1958 Italian general election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 596 seats to the Italian Chamber of Deputies and 246 (of the 253) seats to the Italian Senate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 93.8% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
  Election results maps for the Chamber of Deputies (on the left) and for the Senate (on the right). Light Blue denotes provinces with a Christian Democratic plurality, Red denotes those with a Communist plurality, Gray denotes those with an Autonomist plurality. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
General elections were held in Italy on Sunday 25 May 1958, to select the Third Republican Parliament.[1] The number of MPs to be elected was calculated upon the population's size for the last time.
Contents
1 Electoral system
2 Historical background
3 Parties and leaders
4 Results
4.1 Chamber of Deputies
4.2 Senate of the Republic
5 References
Electoral system
Minor changes were made to the electoral law in 1958, creating a system which would remain unchanged until its abrogation in 1993.
The pure party-list proportional representation was definitely adopted for the Chamber of Deputies. Italian provinces were united in 32 constituencies, each electing a group of candidates. At constituency level, seats were divided between open lists using the largest remainder method with Imperiali quota. Remaining votes and seats were transferred at national level, where they were divided using the Hare quota, and automatically distributed to best losers into the local lists.
For the Senate, 237 single-seat constituencies were established, even if the assembly had 9 more members. The candidates needed a landslide victory of two thirds of votes to be elected: only 5 hoping senators reached this goal. All remained votes and seats were grouped in party lists and regional constituencies, where a D'Hondt method was used: inside the lists, candidates with the best percentages were elected.
Historical background
After De Gasperi's retirement in 1953 Fanfani emerged as the anticipated successor, a role confirmed by his appointment as party secretary from 1954-1959.[2] He reorganized and rejuvenated the national party organization of the Christian Democrats after the dependence on the church and the government which had typified the De Gasperi period.[3]
However, his activist and sometimes authoritarian style, as well as his reputation as an economic reformer, ensured that the moderates within the DC, who opposed the state’s intrusion into the country’s economic life, regarded him with distrust. His indefatigable energy and his passion for efficiency carried him far in politics, but he was rarely able to exploit fully the opportunities that he created. "Fanfani has colleagues, associates, acquaintances and subordinates," one politician once remarked. "But I have never heard much about his friends."
Parties and leaders
| Party | Ideology | Leader | |
|---|---|---|---|
Christian Democracy (DC) | Christian democracy | Amintore Fanfani | |
Italian Communist Party (PCI) | Communism | Palmiro Togliatti | |
Italian Socialist Party (PSI) | Democratic socialism | Pietro Nenni | |
Italian Social Movement (MSI) | Neo-fascism | Arturo Michelini | |
Italian Democratic Socialist Party (PSDI) | Social democracy | Giuseppe Saragat | |
Italian Liberal Party (PLI) | Conservative liberalism | Giovanni Malagodi | |
People's Monarchist Party (PMP) | Conservatism | Achille Lauro | |
Monarchist National Party (PNM) | Conservatism | Alfredo Covelli | |
Italian Republican Party (PRI) | Social liberalism | Oronzo Reale | |
Results
The election gave similar results of five years before and, consequently, the same problems of political instability of the centrist formula. Christian Democracy was polarized by a fraction which liked more leftist politics, and another one which urged for a rightist route. Party's secretary Amintore Fanfani was in the first field, and called for a dialogue with the Italian Socialist Party, which had frozen its relationships with the Italian Communist Party after the Hungarian Revolution. Fanfani led a year-term government, but the reaction of the conservative fraction gave the power to Antonio Segni, followed by Fernando Tambroni who received a decisive vote of confidence by the neo-fascist Italian Social Movement. The MSI had been banned by any type of political power since its birth under the theory of the Constitutional Arch, which stated that any government or opposition party which had voted the Italian Constitution, had to refuse any relationship with fascist and monarchist forces, seen as anti-constitutional groups. Strikes and revolts causing some casualties erupted through the country, and Tambroni had to resign. Fanfani returned to the premiership, this time with an openly centre-left programme supported by the socialist abstention. The government created the middle school for workers' sons, and the ENEL after the electric energy nationalisation.
Chamber of Deputies
 | |||||
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/− | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Christian Democracy | 12,520,207 | 42.35 | 273 | +10 | |
| Italian Communist Party | 6,704,454 | 22.68 | 140 | −3 | |
| Italian Socialist Party | 4,206,726 | 14.23 | 84 | +9 | |
| Italian Social Movement | 1,407,718 | 4.76 | 24 | −5 | |
| Italian Democratic Socialist Party | 1,345,447 | 4.55 | 22 | +3 | |
| Italian Liberal Party | 1,047,081 | 3.54 | 17 | +4 | |
| People's Monarchist Party | 776,919 | 2.63 | 14 | New | |
| Monarchist National Party | 659,997 | 2.23 | 11 | −29 | |
Italian Republican Party–Radical Party | 405,782 | 1.37 | 6 | +1 | |
| Community Movement | 173,227 | 0.59 | 1 | New | |
| South Tyrolean People's Party | 135,491 | 0.46 | 3 | ±0 | |
| Movement for Piedmontese Regional Autonomy | 70,589 | 0.24 | 0 | New | |
| Valdostan Union | 30,596 | 0.10 | 1 | New | |
| Others | 76,035 | 0.26 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Invalid/blank votes | 874,412 | – | – | – | |
| Total | 30,434,681 | 100 | 596 | +6 | |
| Registered voters/turnout | 32,434,852 | 93.83 | – | – | |
| Source: Ministry of the Interior | |||||
Senate of the Republic
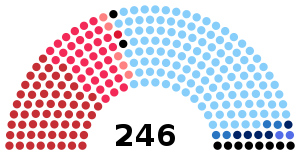 | |||||
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/− | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Christian Democracy | 10,780,954 | 41.23 | 123 | +10 | |
| Italian Communist Party | 5,700,952 | 21.80 | 59 | +8 | |
| Italian Socialist Party | 3,682,945 | 14.08 | 35 | +9 | |
| Italian Democratic Socialist Party | 1,164,280 | 4.45 | 5 | +1 | |
| Italian Social Movement | 1,150,051 | 4.40 | 8 | −1 | |
| Italian Liberal Party | 1,012,610 | 3.87 | 4 | +1 | |
| People's Monarchist Party | 774,242 | 2.96 | 5 | New | |
| Monarchist National Party | 565,045 | 2.16 | 2 | −14 | |
Italian Republican Party–Radical Party | 363,462 | 1.39 | 0 | ±0 | |
MSI–PNM | 291,359 | 1.11 | 0 | ±0 | |
PCI–PSI | 185,557 | 0.71 | 2 | ±0 | |
| Community Movement | 142,897 | 0.55 | 0 | New | |
| South Tyrolean People's Party | 120,068 | 0.46 | 2 | ±0 | |
| Movement for Piedmontese Regional Autonomy | 61,088 | 0.23 | 0 | New | |
PSI–PSDI | 43,191 | 0.17 | 0 | ±0 | |
| For The Autonomy of Aosta Valley | 28,141 | 0.11 | 1 | +1 | |
| Sardinian Action Party | 25,923 | 0.10 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Others | 57,237 | 0.22 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Invalid/blank votes | 1,239,240 | – | – | – | |
| Total | 27,391,239 | 100 | 246 | +9 | |
| Registered voters/turnout | 29,174,858 | 93.9 | – | – | |
| Source: Ministry of the Interior | |||||
References
^ Dieter Nohlen & Philip Stöver (2010) Elections in Europe: A data handbook, p1048 .mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
ISBN 978-3-8329-5609-7
^ Young Initiative, Time Magazine, 12 July 1954
^ Out for the Big Win, Time Magazine, 26 May 1958


