Greatest common divisor
In mathematics, the greatest common divisor (gcd) of two or more integers, which are not all zero, is the largest positive integer that divides each of the integers. For example, the gcd of 8 and 12 is 4.[1][2]
The greatest common divisor is also known as the greatest common factor (gcf),[3]highest common factor (hcf),[4]greatest common measure (gcm),[5] or highest common divisor.[6]
This notion can be extended to polynomials (see Polynomial greatest common divisor) and other commutative rings (see below).
Contents
1 Overview
1.1 Notation
1.2 Example
1.3 Reducing fractions
1.4 Coprime numbers
1.5 A geometric view
2 Calculation
2.1 Using prime factorizations
2.2 Using Euclid's algorithm
2.3 Binary method
2.4 Other methods
2.5 Complexity
3 Properties
4 Probabilities and expected value
5 The gcd in commutative rings
6 See also
7 Notes
8 References
9 Further reading
10 External links
Overview
Notation
In this article we will denote the greatest common divisor of two integers a and b as gcd(a,b). Some authors use (a,b).[1][2][6][7]
Example
What is the greatest common divisor of 54 and 24?
The number 54 can be expressed as a product of two integers in several different ways:
- 54×1=27×2=18×3=9×6.{displaystyle 54times 1=27times 2=18times 3=9times 6.,}
Thus the divisors of 54 are: 1,2,3,6,9,18,27,54.{displaystyle 1,2,3,6,9,18,27,54.,}
Similarly, the divisors of 24 are: 1,2,3,4,6,8,12,24.{displaystyle 1,2,3,4,6,8,12,24.,}
The numbers that these two lists share in common are the common divisors of 54 and 24:
- 1,2,3,6.{displaystyle 1,2,3,6.,}
The greatest of these is 6. That is, the greatest common divisor of 54 and 24. One writes:
- gcd(54,24)=6.{displaystyle gcd(54,24)=6.,}
Reducing fractions
The greatest common divisor is useful for reducing fractions to be in lowest terms. For example, gcd(42, 56) = 14, therefore,
- 4256=3⋅144⋅14=34.{displaystyle {frac {42}{56}}={frac {3cdot 14}{4cdot 14}}={frac {3}{4}}.}
Coprime numbers
Two numbers are called relatively prime, or coprime, if their greatest common divisor equals 1. For example, 9 and 28 are relatively prime.
A geometric view

A 24-by-60 rectangle is covered with ten 12-by-12 square tiles, where 12 is the GCD of 24 and 60. More generally, an a-by-b rectangle can be covered with square tiles of side length c only if c is a common divisor of a and b.
For example, a 24-by-60 rectangular area can be divided into a grid of: 1-by-1 squares, 2-by-2 squares, 3-by-3 squares, 4-by-4 squares, 6-by-6 squares or 12-by-12 squares. Therefore, 12 is the greatest common divisor of 24 and 60. A 24-by-60 rectangular area can be divided into a grid of 12-by-12 squares, with two squares along one edge (24/12 = 2) and five squares along the other (60/12 = 5).
Calculation
Using prime factorizations
Greatest common divisors can in principle be computed by determining the prime factorizations of the two numbers and comparing factors, as in the following example: to compute gcd(18, 84), we find the prime factorizations 18 = 2 · 32 and 84 = 22 · 3 · 7 and notice that the "overlap" of the two expressions is 2 · 3; so gcd(18, 84) = 6. In practice, this method is only feasible for small numbers; computing prime factorizations in general takes far too long.
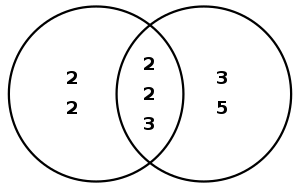
Here is another concrete example, illustrated by a Venn diagram. Suppose it is desired to find the greatest common divisor of 48 and 180. First, find the prime factorizations of the two numbers:
- 48 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3,
- 180 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 5.
What they share in common is two "2"s and a "3":
 [8]
[8]
- Least common multiple = 2 × 2 × ( 2 × 2 × 3 ) × 3 × 5 = 720
- Greatest common divisor = 2 × 2 × 3 = 12.
Using Euclid's algorithm
A much more efficient method is the Euclidean algorithm, which uses a division algorithm such as long division in combination with the observation that the gcd of two numbers also divides their difference. To compute gcd(48,18), divide 48 by 18 to get a quotient of 2 and a remainder of 12. Then divide 18 by 12 to get a quotient of 1 and a remainder of 6. Then divide 12 by 6 to get a remainder of 0, which means that 6 is the gcd. Note that we ignored the quotient in each step except to notice when the remainder reached 0, signalling that we had arrived at the answer. Formally the algorithm can be described as:
- gcd(a,0)=a{displaystyle gcd(a,0)=a}
gcd(a,b)=gcd(b,amodb){displaystyle gcd(a,b)=gcd(b,a,mathrm {mod} ,b)},
where
amodb=a−b⌊ab⌋{displaystyle a,mathrm {mod} ,b=a-bleftlfloor {a over b}rightrfloor }.
If the arguments are both greater than zero then the algorithm can be written in more elementary terms as follows:
gcd(a,a)=a{displaystyle gcd(a,a)=a},
gcd(a,b)=gcd(a−b,b),{displaystyle gcd(a,b)=gcd(a-b,b)quad ,}if a > b
gcd(a,b)=gcd(a,b−a),{displaystyle gcd(a,b)=gcd(a,b-a)quad ,}if b > a
 Play media
Play mediaAnimation showing an application of the Euclidean algorithm to find the greatest common divisor of 62 and 36, which is 2.
Binary method
An alternative method of computing the gcd is the binary gcd method which uses only subtraction and division by 2.
In outline the method is as follows: Let a and b be the two non negative integers. Also set the integer d to 0. There are five possibilities:
a = b.
As gcd(a, a) = a, the desired gcd is a × 2d (as a and b are changed in the other cases, and d records the number of times that a and b have been both divided by 2 in the next step, the gcd of the initial pair is the product of a and 2d).
- Both a and b are even.
In this case 2 is a common divisor. Divide both a and b by 2, increment d by 1 to record the number of times 2 is a common divisor and continue.
a is even and b is odd.
In this case 2 is not a common divisor. Divide a by 2 and continue.
a is odd and b is even.
As in the previous case 2 is not a common divisor. Divide b by 2 and continue.
- Both a and b are odd.
As gcd(a,b) = gcd(b,a) and we have already considered the case a = b, we may assume that a > b. The number c = a − b is smaller than a yet still positive. Any number that divides a and b must also divide c so every common divisor of a and b is also a common divisor of b and c. Similarly, a = b + c and every common divisor of b and c is also a common divisor of a and b. So the two pairs (a, b) and (b, c) have the same common divisors, and thus gcd(a,b) = gcd(b,c). Moreover, as a and b are both odd, c is even, and one may replace c by c/2 without changing the gcd. Thus the process can be continued with the pair (a, b) replaced by the smaller numbers (c/2, b).
Each of the above steps reduces at least one of a and b towards 0 and so can only be repeated a finite number of times. Thus one must eventually reach the case a = b, which is the only stopping case. Then, as quoted above, the gcd is a × 2d.
This algorithm may easily be programmed as follows:
Input: a, b positive integers
Output: g and d such that g is odd and gcd(a, b) = g × 2dd := 0
while a and b are both even do
a := a/2
b := b/2
d := d + 1
while a ≠ b do
if a is even then a := a/2
else if b is even then b := b/2
else if a > b then a := (a – b)/2
else b := (b – a)/2
g := a
output g, d
Example: (a, b, d) = (48, 18, 0) → (24, 9, 1) → (12, 9, 1) → (6, 9, 1) → (3, 9, 1) → (3, 6, 1) → (3, 3, 1) ; the original gcd is thus 2d = 21 times a= b= 3, that is 6.
The Binary GCD algorithm is particularly easy to implement on binary computers. The test for whether a number is divisible by two can be performed by testing the lowest bit in the number. Division by two can be achieved by shifting the input number by one bit. Each step of the algorithm makes at least one such shift. Subtracting two numbers smaller than a and b costs O(loga+logb){displaystyle O(log a+log b)}
O((loga+logb)2){displaystyle O((log a+log b)^{2})}.
For further details see Binary GCD algorithm.
Other methods

gcd(1,x)=y,{displaystyle gcd(1,x)=y,}
 or Thomae's function. Hatching at bottom indicates ellipses.
or Thomae's function. Hatching at bottom indicates ellipses.If a and b are both nonzero, the greatest common divisor of a and b can be computed by using least common multiple (lcm) of a and b:
gcd(a,b)=|a⋅b|lcm(a,b){displaystyle gcd(a,b)={frac {|acdot b|}{operatorname {lcm} (a,b)}}},
but more commonly the lcm is computed from the gcd.
Using Thomae's function f,
- gcd(a,b)=af(ba),{displaystyle gcd(a,b)=afleft({frac {b}{a}}right),}
which generalizes to a and b rational numbers or commensurable real numbers.
Keith Slavin has shown that for odd a ≥ 1:
- gcd(a,b)=log2∏k=0a−1(1+e−2iπkb/a){displaystyle gcd(a,b)=log _{2}prod _{k=0}^{a-1}(1+e^{-2ipi kb/a})}
which is a function that can be evaluated for complex b.[9] Wolfgang Schramm has shown that
- gcd(a,b)=∑k=1aexp(2πikb/a)⋅∑d|acd(k)d{displaystyle gcd(a,b)=sum limits _{k=1}^{a}exp(2pi ikb/a)cdot sum limits _{dleft|aright.}{frac {c_{d}(k)}{d}}}
is an entire function in the variable b for all positive integers a where cd(k) is Ramanujan's sum.[10]
Complexity
The computational complexity of the computation of greatest common divisors has been widely studied.[11] If one uses the Euclidean algorithm and the elementary algorithms for multiplication and division, the computation of the greatest common divisor of two integers of at most n bits is O(n2).{displaystyle O(n^{2}).}
However, if a fast multiplication algorithm is used, one may modify the Euclidean algorithm for improving the complexity, but the computation of a greatest common divisor becomes slower than the multiplication. More precisely, if the multiplication of two integers of n bits takes a time of T(n), then the fastest known algorithm for greatest common divisor has a complexity O(T(n)logn).{displaystyle Oleft(T(n)log nright).}
Previous complexities are valid for the usual models of computation, specifically multitape Turing machines and random-access machines.
The computation of the greatest common divisors belongs thus to the class of problems solvable in quasilinear time. A fortiori, the corresponding decision problem belongs to the class P of problems solvable in polynomial time. The GCD problem is not known to be in NC, and so there is no known way to parallelize it efficiently; nor is it known to be P-complete, which would imply that it is unlikely to be possible to efficiently parallelize GCD computation. Shallcross et al. showed that a related problem (EUGCD, determining the remainder sequence arising during the Euclidean algorithm) is NC-equivalent to the problem of integer linear programming with two variables; if either problem is in NC or is P-complete, the other is as well.[12] Since NC contains NL, it is also unknown whether a space-efficient algorithm for computing the GCD exists, even for nondeterministic Turing machines.
Although the problem is not known to be in NC, parallel algorithms asymptotically faster than the Euclidean algorithm exist; the fastest known deterministic algorithm is by Chor and Goldreich, which (in the CRCW-PRAM model) can solve the problem in O(n/log n) time with n1+ε processors.[13]Randomized algorithms can solve the problem in O((log n)2) time on exp(O(nlogn)){displaystyle exp left(Oleft({sqrt {nlog n}}right)right)}
Properties
- Every common divisor of a and b is a divisor of gcd(a, b).
gcd(a, b), where a and b are not both zero, may be defined alternatively and equivalently as the smallest positive integer d which can be written in the form d = a⋅p + b⋅q, where p and q are integers. This expression is called Bézout's identity. Numbers p and q like this can be computed with the extended Euclidean algorithm.
gcd(a, 0) = |a|, for a ≠ 0, since any number is a divisor of 0, and the greatest divisor of a is |a|.[2][6] This is usually used as the base case in the Euclidean algorithm.- If a divides the product b⋅c, and gcd(a, b) = d, then a/d divides c.
- If m is a non-negative integer, then gcd(m⋅a, m⋅b) = m⋅gcd(a, b).
- If m is any integer, then gcd(a + m⋅b, b) = gcd(a, b).
- If m is a nonzero common divisor of a and b, then gcd(a/m, b/m) = gcd(a, b)/m.
- The gcd is a multiplicative function in the following sense: if a1 and a2 are relatively prime, then gcd(a1⋅a2, b) = gcd(a1, b)⋅gcd(a2, b). In particular, recalling that gcd is a positive integer valued function (that is, gets natural values only) we obtain that gcd(a, b⋅c) = 1 if and only if gcd(a, b) = 1 and gcd(a, c) = 1.
- The gcd is a commutative function: gcd(a, b) = gcd(b, a).
- The gcd is an associative function: gcd(a, gcd(b, c)) = gcd(gcd(a, b), c).
- If none of a1, a2, . . . , ar is zero, then gcd( a1, a2, . . . , ar ) = gcd( gcd( a1, a2, . . . , ar-1 ), ar ).[15][16]
gcd(a, b) is closely related to the least common multiple lcm(a, b): we have
gcd(a, b)⋅lcm(a, b) = |a⋅b|.
- This formula is often used to compute least common multiples: one first computes the gcd with Euclid's algorithm and then divides the product of the given numbers by their gcd.
- The following versions of distributivity hold true:
- gcd(a, lcm(b, c)) = lcm(gcd(a, b), gcd(a, c))
lcm(a, gcd(b, c)) = gcd(lcm(a, b), lcm(a, c)).
- If we have the unique prime factorizations of a = p1e1p2e2 ⋅⋅⋅ pmem and b = p1f1p2f2 ⋅⋅⋅ pmfm where ei ≥ 0 and fi ≥ 0, then the gcd of a and b is
gcd(a,b) = p1min(e1,f1)p2min(e2,f2) ⋅⋅⋅ pmmin(em,fm).
- It is sometimes useful to define gcd(0, 0) = 0 and lcm(0, 0) = 0 because then the natural numbers become a complete distributive lattice with gcd as meet and lcm as join operation.[17] This extension of the definition is also compatible with the generalization for commutative rings given below.
- In a Cartesian coordinate system, gcd(a, b) can be interpreted as the number of segments between points with integral coordinates on the straight line segment joining the points (0, 0) and (a, b).
- For non-negative integers a and b, where a and b are not both zero, provable by considering the Euclidean algorithm in base n:[18]
gcd(na − 1, nb − 1) = ngcd(a,b) − 1.
- An identity involving Euler's totient function:
- gcd(a,b)=∑k|a and k|bφ(k).{displaystyle gcd(a,b)=sum _{k|a{text{ and }}k|b}varphi (k).}
- gcd(a,b)=∑k|a and k|bφ(k).{displaystyle gcd(a,b)=sum _{k|a{text{ and }}k|b}varphi (k).}
Probabilities and expected value
In 1972, James E. Nymann showed that k integers, chosen independently and uniformly from {1,...,n}, are coprime with probability 1/ζ(k) as n goes to infinity, where ζ refers to the Riemann zeta function.[19] (See coprime for a derivation.) This result was extended in 1987 to show that the probability that k random integers have greatest common divisor d is d−k/ζ(k).[20]
Using this information, the expected value of the greatest common divisor function can be seen (informally) to not exist when k = 2. In this case the probability that the gcd equals d is d−2/ζ(2), and since ζ(2) = π2/6 we have
- E(2)=∑d=1∞d6π2d2=6π2∑d=1∞1d.{displaystyle mathrm {E} (mathrm {2} )=sum _{d=1}^{infty }d{frac {6}{pi ^{2}d^{2}}}={frac {6}{pi ^{2}}}sum _{d=1}^{infty }{frac {1}{d}}.}
This last summation is the harmonic series, which diverges. However, when k ≥ 3, the expected value is well-defined, and by the above argument, it is
- E(k)=∑d=1∞d1−kζ(k)−1=ζ(k−1)ζ(k).{displaystyle mathrm {E} (k)=sum _{d=1}^{infty }d^{1-k}zeta (k)^{-1}={frac {zeta (k-1)}{zeta (k)}}.}
For k = 3, this is approximately equal to 1.3684. For k = 4, it is approximately 1.1106.
The gcd in commutative rings
The notion of greatest common divisor can more generally be defined for elements of an arbitrary commutative ring, although in general there need not exist one for every pair of elements.
If R is a commutative ring, and a and b are in R, then an element d of R is called a common divisor of a and b if it divides both a and b (that is, if there are elements x and y in R such that d·x = a and d·y = b).
If d is a common divisor of a and b, and every common divisor of a and b divides d, then d is called a greatest common divisor of a and b.
Note that with this definition, two elements a and b may very well have several greatest common divisors, or none at all. If R is an integral domain then any two gcd's of a and b must be associate elements, since by definition either one must divide the other; indeed if a gcd exists, any one of its associates is a gcd as well. Existence of a gcd is not assured in arbitrary integral domains. However if R is a unique factorization domain, then any two elements have a gcd, and more generally this is true in gcd domains.
If R is a Euclidean domain in which euclidean division is given algorithmically (as is the case for instance when R = F[X] where F is a field, or when R is the ring of Gaussian integers), then greatest common divisors can be computed using a form of the Euclidean algorithm based on the division procedure.
The following is an example of an integral domain with two elements that do not have a gcd:
- R=Z[−3],a=4=2⋅2=(1+−3)(1−−3),b=(1+−3)⋅2.{displaystyle R=mathbb {Z} left[{sqrt {-3}},,right],quad a=4=2cdot 2=left(1+{sqrt {-3}},,right)left(1-{sqrt {-3}},,right),quad b=left(1+{sqrt {-3}},,right)cdot 2.}
The elements 2 and 1 + √−3 are two maximal common divisors (that is, any common divisor which is a multiple of 2 is associated to 2, the same holds for 1 + √−3, but they are not associated, so there is no greatest common divisor of a and b.
Corresponding to the Bézout property we may, in any commutative ring, consider the collection of elements of the form pa + qb, where p and q range over the ring. This is the ideal generated by a and b, and is denoted simply (a, b). In a ring all of whose ideals are principal (a principal ideal domain or PID), this ideal will be identical with the set of multiples of some ring element d; then this d is a greatest common divisor of a and b. But the ideal (a, b) can be useful even when there is no greatest common divisor of a and b. (Indeed, Ernst Kummer used this ideal as a replacement for a gcd in his treatment of Fermat's Last Theorem, although he envisioned it as the set of multiples of some hypothetical, or ideal, ring element d, whence the ring-theoretic term.)
See also
- Bézout domain
- Lowest common denominator
Notes
^ ab Long (1972, p. 33)
^ abc Pettofrezzo & Byrkit (1970, p. 34)
^ Kelley, W. Michael (2004), The Complete Idiot's Guide to Algebra, Penguin, p. 142, ISBN 9781592571611.mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}.
^ Jones, Allyn (1999), Whole Numbers, Decimals, Percentages and Fractions Year 7, Pascal Press, p. 16, ISBN 9781864413786.
^ Barlow, Peter; Peacock, George; Lardner, Dionysius; Airy, Sir George Biddell; Hamilton, H. P.; Levy, A.; De Morgan, Augustus; Mosley, Henry (1847), Encyclopaedia of Pure Mathematics, R. Griffin and Co., p. 589.
^ abc Hardy & Wright (1979, p. 20)
^ Andrews (1994, p. 16) explains his choice of notation: "Many authors write (a,b) for g.c.d.(a,b). We do not, because we shall often use (a,b) to represent a point in the Euclidean plane."
^ Gustavo Delfino, "Understanding the Least Common Multiple and Greatest Common Divisor", Wolfram Demonstrations Project, Published: February 1, 2013.
^ Slavin, Keith R. (2008). "Q-Binomials and the Greatest Common Divisor". Integers Electronic Journal of Combinatorial Number Theory. University of West Georgia, Charles University in Prague. 8: A5. Retrieved 2008-05-26.
^ Schramm, Wolfgang (2008). "The Fourier transform of functions of the greatest common divisor". Integers Electronic Journal of Combinatorial Number Theory. University of West Georgia, Charles University in Prague. 8: A50. Retrieved 2008-11-25.
^ Knuth, Donald E. (1997). The Art of Computer Programming. 2: Seminumerical Algorithms (3rd ed.). Addison-Wesley Professional. ISBN 0-201-89684-2.
^ Shallcross, D.; Pan, V.; Lin-Kriz, Y. (1993). "The NC equivalence of planar integer linear programming and Euclidean GCD" (PDF). 34th IEEE Symp. Foundations of Computer Science. pp. 557–564.
^ Chor, B.; Goldreich, O. (1990). "An improved parallel algorithm for integer GCD". Algorithmica. 5 (1–4): 1–10. doi:10.1007/BF01840374.
^ Adleman, L. M.; Kompella, K. (1988). "Using smoothness to achieve parallelism". 20th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing. New York. pp. 528–538. doi:10.1145/62212.62264. ISBN 0-89791-264-0.
^ Long (1972, p. 40)
^ Pettofrezzo & Byrkit (1970, p. 41)
^ Müller-Hoissen, Folkert; Walther, Hans-Otto (2012), "Dov Tamari (formerly Bernhard Teitler)", in Müller-Hoissen, Folkert; Pallo, Jean Marcel; Stasheff, Jim, Associahedra, Tamari Lattices and Related Structures: Tamari Memorial Festschrift, Progress in Mathematics, 299, Birkhäuser, pp. 1–40, ISBN 9783034804059. Footnote 27, p. 9: "For example, the natural numbers with gcd (greatest common divisor) as meet and lcm (least common multiple) as join operation determine a (complete distributive) lattice." Including these definitions for 0 is necessary for this result: if one instead omits 0 from the set of natural numbers, the resulting lattice is not complete.
^ Knuth, Donald E.; Graham, R. L.; Patashnik, O. (March 1994). Concrete Mathematics: A Foundation for Computer Science. Addison-Wesley. ISBN 0-201-55802-5.
^ Nymann, J. E. (1972). "On the probability that k positive integers are relatively prime". Journal of Number Theory. 4 (5): 469–473. doi:10.1016/0022-314X(72)90038-8.
^ Chidambaraswamy, J.; Sitarmachandrarao, R. (1987). "On the probability that the values of m polynomials have a given g.c.d.". Journal of Number Theory. 26 (3): 237–245. doi:10.1016/0022-314X(87)90081-3.
References
Andrews, George E. (1994) [1971], Number Theory, Dover, ISBN 9780486682525
Hardy, G. H.; Wright, E. M. (1979), An Introduction to the Theory of Numbers (Fifth ed.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-853171-5
Long, Calvin T. (1972), Elementary Introduction to Number Theory (2nd ed.), Lexington: D. C. Heath and Company, LCCN 77171950
Pettofrezzo, Anthony J.; Byrkit, Donald R. (1970), Elements of Number Theory, Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall, LCCN 71081766
Further reading
Donald Knuth. The Art of Computer Programming, Volume 2: Seminumerical Algorithms, Third Edition. Addison-Wesley, 1997.
ISBN 0-201-89684-2. Section 4.5.2: The Greatest Common Divisor, pp. 333–356.
Thomas H. Cormen, Charles E. Leiserson, Ronald L. Rivest, and Clifford Stein. Introduction to Algorithms, Second Edition. MIT Press and McGraw-Hill, 2001.
ISBN 0-262-03293-7. Section 31.2: Greatest common divisor, pp. 856–862.
Saunders MacLane and Garrett Birkhoff. A Survey of Modern Algebra, Fourth Edition. MacMillan Publishing Co., 1977.
ISBN 0-02-310070-2. 1–7: "The Euclidean Algorithm."
External links
Greatest Common Measure: The Last 2500 Years, by Alexander Stepanov






 [8]
[8]







![R=mathbb {Z} left[{sqrt {-3}},,right],quad a=4=2cdot 2=left(1+{sqrt {-3}},,right)left(1-{sqrt {-3}},,right),quad b=left(1+{sqrt {-3}},,right)cdot 2.](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3a3f756caa5d39d36a00f069a49cde49153d1c9f)