1980 United States presidential election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 538 electoral votes of the Electoral College 270 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 52.6%[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
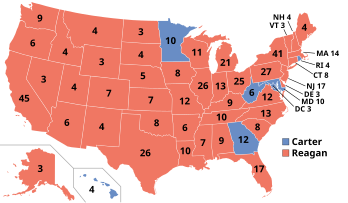  Presidential election results map. Red denotes states won by Reagan/Bush, blue denotes those won by Carter/Mondale. Numbers indicate the electoral votes per state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The United States presidential election of 1980 was the 49th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on November 4, 1980. Republican nominee Ronald Reagan defeated incumbent Democrat Jimmy Carter. Due to the rise of conservativism following Reagan's victory, some historians consider the election to be a realigning election that marked the start of the "Reagan Era".
Carter's unpopularity and poor relations with Democratic leaders encouraged an intra-party challenge by Senator Ted Kennedy, a younger brother of former President John F. Kennedy. Carter defeated Kennedy in the majority of the Democratic primaries, but Kennedy remained in the race until Carter was officially nominated at the 1980 Democratic National Convention. The Republican primaries were contested between Reagan, who had previously served as the Governor of California, former Congressman George H. W. Bush of Texas, Congressman John B. Anderson of Illinois, and several other candidates. All of Reagan's opponents had dropped out by the end of the primaries, and the 1980 Republican National Convention nominated a ticket consisting of Reagan and Bush. Anderson entered the race as an independent candidate, and convinced former Wisconsin Governor Patrick Lucey, a Democrat, to serve as his running mate.
Reagan campaigned for increased defense spending, implementation of supply-side economic policies, and a balanced budget. His campaign was aided by Democratic dissatisfaction with Carter, the Iran hostage crisis, and a worsening economy at home marked by high unemployment and inflation. Carter attacked Reagan as a dangerous right-wing extremist and warned that Reagan would cut Medicare and Social Security.
Reagan won the election by a landslide, taking a large majority of the electoral vote and 50.7% of the popular vote. Reagan received the highest number of electoral votes ever won by a non-incumbent presidential candidate. In the simultaneous Congressional elections, Republicans won control of the United States Senate for the first time since 1955. Carter won 41% of the vote but carried just six states and Washington, D.C. Anderson won 6.6% of the popular vote, and he performed best among liberal Republican voters dissatisfied with Reagan. Reagan, then 69, was the oldest person to ever be inaugurated as President until the inauguration of Donald Trump in 2017, who was 70.
Contents
1 Background
2 Nominations
2.1 Democratic Party
2.1.1 Other major candidates
2.2 Republican Party
2.2.1 Other major candidates
2.3 Other candidates
3 General election
3.1 Campaign
3.1.1 Promises
3.1.2 Events
3.2 Debates
3.3 Endorsements
3.4 Results
4 Statistics
4.1 Results by state
4.2 Close states
5 Voter demographics
6 See also
7 References
8 Further reading
8.1 Books
8.2 Journal articles
9 External links
Background
Throughout the 1970s, the United States underwent a wrenching period of low economic growth, high inflation and interest rates, and intermittent energy crises.[2] By October 1978, Iran—a major oil supplier to the United States at the time—was experiencing a major uprising that severely damaged its oil infrastructure and greatly weakened its capability to produce oil.[3] In January 1979, shortly after Iran's leader Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi fled the country, Iranian opposition figure Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini ended his 14-year exile in France and returned to Iran to establish an Islamic Republic, largely hostile to American interests and influence in the country.[3] In the spring and summer of 1979 inflation was on the rise and various parts of the United States were experiencing energy shortages.[4]
Carter was widely blamed for the return of the long gas lines in the summer of 1979 that were last seen just after the 1973 Yom Kippur War. He planned on delivering his fifth major speech on energy, but he felt that the American people were no longer listening. Carter left for the presidential retreat of Camp David. "For more than a week, a veil of secrecy enveloped the proceedings. Dozens of prominent Democratic Party leaders—members of Congress, governors, labor leaders, academics and clergy—were summoned to the mountaintop retreat to confer with the beleaguered president." His pollster, Pat Caddell, told him that the American people simply faced a crisis of confidence because of the assassinations of John F. Kennedy, Robert F. Kennedy and Martin Luther King, Jr.; the Vietnam War; and Watergate.[5] On July 15, 1979, Carter gave a nationally televised address in which he identified what he believed to be a "crisis of confidence" among the American people. This came to be known as his "malaise" speech, although Carter never used the word in the speech.[6]
Many expected Senator Ted Kennedy to successfully challenge Carter in the upcoming Democratic Primary. Kennedy's official announcement was scheduled for early November. A television interview with Roger Mudd of CBS a few days before the announcement went badly, however. Kennedy gave an "incoherent and repetitive"[7] answer to the question of why he was running, and the polls, which showed him leading the President by 58-25 in August now had him ahead 49–39.[8]
Meanwhile, Carter was given an opportunity for political redemption when the Khomeini regime again gained public attention and allowed the taking of 52 American hostages by a group of Islamist students and militants at the U.S. embassy in Tehran on November 4, 1979. Carter's calm approach towards the handling of this crisis resulted in his approval ratings jump in the 60-percent range in some polls, due to a "rally round the flag" effect.[9]
By the beginning of the election campaign, the prolonged Iran hostage crisis had sharpened public perceptions of a national crisis.[10] On April 25, 1980, Carter's ability to use the hostage crisis to regain public acceptance eroded when his high risk attempt to rescue the hostages ended in disaster when eight servicemen were killed. The unsuccessful rescue attempt drew further skepticism towards his leadership skills.[11]
Following the failed rescue attempt, Carter took overwhelming blame for the Iran hostage crisis, in which the followers of the Ayatollah Khomeini burned American flags and chanted anti-American slogans, paraded the captured American hostages in public, and burned Carter in effigy. Carter's critics saw him as an inept leader who had failed to solve the worsening economic problems at home. His supporters defended the president as a decent, well-intentioned man being unfairly criticized for problems that had been escalating for years.[12]
Another event that polarized the electorate was the U.S.-led 1980 Summer Olympics boycott. Shortly following the Soviet Union's December 1979 invasion of Afghanistan, Carter demanded that the USSR withdraw from Afghanistan or the U.S. would boycott the 1980 Summer Olympics, set to be staged in Moscow. The USSR did not withdraw (for ten years). Carter's stance was controversial—he was both praised for his moral stand and criticized for politicizing the Olympics. With many allied countries joining the U.S. in the boycott, the contrasting spirits of competitive goodwill and campaign animosity, a feature of most presidential campaign years, was absent and the press had additional time to devote to national and international strife.
In a tit for tat response four years later, the Soviet Bloc countries boycotted the 1984 Summer Olympics in Los Angeles.
Nominations
Democratic Party
Democratic Party Ticket, 1980 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Jimmy Carter | Walter Mondale | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
39th President of the United States (1977–1981) | 42nd Vice President of the United States (1977–1981) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other major candidates
The following candidates were frequently interviewed by major broadcast networks, were listed in published national polls, or had held public office. Carter received 10,043,016 votes in the primaries.
Candidates in this section are sorted by date of withdrawal from the nomination race | ||||||||
Ted Kennedy | Jerry Brown | Cliff Finch | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  | ||||||
| U.S. Senator from Massachusetts (1962–2009) | Governor of California (1975–1983) | Governor of Mississippi (1976–1980) | ||||||
Campaign | Campaign | Campaign | ||||||
W: August 11, 1980 7,381,693 votes | W: April 2, 1980 575,296 votes | ?: N/A 48,032 votes | ||||||
The three major Democratic candidates in early 1980 were incumbent President Jimmy Carter, Senator Ted Kennedy of Massachusetts, and Governor Jerry Brown of California. Brown withdrew on April 2. Carter and Kennedy faced off in 34 primaries. Not counting the 1968 election in which Lyndon Johnson withdrew his candidacy, this was the most tumultuous primary race that an elected incumbent president had encountered since President Taft, during the highly contentious election of 1912.
During the summer of 1980, there was a short-lived "Draft Muskie" movement; Secretary of State Edmund Muskie was seen as a favorable alternative to a deadlocked convention. One poll showed that Muskie would be a more popular alternative to Carter than Kennedy, implying that the attraction was not so much to Kennedy as to the fact that he was not Carter. Muskie was polling even with Ronald Reagan at the time, while Carter was seven points behind.[13] Although the underground "Draft Muskie" campaign failed, it became a political legend.[14]
After defeating Kennedy in 24 of 34 primaries, Carter entered the party's convention in New York in August with 60 percent of the delegates pledged to him on the first ballot. Still, Kennedy refused to drop out. At the convention, after a futile last-ditch attempt by Kennedy to alter the rules to free delegates from their first-ballot pledges, Carter was renominated with 2,129 votes to 1,146 for Kennedy. Vice President Walter Mondale was also renominated. In his acceptance speech, Carter warned that Reagan's conservatism posed a threat to world peace and progressive social welfare programs from the New Deal to the Great Society.[15]
Republican Party
Republican Party Ticket, 1980 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ronald Reagan | George H. W. Bush | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
33rd Governor of California (1967–1975) | 11th Director of Central Intelligence (1976–1977) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other major candidates
The following candidates were frequently interviewed by major broadcast networks and cable news channels, were listed in publicly published national polls, or had held a public office. Reagan received 7,709,793 votes in the primaries.
Candidates in this section are sorted by date of withdrawal from the nomination race | ||||
George H. W. Bush | John B. Anderson | Phil Crane | Bob Dole | John Connally |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |  |
| Fmr. Director of Central Intelligence (1976–1977) | Representative from Illinois's 16th district (1961–1981) | Representative from Illinois's 12th district (1973–1993) | Senator from Kansas (1969–1996) | Fmr. Secretary of the Treasury from Texas (1971–1972) |
Campaign | Campaign | Campaign | Campaign | Campaign |
SC: May 26, 1980 ER: June 14, 1980 3,070,033 votes | DI: April 24, 1980 1,572,174 votes | W: April 17, 1980 ER: April 17, 1980 97,793 votes | W: March 15, 1980 ER: March 30, 1980 7,204 votes | W: March 9, 1980 ER: March 25, 1980 82,625 votes |
Howard Baker | Larry Pressler | Lowell P. Weicker Jr. | Harold Stassen | Ben Fernandez |
 |  |  | ||
Senator from Tennessee (1967–1985) | Senator from South Dakota (1979–1997) | Senator from Connecticut (1971–1989) | Governor of Minnesota (1939–1943) | RNC Executive from California (1973–1973) |
W: March 5, 1980 ER: April 20, 1980 181,153 votes | W: January 8, 1980 ER: March 21, 1980 0 votes | W: May 16, 1979 0 votes | ?: n/a 25,425 votes | ?: n/a 25,520 votes |
Former Governor Ronald Reagan of California was the odds-on favorite to win his party's nomination for president after nearly beating incumbent President Gerald Ford just four years earlier. Reagan dominated the primaries, early driving from the field Senate Minority Leader Howard Baker from Tennessee, former governor John Connally of Texas, Senator Robert Dole from Kansas, Representative Phil Crane from Illinois, and Representative John Anderson from Illinois, who dropped out of the race to run as an Independent. George Bush from Texas posed the strongest challenge to Reagan with his victories in the Pennsylvania and Michigan primaries, but it was not enough to turn the tide. Reagan won the nomination on the first round at the 1980 Republican National Convention in Detroit, Michigan, in July, then chose George H. W. Bush, his top rival, as his running mate.
Other candidates
John Anderson was defeated in the Republican primaries, but entered the general election as an independent candidate. He campaigned as a moderate Republican alternative to Reagan's conservatism. However, his campaign appealed primarily to frustrated anti-Carter voters.[16] His support progressively evaporated through the campaign season as his supporters were pulled away by Carter and Reagan. His running mate was Patrick Lucey, a Democratic former Governor of Wisconsin and then Ambassador to Mexico, appointed by President Carter.
The Libertarian Party nominated Ed Clark for President and David Koch for Vice President. They received almost one million votes and were on the ballot in all 50 states plus Washington, D.C. Koch, a co-owner of Koch Industries, pledged part of his personal fortune to the campaign. The Libertarian Party platform was the only political party in 1980 to contain a plank advocating for the equal rights of homosexual men and women as well as the only party platform to advocate explicitly for "amnesty" for all illegal non-citizens.[17] The platform was also unique in favoring the repeal of both the National Labor Relations Act and all state Right to Work laws.[17] Clark emphasized his support for an end to the war on drugs.[18] He advertised his opposition to the draft and wars of choice.[19]
The Clark–Koch ticket received 921,128 votes (1.1% of the total nationwide).[20] This was the highest overall number of votes earned by a Libertarian candidate until the 2012 election, when Gary Johnson and James P. Gray became the first Libertarian ticket to earn more than a million votes, albeit with a lower overall vote percentage than Clark–Koch. It remained the highest percentage of popular votes a Libertarian Party candidate received in a presidential race until Johnson and William Weld became the first Libertarian ticket to receive more than 3 percent of the popular vote in 2016. His strongest support was in Alaska, where he came in third place with 11.7% of the vote, finishing ahead of independent candidate John Anderson and receiving almost half as many votes as Jimmy Carter.
The Socialist Party USA nominated David McReynolds for President and Sister Diane Drufenbrock for Vice President, making McReynolds the first openly gay man to run for President and Drufenbrock the first nun to be a candidate for national office in the U.S.
The Citizens Party ran biologist Barry Commoner for President and Comanche Native American activist LaDonna Harris for Vice President. The Commoner–Harris ticket was on the ballot in twenty-nine states and in the District of Columbia.[21]
The Communist Party USA ran Gus Hall for President and Angela Davis for Vice President.
The American Party nominated Percy L. Greaves, Jr. for President and Frank L. Varnum for Vice President.
Rock star Joe Walsh ran a mock campaign as a write-in candidate, promising to make his song "Life's Been Good" the new national anthem if he won, and running on a platform of "Free Gas For Everyone." Though the 33-year-old Walsh was not old enough to actually assume the office, he wanted to raise public awareness of the election.
General election

President Ronald Reagan's 1980 presidential campaign poster
Campaign

Interest rate crisis of 1980
Under federal election laws, Carter and Reagan received $29.4 million each, and Anderson was given a limit of $18.5 million with private fund-raising allowed for him only. They were not allowed to spend any other money. Carter and Reagan each spent about $15 million on television advertising, and Anderson under $2 million. Reagan ended up spending $29.2 million in total, Carter $29.4 million, and Anderson spent $17.6 million—partially because he (Anderson) didn't get Federal Election Commission money until after the election.[citation needed]
The 1980 election is considered by some to be a realigning election, reaching a climate of confrontation practically not seen since 1932. Reagan's supporters praise him for running a campaign of upbeat optimism.[22]David Frum says Carter ran an attack-based campaign based on "despair and pessimism" which "cost him the election."[23] Carter emphasized his record as a peacemaker, and said Reagan's election would threaten civil rights and social programs that stretched back to the New Deal. Reagan's platform also emphasized the importance of peace, as well as a prepared self-defense.[22]
Immediately after the conclusion of the primaries,[date missing] a Gallup poll held that Reagan was ahead, with 58% of voters upset by Carter's handling of the Presidency.[22] One analysis of the election has suggested that "Both Carter and Reagan were perceived negatively by a majority of the electorate."[24] While the three leading candidates (Reagan, Anderson and Carter) were religious Christians, Carter had the most support of evangelical Christians according to a Gallup poll.[22] However, in the end, Jerry Falwell's Moral Majority lobbying group is credited with giving Reagan two-thirds of the white evangelical vote.[25] According to Carter: "that autumn [1980] a group headed by Jerry Falwell purchased $10 million in commercials on southern radio and TV to brand me as a traitor to the South and no longer a Christian."[26]
The election of 1980 was a key turning point in American politics. It signaled the new electoral power of the suburbs and the Sun Belt. Reagan's success as a conservative would initiate a realigning of the parties, as liberal Republicans and conservative Democrats would either leave politics or change party affiliations through the 1980s and 1990s to leave the parties much more ideologically polarized.[12] While during Barry Goldwater's 1964 campaign, many voters saw his warnings about a too-powerful government as hyperbolic and only 30% of the electorate agreed that government was too powerful, by 1980 a majority of Americans believed that government held too much power.[27]
Promises
Reagan promised a restoration of the nation's military strength, at the same time 60% of Americans polled felt defense spending was too low.[28] Reagan also promised an end to "trust me government" and to restore economic health by implementing a supply-side economic policy. Reagan promised a balanced budget within three years (which he said would be "the beginning of the end of inflation"), accompanied by a 30% reduction in tax rates over those same years. With respect to the economy, Reagan famously said, "A recession is when your neighbor loses his job. A depression is when you lose yours. And recovery is when Jimmy Carter loses his."[22] Reagan also criticized the "windfall profit tax" that Carter and Congress enacted that year in regards to domestic oil production and promised to attempt to repeal it as president.[29] The tax was not a tax on profits, but on the difference between the price control-mandated price and the market price.[30]
On the issue of women's rights there was much division, with many feminists frustrated with Carter, the only candidate who supported the Equal Rights Amendment. After a bitter Convention fight between Republican feminists and antifeminists the Republican Party dropped their forty-year endorsement of the ERA.[31] Reagan, however, announced his dedication to women's rights and his intention to, if elected, appoint women to his cabinet and the first female justice to the Supreme Court.[32] He also pledged to work with all 50 state governors to combat discrimination against women and to equalize federal laws as an alternative to the ERA.[22] Reagan was convinced to give an endorsement of women's rights in his nomination acceptance speech.
Carter was criticized by his own aides for not having a "grand plan" for the recovery of the economy, nor did he ever make any campaign promises; he often criticized Reagan's economic recovery plan, but did not create one of his own in response.[22]
Events

Ronald Reagan campaigning with his wife Nancy and Strom Thurmond in Columbia, South Carolina, October 10, 1980

Ronald Reagan campaigning in Florida.
In August, after the Republican National Convention, Ronald Reagan gave a campaign speech at the annual Neshoba County Fair on the outskirts of Philadelphia, Mississippi, where three civil rights workers were murdered in 1964. He was the first presidential candidate ever to campaign at the fair.[33] Reagan famously announced, "Programs like education and others should be turned back to the states and local communities with the tax sources to fund them. I believe in states' rights. I believe in people doing as much as they can at the community level and the private level."[22] Reagan also stated, "I believe we have distorted the balance of our government today by giving powers that were never intended to be given in the Constitution to that federal establishment." He went on to promise to "restore to states and local governments the power that properly belongs to them."[34] President Carter criticized Reagan for injecting "hate and racism" by the "rebirth of code words like 'states' rights'".[35]

Ronald Reagan shaking hands with supporters at a campaign stop in Indiana.
Two days later, Reagan appeared at the Urban League convention in New York, where he said, "I am committed to the protection and enforcement of the civil rights of black Americans. This commitment is interwoven into every phase of the plans I will propose."[22] He then said that he would develop "enterprise zones" to help with urban renewal.[22]
The media's main criticism of Reagan centered on his gaffes. When Carter kicked off his general election campaign in Tuscumbia, Reagan—referring to the Southern U.S. as a whole—claimed that Carter had begun his campaign in the birthplace of the Ku Klux Klan. In doing so, Reagan seemed to insinuate that the KKK represented the South, which caused many Southern governors to denounce Reagan's remarks.[36] Additionally, Reagan was widely ridiculed by Democrats for saying that trees caused pollution; he later said that he meant only certain types of pollution and his remarks had been misquoted.[37]
Meanwhile, Carter was burdened by a continued weak economy and the Iran hostage crisis.[28]Inflation, high interest rates, and unemployment continued through the course of the campaign, and the ongoing hostage crisis in Iran became, according to David Frum in How We Got Here: The '70s, a symbol of American impotence during the Carter years.[28] John Anderson's independent candidacy, aimed at eliciting support from liberals, was also seen as hurting Carter more than Reagan,[22] especially in such reliably Democratic states such as Massachusetts and New York.
Debates
| No. | Date | Host | Location | Panelists | Moderator | Participants | Viewership (millions) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | Sunday, September 21, 1980 | Baltimore Convention Center | Baltimore, Maryland | Carol Loomis Daniel Greenberg Charles Corddry Lee May Jane Bryant Quinn Soma Golden | Bill Moyers | Governor Ronald Reagan Congressman John Anderson | n/a |
| P1a | Tuesday, October 28, 1980 | Public Auditorium | Cleveland, Ohio | Marvin Stone Harry Ellis William Hilliard Barbara Walters | Howard K. Smith | Governor Ronald Reagan President Jimmy Carter | 80.6[38] |
The League of Women Voters, which had sponsored the 1976 Ford/Carter debate series, announced that it would do so again for the next cycle in the spring of 1979. However, Carter was not eager to participate with any debate. He had repeatedly refused to a debate with Senator Edward M. Kennedy during the primary season, and had given ambivalent signals as to his participation in the fall.
The League of Women Voters had announced a schedule of debates similar to 1976, three presidential and one vice presidential. No one had much of a problem with this until it was announced that Rep. John Anderson might be invited to participate along with Carter and Reagan. Carter steadfastly refused to participate with Anderson included, and Reagan refused to debate without him. It took months of negotiations for the League of Women Voters to finally put it together. It was held on September 21, 1980 in the Baltimore Convention Center. Reagan said of Carter's refusal to debate: "He [Carter] knows that he couldn't win a debate even if it were held in the Rose Garden before an audience of Administration officials with the questions being asked by Jody Powell." [39] The League of Women Voters promised the Reagan campaign that the debate stage would feature an empty chair to represent the missing president. Carter was very upset about the planned chair stunt, and at the last minute convinced the League to take it out. The debate was moderated by Bill Moyers. Anderson, who many thought would handily dispatch the former Governor, managed only a draw, according to many in the media at that time. The Illinois congressman, who had been as high as 20% in some polls, and at the time of the debate was over 10%, dropped to about 5% soon after. Anderson failed to substantively engage Reagan, instead he started off by criticizing Carter: "Governor Reagan is not responsible for what has happened over the last four years, nor am I. The man who should be here tonight to respond to those charges chose not to attend," to which Reagan added: "It's a shame now that there are only two of us here debating, because the two that are here are in more agreement than disagreement." [40] In one moment in the debate, Reagan commented on a rumor that Anderson had invited Senator Ted Kennedy to be his running mate by asking the candidate directly, "John, would you really prefer Teddy Kennedy to me?"[41]
As September turned into October, the situation remained essentially the same. Governor Reagan insisted Anderson be allowed to participate, and the President remained steadfastly opposed to this. As the standoff continued, the second round was canceled, as was the vice presidential debate.
With two weeks to go to the election, the Reagan campaign decided that the best thing to do at that moment was to accede to all of President Carter's demands, and LWV agreed to exclude Congressman Anderson from the final debate, which was rescheduled for October 28 in Cleveland, Ohio.
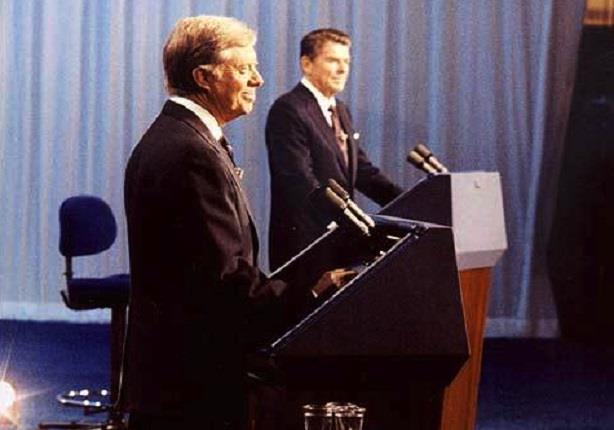

President Carter (left) and former Governor Reagan (right) at the presidential debate on October 28, 1980.
The presidential debate between President Carter and Governor Reagan was moderated by Howard K. Smith and presented by the League of Women Voters. The showdown ranked among the highest ratings of any television program in the previous decade. Debate topics included the Iranian hostage crisis, and nuclear arms treaties and proliferation. Carter's campaign sought to portray Reagan as a reckless "war hawk," as well as a "dangerous right-wing radical". But it was President Carter's reference to his consultation with 12-year-old daughter Amy concerning nuclear weapons policy that became the focus of post-debate analysis and fodder for late-night television jokes. President Carter said he had asked Amy what the most important issue in that election was and she said, "the control of nuclear arms." A famous political cartoon, published the day after Reagan's landslide victory, showed Amy Carter sitting in Jimmy's lap with her shoulders shrugged asking "the economy? the hostage crisis?"
When President Carter criticized Reagan's record, which included voting against Medicare and Social Security benefits, Governor Reagan audibly sighed and replied: "There you go again".[42]
In describing the national debt that was approaching $1 trillion, Reagan stated "a billion is a thousand millions, and a trillion is a thousand billions." When Carter would criticize the content of Reagan's campaign speeches, Reagan began his counter with the words: "Well ... I don't know that I said that. I really don't."
In his closing remarks, Reagan asked viewers: "Are you better off now than you were four years ago? Is it easier for you to go and buy things in the stores than it was four years ago? Is there more or less unemployment in the country than there was four years ago? Is America as respected throughout the world as it was? Do you feel that our security is as safe, that we're as strong as we were four years ago? And if you answer all of those questions 'yes', why then, I think your choice is very obvious as to whom you will vote for. If you don't agree, if you don't think that this course that we've been on for the last four years is what you would like to see us follow for the next four, then I could suggest another choice that you have."
After trailing Carter by 8 points among registered voters (and by 3 points among likely voters) right before their debate, Reagan moved into a 3-point lead among likely voters immediately afterward.[43]
Endorsements
In September 1980, former Watergate scandal prosecutor Leon Jaworski accepted a position as honorary chairman of Democrats for Reagan.[28] Five months earlier, Jaworski had harshly criticized Reagan as an "extremist"; he said after accepting the chairmanship, "I would rather have a competent extremist than an incompetent moderate."[28]
Former Democratic Senator Eugene McCarthy of Minnesota (who in 1968 had challenged Lyndon Johnson from the left, causing the then-President to all but abdicate) endorsed Reagan.[44]
Three days before the November 4 voting in the election, the National Rifle Association endorsed a presidential candidate for the first time in its history, backing Reagan. Reagan had received the California Rifle and Pistol Association's Outstanding Public Service Award. Carter had appointed Abner J. Mikva, a fervent proponent of gun control, to a federal judgeship and had supported the Alaska Lands Bill, closing 40,000,000 acres (160,000 km2) to hunting.[45]
Results

Election results by county.
Ronald Reagan
Jimmy Carter

1980 Presidential Election, Results by Congressional District
The election was held on November 4, 1980.[46] Ronald Reagan and running mate George H. W. Bush beat Carter by almost 10 percentage points in the popular vote. Republicans also gained control of the Senate on Reagan's coattails for the first time since 1952. The electoral college vote was a landslide, with 489 votes (representing 44 states) for Reagan and 49 for Carter (representing six states and Washington, D.C.).[47] NBC News projected Reagan as the winner at 8:15 pm EST (5:15 PST), before voting was finished in the West, based on exit polls; it was the first time a broadcast network used exit polling to project a winner, and took the other broadcast networks by surprise. Carter conceded defeat at 9:50 pm EST.[48][49] Carter's loss was the worst performance by an incumbent President since Herbert Hoover lost to Franklin D. Roosevelt by a margin of 18% in 1932. Also, Carter was the first incumbent Democrat to serve only one full term since James Buchanan and lose re-election since Andrew Johnson; Grover Cleveland served two non-consecutive terms while Harry Truman and Lyndon B. Johnson served one full term in addition to respectively taking over following the deaths of Franklin D. Roosevelt and John F. Kennedy.
Carter carried only Georgia (his home state), Maryland, Minnesota (Mondale's home state), Hawaii, West Virginia, Rhode Island, and the District of Columbia.
John Anderson won 6.6% of the popular vote but failed to win any state outright. He found the most support in New England, fueled by liberal and moderate Republicans who felt Reagan was too far to the right and with voters who normally leaned Democratic but were dissatisfied with the policies of the Carter Administration. His best showing was in Massachusetts, where he won 15% of the popular vote. Conversely, Anderson performed worst in the South, receiving under 2% of the popular vote in South Carolina, Louisiana, Alabama, and Mississippi. Anderson claims that he was accused of spoiling the election for Carter by receiving votes that might have otherwise been cast for Carter.[50] However, 37 percent of Anderson voters polled preferred Reagan as their second choice.[51]
Libertarian Party candidate Ed Clark received 921,299 popular votes (1.06%). The Libertarians succeeded in getting Clark on the ballot in all 50 states and the District of Columbia. Clark's best showing was in Alaska, where he received 11.66% of the vote. The 921,299 votes achieved by the Clark–Koch ticket was the best performance by a Libertarian presidential candidate until 2012, when the Johnson–Gray ticket received 1,273,667 votes. In addition, the popular vote percentage was the highest of a Libertarian presidential candidate until 2016, when the Johnson-Weld ticket received 3.28%.
Reagan won 53% of the vote in reliably Democratic South Boston.[27] His electoral college victory of 489 electoral votes (90.9% of the electoral vote) was the most lopsided electoral college victory for a first-time President-elect.[citation needed] Although Reagan was to win an even greater Electoral College majority in 1984, the 1980 election nonetheless stands as the last time some currently very strong Democratic counties gave a Republican majority or plurality. Notable examples are Jefferson County in Washington State, Lane County, Oregon, Marin and Santa Cruz Counties in California, McKinley County, New Mexico, Polk County, Iowa and Rock Island County, Illinois.[52] Conversely, this was the last time that the Democrats won Georgia and Maryland until 1992. This election is the last time a Republican won the presidency without winning Georgia. This is the first time Massachusetts voted for the Republican candidate since 1956. 1980 is one of only two occurrences of a pair of consecutive elections seeing the incumbent President defeated, the other one happening in 1892. This is the only time in the 20th century a party was voted out after a single four-year term.
Statistics
| Presidential candidate | Party | Home state | Popular vote | Electoral vote | Running mate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | Percentage | Vice-presidential candidate | Home state | Electoral vote | ||||
Ronald Wilson Reagan | Republican | California | 43,903,230 | 50.75% | 489 | George Herbert Walker Bush | Texas | 489 |
James Earl Carter, Jr. (incumbent) | Democratic | Georgia | 35,480,115 | 41.01% | 49 | Walter Frederick Mondale | Minnesota | 49 |
John Bayard Anderson | Independent | Illinois | 5,719,850 | 6.61% | 0 | Patrick Joseph Lucey | Wisconsin | 0 |
Ed Clark | Libertarian | California | 921,128 | 1.06% | 0 | David Koch | Kansas | 0 |
Barry Commoner | Citizens | Missouri | 233,052 | 0.27% | 0 | LaDonna Harris | Oklahoma | 0 |
Gus Hall | Communist | New York | 44,933 | 0.05% | 0 | Angela Davis | California | 0 |
John Rarick | American Independent | Louisiana | 40,906 | 0.05% | 0 | Eileen Shearer | California | 0 |
Clifton DeBerry | Socialist Workers | California | 38,738 | 0.04% | 0 | Matilde Zimmermann | New York | 0 |
Ellen McCormack | Right to Life | New York | 32,320 | 0.04% | 0 | Carroll Driscoll | New Jersey | 0 |
Maureen Smith | Peace and Freedom | California | 18,116 | 0.02% | 0 | Elizabeth Barron | California | 0 |
Harley McLain | Natural People's | North Dakota | 18,116 | 0.02% | 0 | Jewelie Goeller | North Dakota | 0 |
Other | 296 | 0.000003% | — | Other | — | |||
| Total | 86,509,678 | 100% | 538 | 538 | ||||
| Needed to win | 270 | 270 | ||||||
Source (popular vote): Leip, David. "1980 Presidential Election Results". Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. Retrieved August 7, 2005..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
Source (electoral vote): "Electoral College Box Scores 1789–1996". National Archives and Records Administration. Retrieved August 7, 2005.


Results by county, shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote
Results by state
[53]
| States/districts won by Reagan/Bush |
| States/districts won by Carter/Mondale |
| Ronald Reagan Republican | Jimmy Carter Democratic | John Anderson Independent | Ed Clark Libertarian | Margin | State Total | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | electoral votes | # | % | electoral votes | # | % | electoral votes | # | % | electoral votes | # | % | electoral votes | # | % | # | |
Alabama | 9 | 654,192 | 48.75 | 9 | 636,730 | 47.45 | - | 16,481 | 1.23 | - | 13,318 | 0.99 | - | 17,462 | 1.30 | 1,341,929 | AL |
Alaska | 3 | 86,112 | 54.35 | 3 | 41,842 | 26.41 | - | 11,155 | 7.04 | - | 18,479 | 11.66 | - | 44,270 | 27.94 | 158,445 | AK |
Arizona | 6 | 529,688 | 60.61 | 6 | 246,843 | 28.24 | - | 76,952 | 8.81 | - | 18,784 | 2.15 | - | 282,845 | 32.36 | 873,945 | AZ |
Arkansas | 6 | 403,164 | 48.13 | 6 | 398,041 | 47.52 | - | 22,468 | 2.68 | - | 8,970 | 1.07 | - | 5,123 | 0.61 | 837,582 | AR |
California | 45 | 4,524,858 | 52.69 | 45 | 3,083,661 | 35.91 | - | 739,833 | 8.62 | - | 148,434 | 1.73 | - | 1,441,197 | 16.78 | 8,587,063 | CA |
Colorado | 7 | 652,264 | 55.07 | 7 | 367,973 | 31.07 | - | 130,633 | 11.03 | - | 25,744 | 2.17 | - | 284,291 | 24.00 | 1,184,415 | CO |
Connecticut | 8 | 677,210 | 48.16 | 8 | 541,732 | 38.52 | - | 171,807 | 12.22 | - | 8,570 | 0.61 | - | 135,478 | 9.63 | 1,406,285 | CT |
Delaware | 3 | 111,252 | 47.21 | 3 | 105,754 | 44.87 | - | 16,288 | 6.91 | - | 1,974 | 0.84 | - | 5,498 | 2.33 | 235,668 | DE |
D.C. | 3 | 23,313 | 13.41 | - | 130,231 | 74.89 | 3 | 16,131 | 9.28 | - | 1,104 | 0.63 | - | -106,918 | -61.49 | 173,889 | DC |
Florida | 17 | 2,046,951 | 55.52 | 17 | 1,419,475 | 38.50 | - | 189,692 | 5.14 | - | 30,524 | 0.83 | - | 627,476 | 17.02 | 3,687,026 | FL |
Georgia | 12 | 654,168 | 40.95 | - | 890,733 | 55.76 | 12 | 36,055 | 2.26 | - | 15,627 | 0.98 | - | -236,565 | -14.81 | 1,597,467 | GA |
Hawaii | 4 | 130,112 | 42.90 | - | 135,879 | 44.80 | 4 | 32,021 | 10.56 | - | 3,269 | 1.08 | - | -5,767 | -1.90 | 303,287 | HI |
Idaho | 4 | 290,699 | 66.46 | 4 | 110,192 | 25.19 | - | 27,058 | 6.19 | - | 8,425 | 1.93 | - | 180,507 | 41.27 | 437,431 | ID |
Illinois | 26 | 2,358,049 | 49.65 | 26 | 1,981,413 | 41.72 | - | 346,754 | 7.30 | - | 38,939 | 0.82 | - | 376,636 | 7.93 | 4,749,721 | IL |
Indiana | 13 | 1,255,656 | 56.01 | 13 | 844,197 | 37.65 | - | 111,639 | 4.98 | - | 19,627 | 0.88 | - | 411,459 | 18.35 | 2,242,033 | IN |
Iowa | 8 | 676,026 | 51.31 | 8 | 508,672 | 38.60 | - | 115,633 | 8.78 | - | 13,123 | 1.00 | - | 167,354 | 12.70 | 1,317,661 | IA |
Kansas | 7 | 566,812 | 57.85 | 7 | 326,150 | 33.29 | - | 68,231 | 6.96 | - | 14,470 | 1.48 | - | 240,662 | 24.56 | 979,795 | KS |
Kentucky | 9 | 635,274 | 49.07 | 9 | 616,417 | 47.61 | - | 31,127 | 2.40 | - | 5,531 | 0.43 | - | 18,857 | 1.46 | 1,294,627 | KY |
Louisiana | 10 | 792,853 | 51.20 | 10 | 708,453 | 45.75 | - | 26,345 | 1.70 | - | 8,240 | 0.53 | - | 84,400 | 5.45 | 1,548,591 | LA |
Maine | 4 | 238,522 | 45.61 | 4 | 220,974 | 42.25 | - | 53,327 | 10.20 | - | 5,119 | 0.98 | - | 17,548 | 3.36 | 523,011 | ME |
Maryland | 10 | 680,606 | 44.18 | - | 726,161 | 47.14 | 10 | 119,537 | 7.76 | - | 14,192 | 0.92 | - | -45,555 | -2.96 | 1,540,496 | MD |
Massachusetts | 14 | 1,057,631 | 41.90 | 14 | 1,053,802 | 41.75 | - | 382,539 | 15.15 | - | 22,038 | 0.87 | - | 3,829 | 0.15 | 2,524,298 | MA |
Michigan | 21 | 1,915,225 | 48.99 | 21 | 1,661,532 | 42.50 | - | 275,223 | 7.04 | - | 41,597 | 1.06 | - | 253,693 | 6.49 | 3,909,725 | MI |
Minnesota | 10 | 873,241 | 42.56 | - | 954,174 | 46.50 | 10 | 174,990 | 8.53 | - | 31,592 | 1.54 | - | -80,933 | -3.94 | 2,051,953 | MN |
Mississippi | 7 | 441,089 | 49.42 | 7 | 429,281 | 48.09 | - | 12,036 | 1.35 | - | 5,465 | 0.61 | - | 11,808 | 1.32 | 892,620 | MS |
Missouri | 12 | 1,074,181 | 51.16 | 12 | 931,182 | 44.35 | - | 77,920 | 3.71 | - | 14,422 | 0.69 | - | 142,999 | 6.81 | 2,099,824 | MO |
Montana | 4 | 206,814 | 56.82 | 4 | 118,032 | 32.43 | - | 29,281 | 8.05 | - | 9,825 | 2.70 | - | 88,782 | 24.39 | 363,952 | MT |
Nebraska | 5 | 419,937 | 65.53 | 5 | 166,851 | 26.04 | - | 44,993 | 7.02 | - | 9,073 | 1.42 | - | 253,086 | 39.49 | 640,854 | NE |
Nevada | 3 | 155,017 | 62.54 | 3 | 66,666 | 26.89 | - | 17,651 | 7.12 | - | 4,358 | 1.76 | - | 88,351 | 35.64 | 247,885 | NV |
New Hampshire | 4 | 221,705 | 57.74 | 4 | 108,864 | 28.35 | - | 49,693 | 12.94 | - | 2,067 | 0.54 | - | 112,841 | 29.39 | 383,999 | NH |
New Jersey | 17 | 1,546,557 | 51.97 | 17 | 1,147,364 | 38.56 | - | 234,632 | 7.88 | - | 20,652 | 0.69 | - | 399,193 | 13.42 | 2,975,684 | NJ |
New Mexico | 4 | 250,779 | 54.97 | 4 | 167,826 | 36.78 | - | 29,459 | 6.46 | - | 4,365 | 0.96 | - | 82,953 | 18.18 | 456,237 | NM |
New York | 41 | 2,893,831 | 46.66 | 41 | 2,728,372 | 43.99 | - | 467,801 | 7.54 | - | 52,648 | 0.85 | - | 165,459 | 2.67 | 6,201,959 | NY |
North Carolina | 13 | 915,018 | 49.30 | 13 | 875,635 | 47.18 | - | 52,800 | 2.85 | - | 9,677 | 0.52 | - | 39,383 | 2.12 | 1,855,833 | NC |
North Dakota | 3 | 193,695 | 64.23 | 3 | 79,189 | 26.26 | - | 23,640 | 7.84 | - | 3,743 | 1.24 | - | 114,506 | 37.97 | 301,545 | ND |
Ohio | 25 | 2,206,545 | 51.51 | 25 | 1,752,414 | 40.91 | - | 254,472 | 5.94 | - | 49,033 | 1.14 | - | 454,131 | 10.60 | 4,283,603 | OH |
Oklahoma | 8 | 695,570 | 60.50 | 8 | 402,026 | 34.97 | - | 38,284 | 3.33 | - | 13,828 | 1.20 | - | 293,544 | 25.53 | 1,149,708 | OK |
Oregon | 6 | 571,044 | 48.33 | 6 | 456,890 | 38.67 | - | 112,389 | 9.51 | - | 25,838 | 2.19 | - | 114,154 | 9.66 | 1,181,516 | OR |
Pennsylvania | 27 | 2,261,872 | 49.59 | 27 | 1,937,540 | 42.48 | - | 292,921 | 6.42 | - | 33,263 | 0.73 | - | 324,332 | 7.11 | 4,561,501 | PA |
Rhode Island | 4 | 154,793 | 37.20 | - | 198,342 | 47.67 | 4 | 59,819 | 14.38 | - | 2,458 | 0.59 | - | -43,549 | -10.47 | 416,072 | RI |
South Carolina | 8 | 441,207 | 49.57 | 8 | 427,560 | 48.04 | - | 14,150 | 1.59 | - | 4,975 | 0.56 | - | 13,647 | 1.53 | 890,083 | SC |
South Dakota | 4 | 198,343 | 60.53 | 4 | 103,855 | 31.69 | - | 21,431 | 6.54 | - | 3,824 | 1.17 | - | 94,488 | 28.83 | 327,703 | SD |
Tennessee | 10 | 787,761 | 48.70 | 10 | 783,051 | 48.41 | - | 35,991 | 2.22 | - | 7,116 | 0.44 | - | 4,710 | 0.29 | 1,617,616 | TN |
Texas | 26 | 2,510,705 | 55.28 | 26 | 1,881,147 | 41.42 | - | 111,613 | 2.46 | - | 37,643 | 0.83 | - | 629,558 | 13.86 | 4,541,637 | TX |
Utah | 4 | 439,687 | 72.77 | 4 | 124,266 | 20.57 | - | 30,284 | 5.01 | - | 7,226 | 1.20 | - | 315,421 | 52.20 | 604,222 | UT |
Vermont | 3 | 94,598 | 44.37 | 3 | 81,891 | 38.41 | - | 31,760 | 14.90 | - | 1,900 | 0.89 | - | 12,707 | 5.96 | 213,207 | VT |
Virginia | 12 | 989,609 | 53.03 | 12 | 752,174 | 40.31 | - | 95,418 | 5.11 | - | 12,821 | 0.69 | - | 237,435 | 12.72 | 1,866,032 | VA |
Washington | 9 | 865,244 | 49.66 | 9 | 650,193 | 37.32 | - | 185,073 | 10.62 | - | 29,213 | 1.68 | - | 215,051 | 12.34 | 1,742,394 | WA |
West Virginia | 6 | 334,206 | 45.30 | - | 367,462 | 49.81 | 6 | 31,691 | 4.30 | - | 4,356 | 0.59 | - | -33,256 | -4.51 | 737,715 | WV |
Wisconsin | 11 | 1,088,845 | 47.90 | 11 | 981,584 | 43.18 | - | 160,657 | 7.07 | - | 29,135 | 1.28 | - | 107,261 | 4.72 | 2,273,221 | WI |
Wyoming | 3 | 110,700 | 62.64 | 3 | 49,427 | 27.97 | - | 12,072 | 6.83 | - | 4,514 | 2.55 | - | 61,273 | 34.67 | 176,713 | WY |
| TOTALS: | 538 | 43,903,230 | 50.75 | 489 | 35,480,115 | 41.01 | 49 | 5,719,850 | 6.61 | - | 921,128 | 1.06 | - | 8,423,115 | 9.74 | 86,509,678 | US |
Close states
Margin of victory less than 1% (30 electoral votes):
- Massachusetts, 0.15%
- Tennessee, 0.29%
- Arkansas, 0.61%
Margin of victory less than 5% (135 electoral votes):
- Alabama, 1.30%
- Mississippi, 1.32%
- Kentucky, 1.46%
- South Carolina, 1.53%
- Hawaii, 1.90%
- North Carolina, 2.12%
- Delaware, 2.33%
- New York, 2.67%
- Maryland, 2.96%
- Maine, 3.36%
- Minnesota, 3.94%
- West Virginia, 4.51%
- Wisconsin, 4.72%
Margin of victory more than 5%, but less than 10% (113 electoral votes):
- Louisiana, 5.45%
- Vermont, 5.96%
- Michigan, 6.49%
- Missouri, 6.81%
- Pennsylvania, 7.11%
Illinois, 7.93% (tipping point state)- Connecticut, 9.64%
- Oregon, 9.66%
Voter demographics
| The 1980 presidential vote by demographic subgroup | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic subgroup | Carter | Reagan | Anderson | % of total vote | |||
| Total vote | 41 | 51 | 8 | 100 | |||
| Ideology | |||||||
Liberals | 60 | 28 | 12 | 17 | |||
Moderates | 43 | 49 | 8 | 46 | |||
Conservatives | 23 | 73 | 4 | 33 | |||
| Party | |||||||
Democrats | 67 | 27 | 6 | 43 | |||
Republicans | 11 | 85 | 4 | 28 | |||
Independents | 31 | 56 | 13 | 23 | |||
| Sex | |||||||
| Men | 38 | 55 | 7 | 51 | |||
| Women | 46 | 47 | 7 | 49 | |||
| Race | |||||||
White | 36 | 56 | 8 | 88 | |||
Black | 83 | 14 | 3 | 10 | |||
Hispanic | 56 | 37 | 7 | 2 | |||
| Age | |||||||
| 18–21 years old | 45 | 44 | 11 | 6 | |||
| 22–29 years old | 44 | 44 | 11 | 17 | |||
| 30–44 years old | 38 | 55 | 7 | 31 | |||
| 45–59 years old | 39 | 55 | 6 | 23 | |||
| 60 and older | 41 | 55 | 4 | 18 | |||
| Family income | |||||||
| Under $10,000 | 52 | 42 | 6 | 13 | |||
| $10,000–15,000 | 48 | 43 | 8 | 14 | |||
| $10,000–15,000 | 48 | 43 | 8 | 14 | |||
| $15,000–25,000 | 39 | 54 | 7 | 30 | |||
| $25,000–50,000 | 33 | 59 | 8 | 24 | |||
| Over $50,000 | 26 | 66 | 8 | 5 | |||
| Region | |||||||
East | 44 | 48 | 8 | 32 | |||
Midwest | 42 | 52 | 6 | 20 | |||
South | 45 | 52 | 3 | 27 | |||
West | 36 | 54 | 10 | 11 | |||
| Union households | |||||||
Union | 48 | 45 | 7 | 26 | |||
| Non-union | 36 | 56 | 8 | 62 | |||
Source: CBS News and The New York Times exit poll from the Roper Center for Public Opinion Research (15,201 surveyed)[54]
See also
- United States House of Representatives elections, 1980
- United States Senate elections, 1980
- United States gubernatorial elections, 1980
- History of the United States (1964–1980)
- History of the United States (1980–1991)
- Anderson v. Celebrezze
- October Surprise conspiracy theory
- Political activities of the Koch brothers
- First inauguration of Ronald Reagan
- Debategate
References
^ "Voter Turnout in Presidential Elections". Presidency.ucsb.edu. Retrieved 2016-08-18.
^ Frum, David (2000). How We Got Here: The '70s. New York, New York: Basic Books. p. 292. ISBN 0-465-04195-7.
^ ab "Oil Squeeze". Time magazine. 1979-02-05. Archived from the original on 7 March 2008. Retrieved December 18, 2013.
^ "Inflation-proofing". ConsumerReports.org. 2010-02-11. Retrieved December 18, 2013.
^ "Jimmy Carter". American Experience. PBS.
^ ""Crisis of Confidence" Speech (July 15, 1979)". Miller Center, University of Virginia. Archived from the original (text and video) on July 22, 2009.
^ Allis, Sam (2009-02-18). "Chapter 4: Sailing Into the Wind: Losing a quest for the top, finding a new freedom". The Boston Globe. Retrieved March 10, 2009.
^ Time Magazine, 11/12/79
^ Marra, Robin F.; Ostrom, Charles W.; Simon, Dennis M. (1 January 1990). "Foreign Policy and Presidential Popularity: Creating Windows of Opportunity in the Perpetual Election". The Journal of Conflict Resolution. 34 (4): 588–623. JSTOR 174181.
^ [1]
^ "Chapter 3 : The Iranian Hostage Rescue Mission" (PDF). Press.umich.edu. Retrieved 2016-08-18.
^ ab Jerry Lanson (November 6, 2008). "A historic victory. A changed nation. Now, can Obama deliver?". Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved November 5, 2008.
^ Robbins, James S. (2008-05-13). "Clinton Campaign Reminiscent of 1980 Race". CBS News. Retrieved 2016-08-18.
^ [2]
^ William DeGregorio, The Complete Book of U.S. Presidents, Gramercy 1997
^ Kornacki, Steve (April 6, 2011). "The myths that just won't die - History - Salon.com". Salon.com. Archived from the original on April 6, 2011. Retrieved February 7, 2017.
^ ab http://www.presidency.ucsb.edu/platforms.php http://www.lpedia.org/1980_Libertarian_Party_Platform#3._Victimless_Crimes
^ Ed Clark emphasized his opposition to the https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KT3LisckcdU
^ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cXSZCthogmM
^ David Leip (2005). "1980 Presidential General Election Results". Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. Retrieved November 23, 2011.
^ Moore, John (2013-12-16). Elections A-Z. Routledge. ISBN 9781135938703.
^ abcdefghijk Skinner; Kudelia; Mesquita; Rice (2007). The Strategy of Campaigning. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 978-0-472-11627-0. Retrieved October 20, 2008.
^ Frum, David (2000). How We Got Here: The '70s. New York, New York: Basic Books. p. 161. ISBN 0-465-04195-7.
^ Wayne, Stephen J. (1984). The Road to the White House (2nd ed.), p. 210. New York: St. Martin's Press.
ISBN 0-312-68526-2.
^ "When worlds collide: politics, religion, and media at the 1970 East Tennessee Billy Graham Crusade. (appearance by President Richard M. Nixon)". Journal of Church and State. March 22, 1997. Retrieved August 18, 2007.
^ Carter, Jimmy (2010). White House Diary. New York, N.Y: Farrar, Straus and Giroux. p. 469.
^ ab Frum, David (2000). How We Got Here: The '70s. New York, New York: Basic Books. p. 283. ISBN 0-465-04195-7.
^ abcde Frum, David (2000). How We Got Here: The '70s. New York, New York: Basic Books. p. 344. ISBN 0-465-04195-7.
^ Thorndike, Joseph J. (November 10, 2005). "Historical Perspective: The Windfall Profit Tax -- Career of a Concept". TaxHistory.org. Retrieved November 6, 2008.
^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on February 11, 2012. Retrieved January 12, 2015.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link) , CRS Report RL33305, The Crude Oil Windfall Profit Tax of the 1980s: Implications for Current Energy Policy, by Salvatore Lazzari, p. 5.
^ Melich, Tanya (July 18, 2005). "O'Connor's Tenure Began One Hot Summer". Women's eNews. Archived from the original on August 17, 2009. Retrieved May 28, 2010.
^ James Taranto; Leonard Leo (2004). Presidential Leadership. Wall Street Journal Books. ISBN 978-0-7432-7226-1. Retrieved October 20, 2008.
^ Kornacki, Steve (February 3, 2011) The "Southern Strategy," fulfilled Archived April 13, 2011, at the Wayback Machine., Salon.com
^ Kneeland, Douglas E. (August 4, 1980). "Reagan Campaigns at Mississippi Fair; Nominee Tells Crowd of 10,000 He Is Backing States' Rights". New York Times. p. A11.
^ 'The Made-for-TV Election with Martin Sheen' clip 14 on YouTube
^ White House Diary, by Jimmy Carter, pp 461-462.
^ Bridges, Andrew (March 17, 2003). "Here We Go Again!". CBS News. Retrieved October 20, 2008.
^ "CPD: 1980 Debates". www.debates.org. Retrieved 2019-01-08.
^ Shirley, Craig (2009). Rendezvous with Destiny: Ronald Reagan and the Campaign That Changed America. Wilmington, Delaware: ISI Books. p. 478. ISBN 978-1-933859-55-2.
^ Shirley, Craig (2009). Rendezvous with Destiny: Ronald Reagan and the Campaign That Changed America. Wilmington, Delaware: ISI Books. p. 479. ISBN 978-1-933859-55-2.
^ "Fred Barnes on Conversations with Bill Kristol". Conversationswithbillkristol.org. Retrieved 2016-08-18.
^ "The Second 1980 Presidential Debate". PBS. Retrieved October 20, 2008.
^ Inc., Gallup,. "Late Upsets Are Rare, but Have Happened". Retrieved 2016-08-25.
^ MacNeil-Lehrer NewsHour (December 12, 2005). Online NewsHour: "Remembering Sen. Eugene McCarthy". December 12, 2005. PBS.
^ Facts on File 1980 Yearbook, p.844
^ "Voters the choice is yours". St. Petersburg Times. 4 November 1980. Retrieved January 16, 2014.
^ "Reagan in a landslide". Pittsburgh Post-Gazette. 5 November 1980. Retrieved January 16, 2014.
^ Facts on File Yearbook 1980 p. 865
^ Facts on File Yearbook 1980 p. 838
^ Anderson, John B. (2007-09-28). "Let the most popular candidate win". Christian Science Monitor. ISSN 0882-7729. Retrieved 2017-09-01.
^ Kornacki, Steve (2011-04-04). "The myths that just won't die". Salon. Retrieved 2017-08-01.
^ Sullivan, Robert David; 'How the Red and Blue Map Evolved Over the Past Century'; America Magazine in The National Catholic Review; June 29, 2016
^ "1980 Presidential General Election Data - National". Uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved March 18, 2013.
^ "How Groups Voted in 1980". ropercenter.cornell.edu. Retrieved February 1, 2018.
Further reading
Books
Shirley, Craig (2009). Rendezvous with Destiny: Ronald Reagan and the Campaign That Changed America. Wilmington, Delaware: Intercollegiate Studies Institute. ISBN 978-1-933859-55-2.. online review by Lou Cannon
Busch, Andrew E. (2005). Reagan's Victory: The Presidential Election of 1980 and the Rise of the Right. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas. ISBN 0-7006-1407-9.. online review by Michael Barone
- Davies, Gareth, and Julian E. Zelizer, eds. America at the Ballot Box: Elections and Political History (2015) pp. 196–218.
Ehrman, John (2005). The Eighties: American in the Age of Reagan. New Haven: Yale University Press. ISBN 0-300-10662-9.
Ferguson, Thomas; Joel Rogers (1986). Right Turn: The Decline of the Democrats and the Future of American Politics. New York: Hill and Wang. ISBN 0-8090-8191-1.
Germond, Jack W.; Jules Witcover (1981). Blue Smoke & Mirrors: How Reagan Won & Why Carter Lost the Election of 1980. New York: Viking. ISBN 0-670-51383-0.
- Hogue, Andrew P. Stumping God: Reagan, Carter, and the Invention of a Political Faith (Baylor University Press; 2012) 343 pages; A study of religious rhetoric in the campaign
- Mason, Jim (2011). No Holding Back: The 1980 John B. Anderson Presidential Campaign. Lanham, MD: University Press of America.
ISBN 0761852263.
Gerald M. Pomper, ed. (1981). The Election of 1980: Reports and Interpretations. Chatham: Chatham House. ISBN 0-934540-10-1.
- Stanley, Timothy. Kennedy vs. Carter: The 1980 Battle for the Democratic Party's Soul (University Press of Kansas, 2010) 298 pages. A revisionist history of the 1970s and their political aftermath that argues that Ted Kennedy's 1980 campaign was more popular than has been acknowledged; describes his defeat by Jimmy Carter in terms of a "historical accident" rather than perceived radicalism.
Troy, Gil (2005). Morning in America: How Ronald Reagan Invented the 1980s. Princeton: Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-691-12166-4.
West, Darrell M. (1984). Making Campaigns Count: Leadership and Coalition-Building in 1980. Westport: Greenwood Press. ISBN 0-313-24235-6.
Journal articles
Himmelstein, Jerome; J. A. McRae Jr. (1984). "Social Conservatism, New Republicans and the 1980 Election". Public Opinion Quarterly. 48 (3): 595–605. doi:10.1086/268860.
Lipset, Seymour M.; Earl Raab (1981). "Evangelicals and the Elections". Commentary. 71: 25–31.
Miller, Arthur H.; Martin P. Wattenberg (1984). "Politics from the Pulpit: Religiosity and the 1980 Elections". Public Opinion Quarterly. 48: 300–12. doi:10.1086/268827.
External links
United States presidential election of 1980 at Encyclopædia Britannica
- The Election Wall's 1980 Election Video Page
- 1980 popular vote by counties
- 1980 popular vote by states
- 1980 popular vote by states (with bar graphs)
- Campaign commercials from the 1980 election
How close was the 1980 election? at the Wayback Machine (archived August 25, 2012)—Michael Sheppard, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
(in Russian) Portrayal of 1980 presidential elections in the U.S. by the Soviet television
- Election of 1980 in Counting the Votes








