Luoyang
.mw-parser-output .stack-container{box-sizing:border-box;float:right}.mw-parser-output .stack-object{margin:1px;overflow:hidden}
Luoyang .mw-parser-output .nobold{font-weight:normal} 洛阳市 | |
|---|---|
| Prefecture-level city | |
 Top: Longmen Grottoes, Bottom left: White Horse Temple, Bottom right: Paeonia suffruticosa in Luoyang and Longmen Bridge | |
 Location of Luoyang City jurisdiction in Henan | |
 Luoyang Location in China | |
| Coordinates: 34°40′11″N 112°26′32″E / 34.66972°N 112.44222°E / 34.66972; 112.44222Coordinates: 34°40′11″N 112°26′32″E / 34.66972°N 112.44222°E / 34.66972; 112.44222 | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Henan |
| Government | |
| • Party Secretary | Li Ya |
| • Mayor | Bao Changyong |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 15,229.15 km2 (5,880.01 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 810.4 km2 (312.9 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 733.7 km2 (283.3 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 144 m (472 ft) |
| Population (2010 census) | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 6,549,941 |
| • Density | 430/km2 (1,100/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 1,926,079 |
| • Urban density | 2,400/km2 (6,200/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,857,003 |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Area code(s) | 379 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-HA-03 |
| GDP | ¥52541 per capita (2015) |
| Ethnicities | Han, Hui, Manchu, Mongolian |
| County-level divisions | 15 |
| License plate prefixes | 豫C |
| Website | www.ly.gov.cn |
| Luoyang | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 "Luoyang" in Simplified (top) and Traditional (bottom) Chinese characters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 洛阳 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 洛陽 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | "Northern bank of the Luo [River]" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Luoyang (Luòyáng) is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyang to the south, Sanmenxia to the west, Jiyuan to the north, and Jiaozuo to the northeast. As of the final 2010 census, Luoyang had a population of 6,549,941 inhabitants with 1,857,003 people living in the built-up (or metro) area made of the city's five urban districts, all of which except the Jili District are not urbanized yet.[1]
Situated on the central plain of China, Luoyang is one of the cradles of Chinese civilization, and is one of the Four Great Ancient Capitals of China.
Contents
1 Names
2 History
3 World Heritage
4 Ancient city sites
5 Administrative divisions
6 Geography
6.1 Climate
7 Culture
8 Education
9 Transportation
10 Twin towns and sister cities
11 Famous residents
12 See also
13 References
14 Further reading
15 External links
Names
The name "Luoyang" originates from the city's location on the north or sunny ("yang") side of the Luo River. Since the river flows from west to east and the sun is to the south of the river, the sun always shines on the north side of the river. Luoyang has had several names over the centuries, including "Luoyi" (洛邑) and "Luozhou (洛州)", though Luoyang has been its primary name. It has been called, during various periods, "Dongdu" (东都, meaning the Eastern Capital, during the Tang Dynasty), "Xijing" (西京, meaning the Western Capital, during the Song Dynasty), or "Jingluo" (京洛, meaning the general capital for China). During the rule of Wu Zetian, the city was known as Shendu (神都 divine capital)
History

Longmen Grottoes

Museum of Luoyang Eastern Zhou Royal Horse and Chariot Pits

Map of Luoyang in Eastern Han Dynasty when it was the capital of China

White Horse Temple gate
The greater Luoyang area has been sacred ground since the late Neolithic period.[citation needed] This area at the intersection of the Luo river and Yi River was considered to be the geographical center of China.[citation needed] Because of this sacred aspect, several cities – all of which are generally referred to as "Luoyang" – have been built in this area. In 2070 BC, the Xia Dynasty king Tai Kang moved the Xia capital to the intersection of the Luo and Yi and named the city Zhenxun (斟鄩). In 1600 BC, Tang of Shang defeated Jie, the final Xia Dynasty king, and built Western Bo (西亳), a new capital on the Luo River. The ruins of Western Bo are located in Luoyang Prefecture.
In the 1036 BC a settlement named Chengzhou (成周) was constructed by the Duke of Zhou for the remnants of the captured Shang nobility. The Duke also moved the Nine Tripod Cauldrons to Chengzhou from the Zhou Dynasty capital at Haojing. A second Western Zhou capital, Wangcheng (also: Luoyi) was built 15 km (9.3 mi) west of Chengzhou. Wangcheng became the capital of the Eastern Zhou Dynasty in 771 BC. The Eastern Zhou Dynasty capital was moved to Chengzhou in 510 BC. Later, the Eastern Han Dynasty capital of Luoyang would be built over Chengzhou. Modern Luoyang is built over the ruins of Wangcheng, which are still visible today at Wangcheng Park.[2]
In 25 AD, Luoyang was declared the capital of the Eastern Han Dynasty on November 27 by Emperor Guangwu of Han.[3] For several centuries, Luoyang was the focal point of China. In AD 68, the White Horse Temple, the first Buddhist temple in China, was founded in Luoyang. The temple still exists, though the architecture is of later origin, mainly from the 16th century. An Shigao was one of the first monks to popularize Buddhism in Luoyang.
The ambassador Banchao restored the Silk Road in Eastern Han Dynasty and this has made the capital city Luoyang the start of Silk Road
In 166 AD, the first Roman mission, sent by "the king of Da Qin [the Roman Empire], Andun" (Marcus Aurelius Antoninus, r. 161–180 AD), reached Luoyang after arriving by sea in Rinan Commandery in what is now central Vietnam.[4]
The late 2nd century saw China decline into anarchy:
The decline was accelerated by the rebellion of the Yellow Turbans, who, although defeated by the Imperial troops in 184 AD, weakened the state to the point where there was a continuing series of rebellions degenerating into civil war, culminating in the burning of the Han capital of Luoyang on 24 September 189 AD. This was followed by a state of continual unrest and wars in China until a modicum of stability returned in the 220s, but with the establishment of three separate kingdoms, rather than a unified empire.[5]
In 190 AD, Chancellor Dong Zhuo ordered his soldiers to ransack, pillage, and raze the city as he retreated from the coalition set up against him by regional lords all across China. The court was subsequently moved to the more defensible western city of Chang'an. Following a period of disorder, during which warlord Cao Cao held the last Han emperor Xian in Xuchang (196–220), Luoyang was restored to prominence when his son Cao Pi, Emperor Wen of the Wei Dynasty, declared it his capital in 220 AD. The Jin Dynasty, successor to Wei, was also established in Luoyang.
When Jin was overrun by Xiongnu forces in 311 AD, it was forced to move its capital to Jiankang (modern day Nanjing). The Xiongnu warriors then sacked and nearly totally destroyed Luoyang. The same fate befell Chang'an in 316 AD.[6]
In winter 416, Luoyang fell to Liu Yu's general Tan Daoji. In 422, Luoyang was captured by Northern Wei. Liu Song general Dao Yanzhi took the city back, but by 439 the Wei conquered the city definitively. In 493 AD, Emperor Xiaowen of the Northern Wei dynasty moved the capital from Datong to Luoyang and started the construction of the rock-cut Longmen Grottoes. More than 30,000 Buddhist statues from the time of this dynasty have been found in the caves. Many of these sculptures were two-faced. At the same time, the Shaolin Temple was also built by the Emperor to accommodate an Indian monk on the Mont Song right next to Luoyang City. The Yongning Temple (永宁寺), the tallest pagoda in China, was also built in Luoyang.
When Emperor Yang of Sui took control in 604 AD he founded the new Luoyang on the site of the existing city using a layout inspired by his father Emperor Wen of Sui's work in newly rebuilt Chang'an.[7][8]
During the Tang Dynasty, Luoyang was Dongdu (东都), the "Eastern Capital", and at its height had a population of around one million, second only to Chang'an, which, at the time, was the largest city in the world.[9]
At the interval of Tang Dynasty, the first and the only empress in Chinese history – Empress Wu, moved the capital of her Zhou Dynasty to Luoyang and named it as Shen Du (Capital of the God). She constructed the tallest palace in Chinese history, which is now in the site of Sui Tang Luoyang city.
During the short-lived Five Dynasties, Luoyang was the capital of the Later Liang (only for a few years before the court moved to Kaifeng) and Later Tang.
During the North Song Dynasty, Luoyang was the 'Western Capital' and birthplace of Zhao Kuangyin, the founder of the Song Dynasty. It served as a prominent culture center, housing some of the most important philosophers.
During the Jin Dynasty, Luoyang was the "Middle Capital".
Since the Yuan Dynasty, Luoyang was no longer the capital of China in the rest of the ancient dynasties. The population was reduced to that of an average county. However, for one last time, Luoyang city was the capital of the Republic of China for a brief period of time during the Japanese invasion. By 1949, Luoyang's population was 75,000.
After the People's Republic of China was established, Luoyang was revived as a major heavy industrial hub. In the first five-year plan of China, 7 of 156 Soviet-aided major industrial programmes was launched in Luoyang's Jianxi District, including Dongfanghong Tractor Factory, Luoyang Mining Machines Factory and Luoyang Bearing Factory. Later, during the Third Front construction, a group of heavy industry factories was moved to or founded in Luoyang, including Luoyang Glass Factory. Industrial development significantly shifted Luoyang's demographic makeup, and about half of Luoyang's population are new immigrants after 1949 from outside the province or their descendants.
World Heritage
Longmen Grottoes (2000.11.30)[10]
The Grand Canal – Huiluo Barn, Hanjia Barn (2014.6.22)[11]
Silk Roads – Han Wei Luoyang City Site, Dingding Gate Site of Sui Tang Luoyang City, Xin'an Hangu Guan Site (2014.6.22)[12]
Ancient city sites
Erlitou Site (Zhenxun) of Xia Dynasty
- Yanshi Shang City Site (Xibo) of Shang Dynasty
- Wangcheng Site of Eastern Zhou Dynasty
- Luoyang City Site of Han and Wei Dynasty
- Luoyang City Site of Sui and Tang Dynasty
Administrative divisions

Luoyang Museum

Luoyang-Longmen HST Station
The prefecture-level city of Luoyang administers 5 "built-up" urban districts, 1 additional district, 1 county-level city, and 9 more rural counties:
- Luoyang proper
Jianxi District (涧西区)
Xigong District (西工区)
Laocheng District (老城区)
Chanhe Hui District (瀍河回族区)
Luolong District (洛龙区)
Jili District (non-urban, 吉利区)

Qiyun Pagoda in White Horse Temple
Yanshi City(偃师市)
Mengjin County (孟津县)
Xin'an County (新安县)
Luoning County (洛宁县)
Yiyang County (宜阳县)
Yichuan County (伊川县)
Song County (嵩县)
Luanchuan County (栾川县)
Ruyang County (汝阳县)
During the 2010 census, the 5 "built-up" urban districts held a population of 1,857,003, making it the fourth-largest city in Henan. The entire area of Luoyang’s municipal government held 6,549,941 inhabitants total.
| Map |
|---|
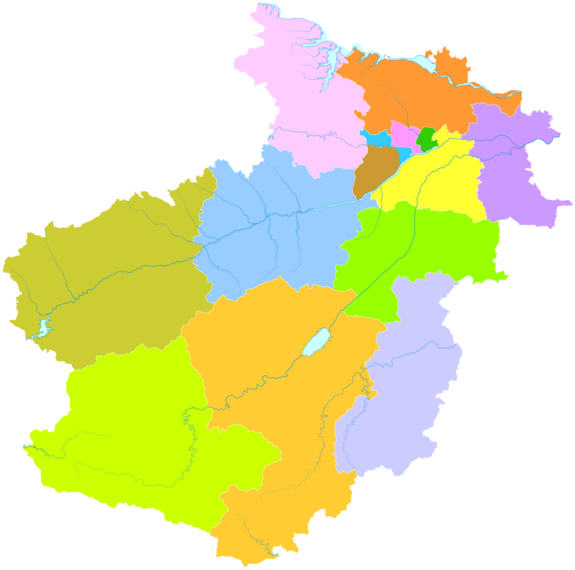 1 2 3 4 5 Luolong Mengjin County Xin'an County Luanchuan County Song County Ruyang County Yiyang County Luoning County Yichuan County Yanshi (city) 1. Laocheng 2. Xigong 3. Chanhe Hui 4. Jianxi 5. Jili |
Geography
As its name states, the Old Town of Luoyang is located on the north bank of the Luo, a southern tributary of the middle reaches of the Yellow River. The districts of the modern urban center include both banks and some of the surrounding mountains.
The countryside controlled by the municipal government includes still more rugged land: mountains comprise 45.51% of the total area; hills, 40.73%; and plains, 13.8%.[13]
Climate
| Climate data for Luoyang (1971–2000 normals, extremes 1951–2000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 22.2 (72) | 24.3 (75.7) | 31.2 (88.2) | 35.5 (95.9) | 40.6 (105.1) | 44.2 (111.6) | 41.9 (107.4) | 41.7 (107.1) | 38.2 (100.8) | 34.8 (94.6) | 27.0 (80.6) | 23.5 (74.3) | 44.2 (111.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 0.8 (33.4) | 2.9 (37.2) | 8.6 (47.5) | 15.9 (60.6) | 21.3 (70.3) | 26.0 (78.8) | 27.0 (80.6) | 25.9 (78.6) | 21.1 (70) | 15.4 (59.7) | 8.6 (47.5) | 2.6 (36.7) | 14.7 (58.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −17.4 (0.7) | −18.2 (−0.8) | −9.1 (15.6) | −3.6 (25.5) | 4.4 (39.9) | 12.2 (54) | 16.5 (61.7) | 13.5 (56.3) | 6.9 (44.4) | −2.3 (27.9) | −8.6 (16.5) | −14.9 (5.2) | −18.2 (−0.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 9.0 (0.354) | 15.9 (0.626) | 26.4 (1.039) | 36.9 (1.453) | 50.2 (1.976) | 62.9 (2.476) | 140.2 (5.52) | 97.4 (3.835) | 84.1 (3.311) | 45.2 (1.78) | 19.5 (0.768) | 11.8 (0.465) | 599.5 (23.603) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1mm) | 3.5 | 5.1 | 6.2 | 7.0 | 6.9 | 8.0 | 12.2 | 10.7 | 9.4 | 7.8 | 5.0 | 3.4 | 85.2 |
| Source: Weather.com.cn,[14] data.ac.cn[15] | |||||||||||||
Culture

Guanlin Temple in May 2007.
- Sites
The Longmen Grottoes south of the city were listed on the UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites in November 2000. Guanlin—a series of temples built in honor of Guan Yu, a hero of the Three Kingdoms period—is nearby. The White Horse Temple is located 12 km (7.5 mi) east of the modern town.
The Luoyang Museum (est. 1958) features ancient relics dating back to the Xia, Shang, and Zhou dynasties. The total number of exhibits on display is 1,700.[16] China's only tomb museum, the Luoyang Ancient Tombs Museum, opened to the public in 1987 and is situated north of the modern town.
The Gaocheng Astronomical Observatory (also known as the Dengfeng Observatory or the Tower of Chou Kong) stands 80 km (50 mi) south-east of Luoyang. It was constructed in 1276 during the Yuan Dynasty by Guo Shoujing as a giant gnomon for "the measurement of the sun's shadow". Prior to the Jesuit China Missions, it was used for establishing the summer and winter solstices in traditional Chinese astronomy.[17]
- Cuisine
Luoyang is famed for its Water Banquet, which consists of 8 cold and 16 warm dishes all cooked in various broths, gravies, or juices.
- Botany
Luoyang is also celebrated for the cultivation of peonies, its city flower. Since 1983, each mid-April the city hosts the Peony Culture Festival of Luoyang China. More than 19 million tourists visited Luoyang during the 2014 festival.[18]
- Music
"Spring in Luoyang" (洛阳春, Luòyáng Chūn), an ancient Chinese composition, became popular in Korea during the Goryeo dynasty (918–1392) and is still performed in its dangak (Koreanized) version Nakyangchun (낙양춘). Lou Harrison, an American composer, has also created an arrangement of the work.
- Dialect
Residents of Luoyang typically speak a dialect of Zhongyuan Mandarin. Although Luoyang's dialect was a prestige dialect of spoken Chinese from the Warring States period of the Zhou until the Ming Dynasty, it differs from the Beijing form of Mandarin which became the basis of the standard modern dialect.
- Outer space
Asteroid (239200) 2006 MD13 is named after Luoyang.
Education
Luoyang Institute of Science and Technology (洛阳理工学院)
Henan University of Science and Technology (河南科技大学)
Luoyang Normal University (洛阳师范学院)
PLA Foreign Language Institute, formerly known as the Luoyang PLA College of Foreign Languages (解放军洛阳外语学院)
Transportation
- Luoyang Railway Station
- Luoyang East Railway Station
- Luoyang Guanlin Railway Station
- Luoyang Longmen Railway Station
- Luoyang Beijiao Airport
- G30 Lianyungang–Khorgas Expressway
- G36 Nanjing–Luoyang Expressway
- G55 Erenhot–Guangzhou Expressway
- China National Highway 207
- China National Highway 310
Twin towns and sister cities
Luoyang is twinned with:
 La Crosse, Wisconsin, United States
La Crosse, Wisconsin, United States
Famous residents
Laozi, legendary founder of Taoism
- The emperors of the Eastern Zhou dynasty
Guiguzi, geomancer and numerologist- The emperors of the Eastern Han dynasty
Xuanzang, Buddhist monk and hero of the Journey to the West
Liu Yuxi, poet
Emperor Taizu of Song, founder of the Song Dynasty
Gao Hong, pipa player
Du Wei, soccer player
Wang Yibo, idol, UNIQ
Chen Dong, astronaut of Shenzhou 11
Meng Meiqi, idol, Cosmic Girls
See also
- List of twin towns and sister cities in China
- Historical capitals of China
- Luoyang Longmen Railway Station
- Sino-Roman Relations
- Silk Road transmission of Buddhism
- Roman Catholic Diocese of Luoyang
References
^ "China: Hénán". China Population. Retrieved 11 August 2018..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ China.org.cn, 2009
^ Robert Hymes (2000). John Stewart Bowman, ed. Columbia Chronologies of Asian History and Culture. Columbia University Press. p. 13. ISBN 978-0-231-11004-4.
^ Hill (2009), p. 27.
^ Hill (2009), p. xvi,
^ Grousset, Rene (1970). The Empire of the Steppes. Rutgers University Press. pp. 56–57. ISBN 0-8135-1304-9.
^ Marks, Robert B. (2011). China: Its Environment and History. ISBN 1442212756. p. 116
^ Schinz, Alfred (1996). The Magic Square: Cities in Ancient China. ISBN 3930698021. p. 167-169.
^ Abramson (2008), p. viii.
^ http://whc.unesco.org/en/list/1003
^ http://whc.unesco.org/en/list/1443
^ http://whc.unesco.org/en/list/1442
^ 洛阳市人民政府网站 [Luòyángshì Rénmín Zhèngfǔ Wǎngzhàn, Luoyang Municipal People’s Government Website] op. cit. 北京2008年奥运火炬接力官方网站 [Běijīng 2008 Nián Àoyùn Huǒjù Jiēlì Guānfāng Wǎngzhàn, Beijing 2008 Torch Relay Official Website]. 〈洛阳地理及气候概况〉 ["Luòyáng Dìlǐ Jí Qìhòu Gàikuàng", "Overview of Luoyang’s Geography and Climate"]. 20 Mar 2008. Accessed 16 Jan 2014. (in Chinese)
^ 洛阳 – 气象数据 – 中国天气网. weather.com.cn. Retrieved 2018-08-08.
^ 气候资源数据库. data.ac.cn. 2018-08-08.
^ China Culture. "Luoyang Museum Archived 2016-02-15 at the Wayback Machine.".
^ Needham, Joseph. Science and Civilisation in China’’.
^ https://baike.baidu.com/item/中国洛阳牡丹文化节/1534157?fromtitle=洛阳牡丹花会&fromid=4516674&fr=aladdin
Further reading
- Abramson, Marc. Ethnic Identity in Tang China. University of Pennsylvania Press (Philadelphia), 2008.
ISBN 978-0-8122-4052-8. - Cotterell, Arthur. The Imperial Capitals of China: An Inside View of the Celestial Empire. Pimlico (London), 2008.
ISBN 978-1-84595-010-1. - Hill, John E. Through the Jade Gate to Rome: A Study of the Silk Routes during the Later Han Dynasty, 1st to 2nd Centuries CE. BookSurge (Charleston), 2009.
ISBN 978-1-4392-2134-1. - Jenner, W. J. Memories of Loyang. Clarendon Press (Oxford), 1981.
- Yang Hsüan-chih. Lo-yang ch‘ien-lan chi, translated by Wang Yi-t‘ung as A Record of Buddhist Monasteries in Lo-yang. Princeton University Press (Princeton), 1984.
ISBN 0-691-05403-7.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Luoyang. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Luoyang. |
Official website of the Luoyang Municipal Government (in Chinese)
- "Wangcheng Park in Luoyang" at China.org
| Preceded by Zongzhou | Primary capital of China 771–256 BCE | Succeeded by — then Xianyang |
| Preceded by Chang'an | Primary capital of China 25–190 CE | Succeeded by — then Chang'an |

