
^ abc Tanks 2010, p. 136.
^ Cohen 2011, pp. 28–29.
^ Vladimir Ivanov (20 August 2008). Цена победы в Южной Осетии (in Russian). Nezavisimaya Gazeta.
- Books and Reports
.mw-parser-output .refbegin{font-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul{list-style-type:none;margin-left:0}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>dd{margin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100{font-size:100%}
Cornell, Svante E. (2001). Small Nations and Great Powers (PDF). RoutledgeCurzon.
George, Julie A (2009). The Politics of Ethnic Separatism in Russia and Georgia. Palgrave Macmillan.
Saparov, Arsène (2014). From Conflict to Autonomy in the Caucasus: The Soviet Union and the Making of Abkhazia, South Ossetia and Nagorno Karabakh. Routledge.
Chifu, Iulian; Nantoi, Oazu; Sushko, Oleksandr (2009). "The Russian Georgian war: a trilateral cognitive institutional approach of the crisis decision – making" (PDF). Editura Curtea Veche.
Colonel George T. Donovan, Jr. (2009). Russian Operational Art in the Russo-Georgian War of 2008 (PDF). U.S. Army War College.
Cohen, Ariel; Hamilton, Robert E. (2011). The Russian Military and the Georgia War: Lessons and Implications. Strategic Studies Institute. Archived from the original on 15 June 2011.CS1 maint: BOT: original-url status unknown (link)
Maria Raquel Freire; Roger E. Kanet, eds. (2012). Russia and its Near Neighbours. Palgrave Macmillan.
Van Herpen, Marcel H. (2014). Putin's Wars: The Rise of Russia's New Imperialism. Rowman & Littlefield.
Laaneots, Ants (April 2016). "The Russian-Georgian War Of 2008: Causes And Implication" (PDF). Estonian National Defence College.
"Report. Volume I" (PDF). IIFFMCG. September 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 October 2009.
"Report. Volume II" (PDF). IIFFMCG. September 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 July 2011.
"Report. Volume III" (PDF). IIFFMCG. September 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 July 2011.
"The Tanks of August" (PDF). Centre for Analysis of Strategies and Technologies. 2010.
Further reading
Asmus, Ronald D. (2010). A Little War That Shook the World: Georgia, Russia, and the Future of the West. New York: Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 9780230102286.
Cornell, Svante E.; Starr, S. Frederick (2009). The Guns of August 2008: Russia's War in Georgia. Studies of Central Asia and the Caucasus. Armonk, New York: M.E. Sharpe. ISBN 9780765625090.
Allison, Roy (2013). Russia, the West, and Military Intervention. Great Britain: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199590636.
- Jones, Stephen F. The Making of Modern Georgia, 1918–2012: The First Georgian Republic and its Successors (2014).
- Mankoff, Jeffrey. Russian Foreign Policy: The Return of Great Power Politics (2nd ed. 2011).
- Niedermaier, Ana K. Countdown to War in Georgia, Russia's Foreign Policy and Media Coverage of the Conflict in South Ossetia and Abkhazia (2008); a Russian perspective.
- Stent, Angela E. The Limits of Partnership: U.S.-Russian Relations in the Twenty-First Century (2015).
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Russo-Georgian War. |
Georgia
- Chronology of Bombing Facts by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Georgia
Russia
- On the situation around Abkhazia and South Ossetia @ President of Russia
International
- EU Monitoring Mission in Georgia
- OSCE Mission to Georgia (closed)
- The EU Investigation Report on the August 2008 War and the Reactions from Georgia and Russia in the Caucasus Analytical Digest No. 10
Media
War in Georgia. International Crisis Group's multimedia presentation- BBC hub
- Fighting in South Ossetia Photos
- Boston.com Gallery
- Russian air attacks in Georgia
Documentaries
- Andre Nekrasov's Russian Lessons
- The Secrets Of Russia's Propaganda Machine